High Availability for Oracle ASM using HP Serviceguard Solutions, September 2010
Table Of Contents
- High Availability for Oracle ASM using HP Serviceguard Solutions
- Introduction
- Terms and definitions
- ASM background
- HP Serviceguard support for ASM on HP-UX 11i v2
- HP Serviceguard support for ASM on HP-UX 11i v3 and later
- Framework for ASM support with Serviceguard
- Installing, configuring, and troubleshooting
- Related documentation
- Appendix
- Call to action
10
HP Serviceguard Toolkit internal file structure
HP provides a set of scripts for the framework proposed for ASM integration with Serviceguard. The
Serviceguard ECMT Oracle scripts contain the instance specific logic to start/stop/monitor both the
ASM and the database instance. These scripts support both legacy and the modular method of
packaging. Even though Legacy method of packaging is supported, it is deprecated now and will not
be supported in future. Hence, it is recommended to use modular style of packaging. For more
information on creating a modular package, look at the Serviceguard manual “Managing
Serviceguard” latest edition at
http://www.hp.com/go/hp HP Serviceguard”.
Serviceguard provides tools to migrate existing legacy packages to modular packages. For more
information, look at the white paper “Migrating Packages from Legacy to Modular Style” available at
ux-serviceguard-docs
http://www.hp.com/go/hp HP Serviceguard. ux-serviceguard-docs
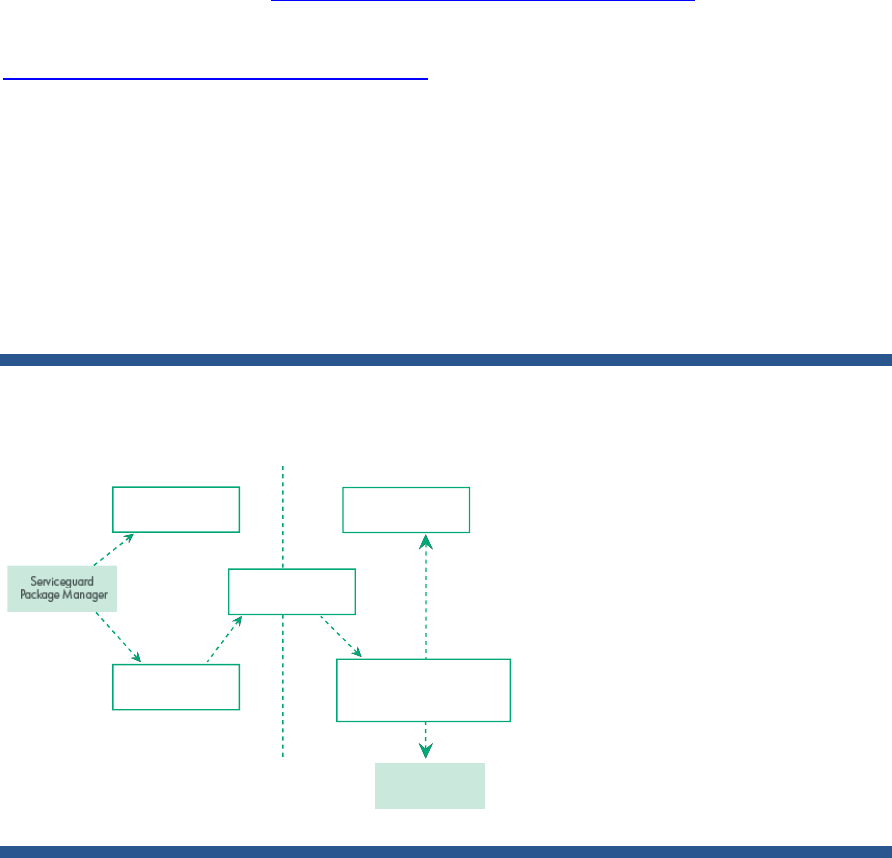
Legacy packages use the package configuration file and the package control script for the ASM or
database instance on the Serviceguard specific side. The package configuration file parameters are
stored in the Serviceguard configuration database (CDB) at cmapplyconf time, and are used by the
package manager in its actions on behalf of this package. The control script invokes the ASM or the
database instance specific functions for start/stop/monitor through the toolkit interface script
(toolkit.sh). On the instance specific side, there is a toolkit configuration file (haoracle.conf) which is
sourced by the start/stop/monitor (haoracle.sh, haoracle_sql.sh, haoracle.mon, and halistener.mon)
script files. The toolkit interface script allows the start/stop/monitor calls to remain unaffected by
changes in the instance specific scripts. Figure 5 shows the internal file structure for legacy packages.
Figure 5: Internal file structure for legacy packages
Modular packages use the package configuration file for the ASM or database instance on the
Serviceguard specific side. The package configuration parameters are stored in the Serviceguard
configuration database at cmapplyconf time, and are used by the package manager in its actions on
behalf of this package. The Serviceguard master control script invokes the ASM or the database
instance specific functions for start/stop/monitor through the Oracle toolkit module script. The toolkit
module script in turn calls the legacy scripts toolkit.sh, haoracle.sh, haoracle_sql.sh, haoracle.mon,
haoracle.conf, and halistener.mon to start/stop/monitor the ASM or database instance. Figure 7
shows the internal file structure for modular packages.
Serviceguard specific
configuration and logic
ASM/DB instance
Configuration File
Serviceguard
Package Manager
Instance specific
configuration and logic
ASM/DB Instance
Start/stop/monitor
sources
executes
sources
calls
calls
ASM/DB instance
Control Script
Toolkit Interface
Script (toolkit.sh)
Toolkit start/stop/ monitor scripts
(haoracle.sh, haoracle.mon,
haoracle_sql.sh, halistener.mon)
Toolkit Configuration file
(haoracle.conf)










