HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Performance Control User Guide Abstract This user's guide describes and provides instructions for using XP Performance Control.
Legal and notice information © Copyright 2008, 2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
Contents 1 Overview of HP StorageWorks XP Performance Control Software .............. 7 2 About XP Performance Control ........................................................... 11 Components ............................................................................................................................ Overview of XP Performance Control ........................................................................................... Performance of High-Priority Hosts ................................
6 Troubleshooting ............................................................................... 49 Troubleshooting XP Performance Control ...................................................................................... 49 Calling HP Technical Support ..................................................................................................... 49 7 Support and Other Resources ............................................................ 51 Related Documentation ...............................
Figures 1 Performance Management Process Flow Diagram .......................................................... 8 2 Line graphs that indicate changes in port traffic .......................................................... 13 3 The port tab in the Performance Control Window ........................................................ 18 4 The WWN tab in the Performance Control Window .................................................... 20 5 Network A (One-to-one connections between HBAs and ports) ..........
Tables 1 Relationship between the thresholds of the prioritized WWN and the upper limits of the non-prioritized WWN ............................................................................................. 32 2 Relationship between the thresholds of the prioritized port and the upper limits of the non-prioritized port .................................................................................................
1 Overview of HP StorageWorks XP Performance Control Software Performance Monitor provides usage statistics about physical hard disk drive, volumes, processors, or other resources in your storage system. Performance Monitor also provides statistics about workloads on disk drives and traffic between hosts and the storage system. The Auto LUN window displays a line graph indicating changes in the usage rates, workloads, or traffic.
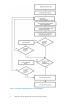
Figure 1 Performance Management Process Flow Diagram .
HP StorageWorks XP Auto LUN Software lets you balance workload among hard disk drives, volumes (LUs) and processors to remove bottlenecks from your system. If Performance Monitor indicates that a great number of I/Os are made to some hard disk drives, you can use XP Auto LUN to distribute workloads to other disk drives. For details, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Auto LUN Software User Guide. Restrictions: The Auto Migration function is not supported in this version.
Overview of HP StorageWorks XP Performance Control Software
2 About XP Performance Control This chapter gives an overview of performance management operations. • Components, page 11 • Overview of XP Performance Control, page 11 • Interoperability with Other Products, page 12 Components To use XP Performance Control, you need: • The storage system • The Performance Monitor program products (Performance Monitor is required. XP Auto LUN is optional.
If production servers suffer lowered performance, productivity in business activities is likely to be reduced. For this reason, the system administrator needs to maintain performance of production servers at a high level. Computer systems in business organizations often include development servers as well as production servers. Development servers are used for developing, testing and debugging business applications.
I/O rate graph for 1A, the line in the graph indicates changes in the average I/O rate calculated every minute (see Graph 2). If you select the Detail check box in the Performance Management windows, the graph displays changes in the maximum, average, and minimum I/O rates at 1–minute. XP Performance Control applies upper limits and thresholds to the average I/O rate or the average transfer rate calculated every gathering interval.
for initiator ports and external ports by using XP Performance Control, the initiator ports and the external ports become the prioritized ports that are not under threshold control, regardless of settings. If the port attributes are changed from Initiator/External to Target/RCU Target, the settings by XP Performance Control take effect instantly and the ports are subject to threshold or upperlimit control. The statistics of All Prio. and All Non-Prio.
3 Preparing for XP Performance Control Operations System Requirements To use XP Performance Control, you need: • A storage system • Performance Monitor software (XP Auto LUN and XP Performance Control are optional, but Performance Monitor is required) • A web client computer (intended for use as a Remote Web Console) connected to storage system via LAN. To use XP Performance Control, you use the web client computer to log on to the SVP (web server).
Preparing for XP Performance Control Operations
4 Performance Control Window The Performance Control window has two tabs: Port tab and WWN tab. If one-to-one connections are established between Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) and ports, use the Port tab. If many-to-many connections are established between HBAs and ports, use the WWN tab. For operations using these tabs, see Chapter 5 on page 25. If the user type of your user ID is storage partition administrator, you cannot use XP Performance Control.
Figure 3 The port tab in the Performance Control Window . Item Description Can show either Port Control, WWN Control • If Port Control is shown, the system is controlled by the upper limits and threshold specified in the Port tab. • If WWN Control is shown, the system is controlled by the upper limits and threshold specified in the WWN tab. Current control status • If No Control is displayed, the system performance is not controlled by XP Performance Control.
Item Statistic type list Description Use this list to change the type of performance statistics to be displayed in the list. • If IOPS (I/Os per second) is selected, the list displays I/O rates for ports. • If MB/s (megabytes per second) is selected, the list displays the transfer rates for ports. list of ports, including the I/O rate or the transfer rate for each port. Here you can specify the port attributes, and the threshold and upper-limit of the port traffic.
Item Description Reset Restores the last applied settings in the window. When you click this button, all the changes displayed in blue text in the window are canceled. Changes the settings in this window as explained below, and then applies the resulting settings to the storage system: Initialize • All the ports become prioritized ports. • The threshold value for all the ports becomes 0 (zero). • The window will display a hyphen (-) instead of 0 (zero).
Item Description The current system control. • Port Control: The system is controlled by the upper limits and threshold specified in the Port tab. Current Control Status • WWN Control: The system is controlled by the upper limits and threshold specified in the WWN tab. • No Control: The system performance is not controlled by XP Performance Control. TIP: If Port Control appears when the WWN tab is active, click Apply to switch control so that WWN Control is displayed.
Item Description Performance Control groups and HBAs (WWNs) in each Performance Control group: • Performance Control groups ( ), which contain one or more WWN, appear below the Subsystem folder. For details on the Performance Control groups, see “Grouping HBAs” on page 44. • If you double-click a Performance Control group, HBAs in that group appear in the tree. The WWN and Performance Control name appear to the right of the HBA icon ( Lower-left tree ).
Item Description A list of WWNs and the I/O rate or transfer rate for each HBA corresponding to the selection in the upper-left tree or lower-left tree. Use this list to specify the HBA attributes and the upper limit of the HBA traffic. The measurement unit for the values in the list can be specified by the choice in the upper-left corner of the list. The displayed items will change depending on the selected tree and item. The HBA traffic (I/O rate and transfer rate) is monitored by Performance Monitor.
Item Description • The Upper columns let you specify the upper limit on the I/O rate and transfer rate for each HBA. Either the IOPS or MB/s column in the list is activated depending on the selection from the list above. Use the IOPS column to specify the upper limit for I/O rates. Use the MB/s column to specify the upper limit for transfer rates. To specify an upper limit, double-click a cell to display the cursor in the cell.
5 XP Performance Control Operations This chapter describes the following XP Performance Control operations: • • • • Overview of XP Performance Control Operations, page 25 Starting XP Performance Control, page 32 Port Tab Operations, page 33 WWN Tab Operations, page 36 Overview of XP Performance Control Operations Which procedures you use in XP Performance Control depend on the connection between HBAs and storage system ports.
Figure 5 Network A (One-to-one connections between HBAs and ports) . If one-to-one connections are established between HBAs and ports, take the following major steps: 1. Set priority to ports on the storage system using the Port tab of the Performance Control window. In network A, the ports 1A and 1C are connected to high-priority production servers. The port 2A is connected to a low-priority development server.
I/O rate for prioritized ports (1A and 1C) at 400 IO/s. To maintain the I/O rate at 400 IO/s, you must set an upper-limit to the I/O rate for the port 2A. Figure 7 Traffic at ports . For detailed information about monitoring traffic, see “Setting Priority for Ports on the Storage System” on page 34 and “Analyzing Traffic Statistics in the Port Tab” on page 33. 3. Set an upper-limit for the I/O rate for traffic at the non-prioritized port.
If Many-to-Many Connections Link HBAs and Ports Figure 8 is an example of a network on which a production server and a development server are connected to the storage system. (Henceforth, this network is referred to as network B). The HBA (wwn01) in the production server is connected to four ports (1A, 1C, 2A and 2C). The HBAs (wwn02 and wwn03) in the development server are also connected to the four ports. Figure 8 Network B (many-to-many connections are established between HBAs and ports) .
Figure 9 Specifying HBAs to be Monitored . For more detailed instruction, see “Setting Priority for Ports on the Storage System” on page 34. XP Performance Control is unable to monitor and control the performance of hosts whose HBAs icons are placed below the Non-Monitor icon. 3. Set priority to HBAs using the WWN tab of the Performance Control window. In network B, the production server is given high priority and the development server is given low-priority.
4. Monitor traffic between host bus adapter and ports. You must obtain statistics about traffic between HBA and ports. If your network is configured as network B, you must do the following: • Measure traffic between port 1A and the three HBAs (wwn01, wwn02 and wwn03). • Measure traffic between port 1C and the three HBAs. • Measure traffic between port 2A and the three HBAs. • Measure traffic between port 2C and the three HBAs.
Figure 12 Setting upper limits . 6. Check the result of applying upper-limit values. After applying upper-limit values, you must measure traffic at ports. View traffic statistics for the prioritized WWN to check whether the host performance is improved to a desirable level. In network B, the desirable I/O rate for the prioritized WWN is 400 IO/s. If the I/O rate reaches 400 IO/s, production server performance has reached to a desirable level.
Table 1 shows the relationship between the thresholds and the upper limits: Table 1 Relationship between the thresholds of the prioritized WWN and the upper limits of the non-prioritized WWN Threshold Settings A Number Other Than Zero Is Set as the upper-limit of the Non-prioritized WWN Zero Is Set as the upperlimit of the Non-prioritized WWN When thresholds are set to prioritized WWNs, depending on the I/O rate or the transfer rate, the following controls are executed.
• Use the WWN tab (Figure 4 on page 20) if a many-to-many connection is established between HBAs and storage system ports. For details on operations in the WWN tab, see “WWN Tab Operations” on page 36.
itized ports. For details on the upper-limit values and threshold values, see “If One-to-One Connections Link HBAs and Ports” on page 25. Setting Priority for Ports on the Storage System If a one-to-one connection is established between HBAs and ports, you need to measure traffic between high-priority HBAs and prioritized ports. You also need to measure traffic between low-priority HBAs and non-prioritized ports.
NOTE: The Attribute column of the list indicates whether ports are prioritized or non-prioritized. If you cannot find any non-prioritized port in the list, check the list at the top right corner of the window. If the list displays Prioritize, select All or Non-Prioritize from the list. 5. Do one of the following: • To limit the I/O rate for the non-prioritized port, double-click the desired cell in the IOPS column in Upper. Next, enter the upper-limit value in the cell.
4. Do one of the following: • To specify a threshold for each prioritized port, locate the desired prioritized port, which is indicated by Prio. in the Attribute column. Next, double-click the cell in the IOPS or MB/s column in Threshold, and then enter the threshold value. In the list, either of the IOPS or the MB/s column is activated depending on the rate selected at step 3 above. Repeat this operation to set the thresholds for all the prioritized ports.
connections are established between HBAs and ports, you cannot set individual thresholds for prioritized WWNs. For the system configuration of many-to-many connections between HBAs and ports, see “If Many-to-Many Connections Link HBAs and Ports” on page 28. This section describes procedures you can perform for HBAs and the entire storage system.
NOTE: If you are using Windows, you can drag and drop the desired WWNs from Non-Monitor to Monitor. When you drop a WWN at Monitor, the Add WWN window is displayed in which you can specify the Performance Control name only. Figure 13 The Add WWN Window . If you add a port or HBA to the storage system after you specify the settings, the traffic statistics related to the connections to the newly added port or HBA will not be monitored.
NOTE: • If the selected HBA is connected to multiple ports, when you select the HBA and the Delete WWN pop-up menu, a message will appear. This message will ask you to move the HBA from Monitor to Non-Monitor. • If the selected HBA is contained in a Performance Control group, a message will appear that tells you to delete the HBA from the Performance Control group. You cannot change an HBA which is contained in a Performance Control group from Monitor to Non-Monitor.
NOTE: • The traffic statistics that apply only to the HBAs below Monitor appear in the list. • The WWN Total traffic statistics are displayed in the list when you select an icon in the lowerleft tree. If you select the Subsystem folder in the lower-left tree, the sum of the traffic of the HBAs registered in each Performance Control group is displayed. For details on Performance Control groups, see “Grouping HBAs” on page 44. 6.
The upper limit values need to be set for the Non-prio WWNs. For detail about setting upper limit values, see “Setting Upper-Limit Values for Non-Prioritized WWNs” on page 41. 10. Repeat steps 4 to 9 for ports. If one HBA is connected to multiple ports and you specify the priority of the HBA for one port, the specified priority will be automatically applied to the HBA settings for other connected ports. 11. Click Apply in the Performance Control window.
• To limit the I/O rate of the non-prioritized WWN, double-click the desired cell in the IOPS column in Upper. Next, enter the upper-limit value in the cell. • To limit the transfer rate of the non-prioritized WWNs, double-click the desired cell in the MB/s column in Upper. Next, enter the upper-limit value in the cell. In the list, either of the IOPS cells or the MB/s cells are activated depending on the rate you specified in step 3.
Changing the Performance Control Name of an HBA Use the Performance Control window to assign a Performance Control name to an HBA. Although you can identify HBAs by WWNs, you will be able to identify HBAs more easily if you assign Performance Control names. WWNs are 16-digit hexadecimal numbers and cannot be changed. However, Performance Control names do not need to be 16-digit hexadecimal numbers and can be changed. The following is the procedure for changing an already assigned Performance Control name.
2. 3. 4. Click the WWN tab (Figure 4 on page 20). In the upper-left tree, select the old HBA ( ) from below Monitor and then right-click the selection. From the pop-up menu, select Change WWN and Performance Control Name. The Change WWN and Performance Control Name window is displayed (Figure 14). 5. Enter the WWN of the new HBA in the WWN combo box. You can select the WWN of the newly connected HBA in the WWN combo box.
6. Select an HBA from the upper-left tree and select a Performance Control group from the lowerleft tree. Next, click Add WWN. Repeat this operation until all the HBAs you want are added to the Performance Control group. NOTE: • Select an HBA from below Monitor. You cannot add HBAs from below Non-Monitor to Performance Control groups. • If you select an HBA that is already contained in a Performance Control group from the upperleft tree, the Add WWN button IS NOT activated.
You can use a Performance Control group to switch priority of multiple HBAs from prioritized to non-prioritized, or vice versa. To switch priority: 1. Start XP Performance Control (see “Starting XP Performance Control” on page 32). The Performance Control window is displayed. 2. 3. Click the WWN tab (Figure 4 on page 20). 4. 5. In the lower-left tree, select and right-click a Performance Control group ( ).
The Change upper-limit window is displayed (Figure 16). b. 5. To assign an upper-limit to the I/O rate, enter the upper-limit value and then select IOPS from the list. Next, click OK. To assign an upper-limit to the transfer rate, enter the upper-limit value and then select MB/s from the list. Next, click OK. In the Performance Control window, click Apply. The settings in the window are applied to the storage system. Figure 16 The Change Upper-Limit Window .
Figure 17 The Rename Performance Control Group Window . Deleting a Performance Control Group To delete a Performance Control group, take the following steps: 1. Start XP Performance Control (see “Starting XP Performance Control” on page 32). The Performance Control window is displayed. 2. 3. Click the WWN tab (Figure 4 on page 20). 4. 5. 48 In the lower-left tree, select and right-click a Performance Control group ( Click Delete Performance Control Group from the pop-up menu.
6 Troubleshooting This chapter provides troubleshooting information for XP Performance Control.
Troubleshooting
7 Support and Other Resources Related Documentation • • • • • HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 LUN Manager User Guide HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console User Guide HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Business Copy Software User Guide HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Continuous Access Software User Guide Hitachi ShadowImage™ for Mainframe User Guide: HP XP24000 Disk Array, HP XP20000 Disk Array • Hitachi TrueCopy™ for Mainframe User Guide: HP XP24000 Disk Array, HP XP20000 Disk Array • Hitachi Uni
• 1 block = 512 bytes HP Technical Support For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website: http://www.hp.
Glossary ACP Array control processor. CU Control unit. DASD Direct-access storage device. DFW DASD fast write. DKA Disk adapter. See also ACP DKCMAIN Disk controller main. ESCON Enterprise systems connection An optical interface used to connect the mainframe to the control unit; a predecessor to FICON. LD, LDEV Logical device. An LDEV is created when a RAID group is carved into pieces according to the selected host emulation mode (that is, OPEN-3, OPEN-8, OPEN-9).
Glossary
Index Symbols components, 11 C conventions storage capacity values, 51 D development server, 12 document related documentation, 51 documentation HP website, 51 providing feedback, 52 H help obtaining, 52 high-priority hosts, 11 host bus adapter, 25 HP technical support, 49, 52 technical support, 49, 52 I interoperability, 12 M many-to-many connections, 28 N non-prioritized port, 26, 34 non-prioritized WWN, 40 O one-to-one connections, 25 operations, 25 overview, 7 P Performance Control group, 44 Per
X XP Performance Control system requirements, 15 56