HP Serviceguard Enterprise Cluster Master Toolkit User Guide (5900-2145, April 2013)
Table Of Contents
- HP Serviceguard Enterprise Cluster Master Toolkit User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Using the Oracle Toolkit in an HP Serviceguard Cluster
- Overview
- Supported Versions
- Support for Oracle Database Without ASM
- Supporting Oracle ASM Instance and Oracle Database with ASM
- What is Automatic Storage Management (ASM)?
- Why ASM over LVM?
- Configuring LVM Volume Groups for ASM Disk Groups
- Sample command sequence for configuring LVM Volume Groups
- Serviceguard support for ASM on HP-UX 11i v3 onwards
- Framework for ASM support with Serviceguard
- Installing, Configuring, and Troubleshooting
- Setting up DB instance and ASM instance
- Setting up the Toolkit
- ASM Package Configuration Example
- Modifying a Legacy Database Package Using an Older Version of Oracle ECMT Scripts to use the Scripts Provided for ASM Support
- Adding the Package to the Cluster
- Node-specific Configuration
- Error Handling
- Network Configuration
- Database Maintenance
- Configuring and packaging Oracle single-instance database to co-exist with SGeRAC packages
- Configuring Oracle single-instance database that uses ASM in a Coexistence Environment
- Attributes newly added to ECMT Oracle toolkit
- Configuring a modular failover package for an Oracle database using ASM in a coexistence environment
- Configuring a legacy failover package for an Oracle database using ASM in a Coexistence Environment
- ECMT Oracle Toolkit Maintenance Mode
- Supporting EBS database Tier
- Oracle ASM Support for EBS DB Tier
- 3 Using the Sybase ASE Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster on HP-UX
- Overview
- Sybase Information
- Setting up the Application
- Setting up the Toolkit
- Sybase Package Configuration Example
- Creating the Serviceguard package using Modular method
- Adding the Package to the Cluster
- Node-specific Configuration
- Error-Handling
- Network configuration
- Database Maintenance
- Cluster Verification for Sybase ASE Toolkit
- 4 Using the DB2 Database Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster in HP-UX
- 5 Using MySQL Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- MySQL Package Configuration Overview
- Setting Up the Database Server Application
- Setting up MySQL with the Toolkit
- Package Configuration File and Control Script
- Creating Serviceguard Package Using Modular Method
- Applying the Configuration and Running the Package
- Database Maintenance
- Guidelines to Start Using MySQL Toolkit
- 6 Using an Apache Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- 7 Using Tomcat Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- Tomcat Package Configuration Overview
- Multiple Tomcat Instances Configuration
- Configuring the Tomcat Server with Serviceguard
- Setting up the Package
- Creating Serviceguard Package Using Modular Method
- Setting up the Toolkit
- Error Handling
- Tomcat Server Maintenance
- Configuring Apache Web Server with Tomcat in a Single Package
- 8 Using SAMBA Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster
- 9 Using HP Serviceguard Toolkit for EnterpriseDB PPAS in an HP Serviceguard Cluster
- 10 Support and Other resources
- 11 Acronyms and Abbreviations
- Index
RUN_SCRIPT /etc/cmcluster/pkg/db2_pkg/pkg.cntl
HALT_SCRIPT /etc/cmcluster/pkg/db2_pkg/pkg.cntl
11. The DB2 Configuration file, in the package directory, modify the hadb2.conf configuration
file for this DB2 instance. Edit the hadb2.conf as indicated by the comments in that script.
For example,
INSTANCE_NAME=db2_payroll_inst
PARTITION_NUMBER[0]=0
PARTITION_NUMBER[1]=1
MONITOR_PROCESSES[0]=db2sysc
MONITOR_PROCESSES[1]=db2acd
MAINTENANCE_FLAG=YES
MONITOR_INTERVAL=30
TIME_OUT=30
12. After setting up the Serviceguard environment, each clustered DB2 instance must have the
following files in the related package directory. For example, the DB2 package, located at
/etc/cmcluster/pkg/db2_pkg, must contain the following files list in Table 12.
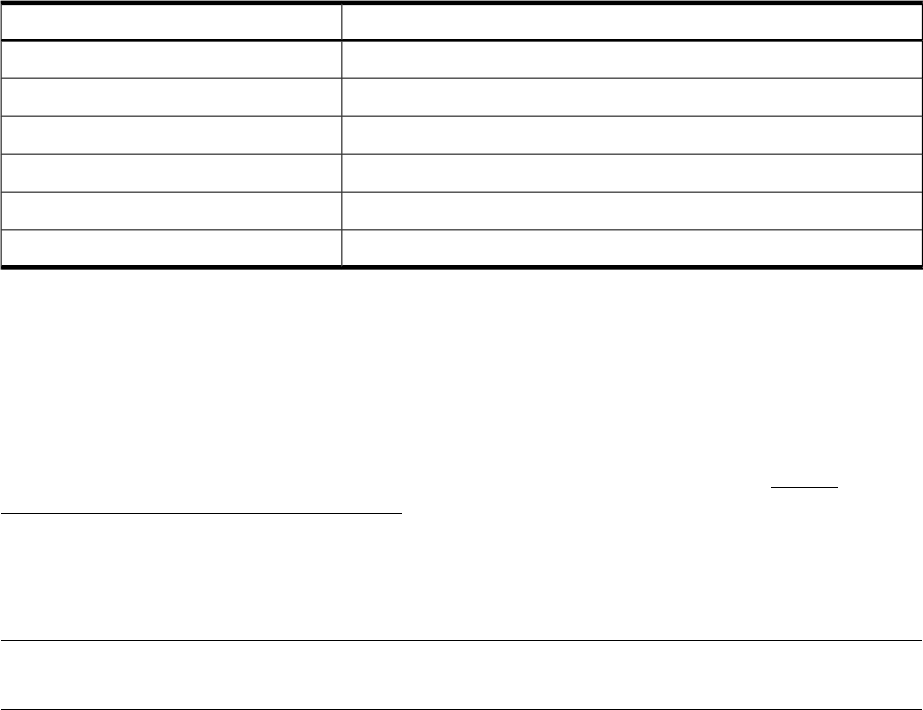
Table 11 DB2 Package Files
DescriptionFile Name
Serviceguard package control script for legacy packaging style.$PKG.cntl
Serviceguard package configuration file.$PKG.conf
Main shell script of the toolkit.hadb2.sh
Monitor the health of the application.hadb2.mon
Toolkit DB2 configuration file.hadb2.conf
Interface between pkg.cntl and hadb2.sh.toolkit.sh
Adding the Package to the Cluster
After the setup is complete, add the package to the SG cluster, and then start it up.
cmapplyconf -P pkg.conf
cmmodpkg -e -n <node1> —n <node2> db2_payroll
cmmodpkg —e db2_payroll
For more information, see the latest Managing Serviceguard manual available at http://
www.hp.com/go/hpux-serviceguard-docs —>HP Serviceguard .
Database Maintenance
At regular intervals, the DB2 database needs maintenance like changing configuration, without
migrating the instance to standby node. The following procedure should be used:
NOTE: In the example, consider that the package name is db2_payroll, package directory
is/etc/cmcluster/pkg/db2_pkg.
Steps for Database maintenance:
• Disable the failover of the package through the cmmodpkg command:
$ cmmodpkg -d db2_payroll
• Pause the monitor script.
Create an empty file /etc/cmcluster/pkg/db2_pkg/db2.debug
$ touch /etc/cmcluster/pkg/db2_pkg/db2.debug
Adding the Package to the Cluster 85










