High Availability for Oracle ASM using HP Serviceguard Solutions, September 2010
Table Of Contents
- High Availability for Oracle ASM using HP Serviceguard Solutions
- Introduction
- Terms and definitions
- ASM background
- HP Serviceguard support for ASM on HP-UX 11i v2
- HP Serviceguard support for ASM on HP-UX 11i v3 and later
- Framework for ASM support with Serviceguard
- Installing, configuring, and troubleshooting
- Related documentation
- Appendix
- Call to action
3
ASM background
What is Automatic Storage Management?
Automatic Storage Management is a feature provided in Oracle 10g or later to simplify the database
files management. ASM provides file system and volume management capabilities directly inside the
Oracle database kernel, allowing volumes and disk management with familiar SQL statements in
Oracle. This is an alternative to platform file systems and volume managers for the management of
most file types used to store the Oracle database, including Oracle data files, control files, and online
and archived redo log files. File types not supported by ASM include Oracle database server
binaries, trace files, audit files, alert logs, backup files, export files, tar files, and core files. Storage
for application binaries and data cannot be managed by ASM. ASM uses disk groups to store data
files; an ASM disk group is a collection of disks that ASM manages as a unit. Within a disk group,
ASM exposes a file system interface for Oracle database files. The contents of files that are stored in
a disk group are evenly distributed, or striped to eliminate hot spots and to provide uniform
performance across the disks.
A major advantage of ASM is the ease of management it provides for database files:
• The system administrator has only to specify the set of raw devices to be used in an ASM disk
group; the tasks of configuring and administering volume/disk groups and file systems are
eliminated. Oracle ASM makes use of the Oracle feature called Oracle-Managed Files and
performs the tasks of creating, deleting, and extending files on behalf of database instances;
additionally, it manages their mirroring and striping.
• If a device is added to, or deleted from, an ASM disk group, ASM automatically rebalances
database file striping based on the new disk layout.
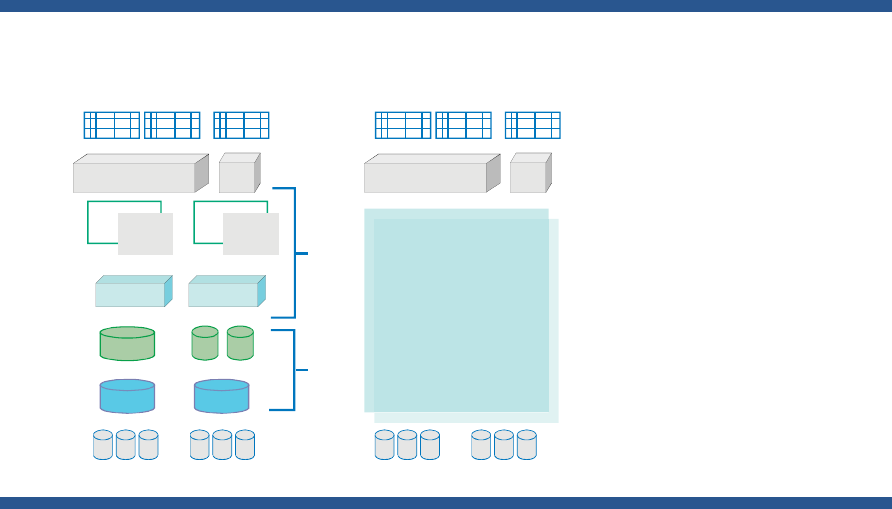
Figure 1 contrasts the Oracle storage hierarchy as it appears when platform or third-party volume
managers and file systems are used for Oracle data files, compared to when ASM is used. The layers
corresponding to file systems and volume managers are absorbed into ASM. The files and directories
in the storage hierarchy are not visible using standard operating system commands; to display them
the customer must use Oracle utilities.
Figure 1: Oracle database storage hierarchy without and with ASM
Without ASM With ASM
Table
Tablespaces
VxFS
CFS...
LVM,
VxVM,
CVM
Files
File systems
Logical volumes
Volume groups
Disks/Disk Array
Logical units
0111000
00100...
0111000
00100...
Files and D isk Groups Managed by
ASM, displayed via Oracle utilities










