HP Serviceguard Enterprise Cluster Master Toolkit User Guide (5900-2145, April 2013)
Table Of Contents
- HP Serviceguard Enterprise Cluster Master Toolkit User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Using the Oracle Toolkit in an HP Serviceguard Cluster
- Overview
- Supported Versions
- Support for Oracle Database Without ASM
- Supporting Oracle ASM Instance and Oracle Database with ASM
- What is Automatic Storage Management (ASM)?
- Why ASM over LVM?
- Configuring LVM Volume Groups for ASM Disk Groups
- Sample command sequence for configuring LVM Volume Groups
- Serviceguard support for ASM on HP-UX 11i v3 onwards
- Framework for ASM support with Serviceguard
- Installing, Configuring, and Troubleshooting
- Setting up DB instance and ASM instance
- Setting up the Toolkit
- ASM Package Configuration Example
- Modifying a Legacy Database Package Using an Older Version of Oracle ECMT Scripts to use the Scripts Provided for ASM Support
- Adding the Package to the Cluster
- Node-specific Configuration
- Error Handling
- Network Configuration
- Database Maintenance
- Configuring and packaging Oracle single-instance database to co-exist with SGeRAC packages
- Configuring Oracle single-instance database that uses ASM in a Coexistence Environment
- Attributes newly added to ECMT Oracle toolkit
- Configuring a modular failover package for an Oracle database using ASM in a coexistence environment
- Configuring a legacy failover package for an Oracle database using ASM in a Coexistence Environment
- ECMT Oracle Toolkit Maintenance Mode
- Supporting EBS database Tier
- Oracle ASM Support for EBS DB Tier
- 3 Using the Sybase ASE Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster on HP-UX
- Overview
- Sybase Information
- Setting up the Application
- Setting up the Toolkit
- Sybase Package Configuration Example
- Creating the Serviceguard package using Modular method
- Adding the Package to the Cluster
- Node-specific Configuration
- Error-Handling
- Network configuration
- Database Maintenance
- Cluster Verification for Sybase ASE Toolkit
- 4 Using the DB2 Database Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster in HP-UX
- 5 Using MySQL Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- MySQL Package Configuration Overview
- Setting Up the Database Server Application
- Setting up MySQL with the Toolkit
- Package Configuration File and Control Script
- Creating Serviceguard Package Using Modular Method
- Applying the Configuration and Running the Package
- Database Maintenance
- Guidelines to Start Using MySQL Toolkit
- 6 Using an Apache Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- 7 Using Tomcat Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- Tomcat Package Configuration Overview
- Multiple Tomcat Instances Configuration
- Configuring the Tomcat Server with Serviceguard
- Setting up the Package
- Creating Serviceguard Package Using Modular Method
- Setting up the Toolkit
- Error Handling
- Tomcat Server Maintenance
- Configuring Apache Web Server with Tomcat in a Single Package
- 8 Using SAMBA Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster
- 9 Using HP Serviceguard Toolkit for EnterpriseDB PPAS in an HP Serviceguard Cluster
- 10 Support and Other resources
- 11 Acronyms and Abbreviations
- Index
On ASM instance failure, all dependent database instances are brought down and are started on
the adoptive node.
How Toolkit Starts, Stops, and Monitors the Database instance
The Toolkit failover package for the database instance provides start and stop functions for the
database instance and has a service for checking the status of the database instance.
There is a separate package for each database instance. Each database package has a simple
dependency on the ASM package. The package activates the volume groups in exclusive mode.
The start function runs su to the Oracle software owner user id. This function mounts the ASM disk
groups associated with the instance and starts the database instance specified by the user using
the sqlplus commands.
The stop function executes su to the Oracle software owner user id. The database instance is
shutdown using the sqlplus commands and the disk groups associated with the instance are
dismounted. After dismounting the disk groups, the logical volumes are checked to see if ASM has
closed its file descriptors. If file descriptors are still open, necessary steps are taken to ensure that
file descriptors are closed. The package then deactivates the volume groups.
The monitor function contains a continuous loop to check whether the specified database instance
processes are healthy. If the monitor function finds any dead process the database instance has
either failed or was inappropriately shut down, that is, without using cmhaltpkg. The service that
invokes the function fails at this point and the Serviceguard package manager fails the corresponding
database failover package.
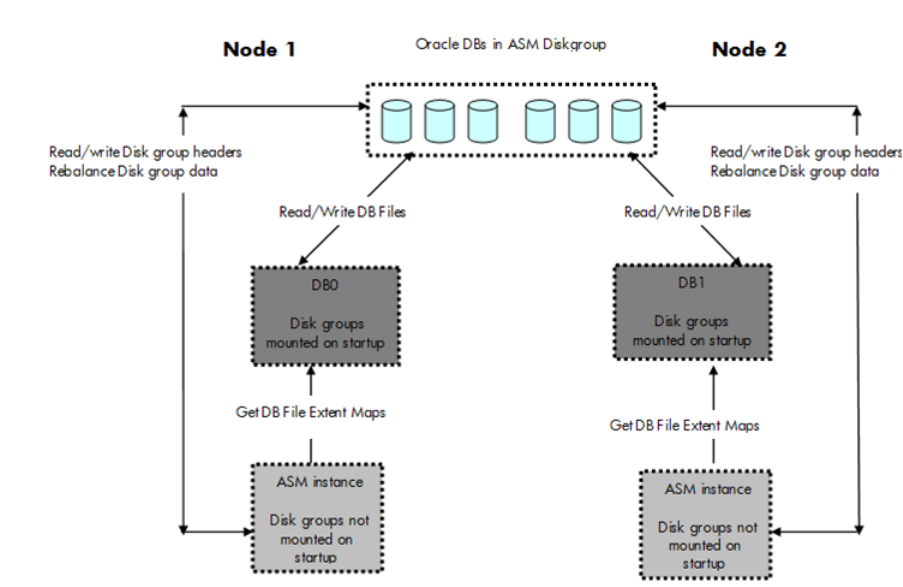
Consider two database instances DB0 and DB1. Each database instance uses its own disk group
with the disk group members on its own volume group. Figure 3, depicts the scenario when the
ASM instance and the database instances DB0 and DB1 start on nodes 1 and 2 respectively.
Figure 3 Serviceguard ASM environment
Figure 4, shows the scenario when DB1 fails on node 2.
36 Using the Oracle Toolkit in an HP Serviceguard Cluster










