HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 SNMP Agent Reference Guide (AE131-96088, May 2011)
Table Of Contents
- XP24000/XP20000 SNMP Agent Reference Guide
- 1 Overview of SNMP
- 2 Using the SNMP GUI
- 3 Performing SNMP Operations
- 4 SNMP Supported MIB
- 5 SNMP Failure Trap Reference
- 6 Troubleshooting
- 7 Support and Other Resources
- Glossary
- Index
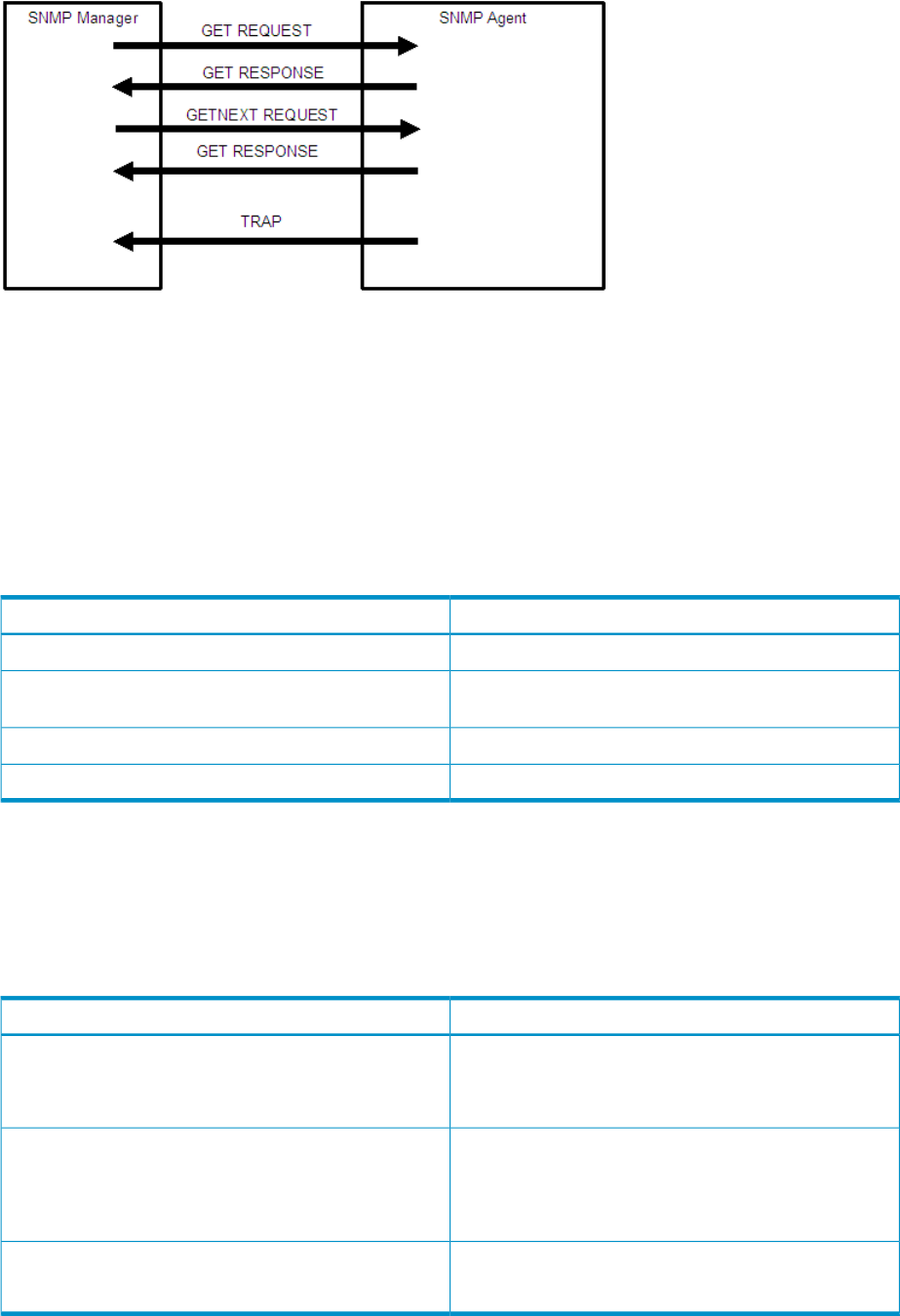
Figure 3 Example of SNMP Operations
SNMP Agent Functions
SNMP Traps
An SNMP agent reports a storage system error to a SNMP manager using the trap report function.
If an error occurs, an SNMP agent issues an SNMP trap to an SNMP manager to report a failure.
Issuing an SNMP trap, an SNMP agent also reports a product number, nickname, reference code,
and an identifier of the component.
The following table lists the events that trigger an SNMP agent trap.
Table 1 SNMP Trap Triggering Events
DescriptionEvents
All operations in a storage system stopped.Acute failure detected.
Operation in a component where a failure occurred
stopped.
Serious failure detected.
Partial failure.Moderate failure detected.
Minor failure.Service failure detected.
An SNMP agent logs the most recent 256 traps, so you can see the trap history of a particular
device.
SNMP Agent Operations
The following table lists the types SNMP Agent operations.
Table 2 SNMP Agent Operations
DescriptionOperation
Obtains a specific MIB object value.
GET REQUEST is the request from an SNMP manager, and
GET RESPONSE is the agent's response to that request.
GET
Continuously finds a MIB object.
GETNEXT REQUEST is the request from an SNMP manager,
and GETNEXT RESPONSE is the agent's response to that
request.
GETNEXT
Reports an event (failure) to an SNMP manager.
TRAP occurs without a request from the SNMP manager.
TRAP
SNMP Agent Overview 7










