HP StorageWorks External Storage XP user guide (T1706-96006, June 2006)
Table Of Contents
- HP StorageWorks External Storage XP user guide
- Contents
- About this guide
- 1 Overview of connecting external arrays
- 2 Preparing for External Storage XP operations
- System requirements
- External Storage XP requirements
- Installing External Storage XP
- Preparing for External Storage XP settings
- Powering arrays on or off
- Using mapped external LUs from the host connected to the local array
- Uninstalling External Storage XP
- Limitations on External Storage XP operations
- Figure 11 Example of external LU with 2 TB or less
- Figure 12 External LU capacity is larger than the specified emulation type’s basic capacity (OPEN-3 example)
- Figure 13 External LU capacity is smaller than the specified emulation type’s basic capacity
- Table 4 When external LU’s emulation type is OPEN
- Table 5 When external LU’s emulation type is for mainframes
- Combining External Storage XP with other HP StorageWorks products
- 3 Managing cache with external storage
- Guidelines for using cache with external storage
- Determining, setting, or changing the external LU cache mode
- Partitioning cache for external storage
- Determining the number and size of needed partitions
- Creating Cache partitions
- Changing storage system modes
- 4 External Storage XP panes
- 5 Configuring external LUs
- Overview of configuring external LUs
- Setting an external array’s port
- Setting a local array’s port attributes
- Mapping external LUs (Add LU)
- Setting alternate paths for external LUs
- Adding alternate paths by selecting multiple external LUs (Add Paths)
- Deleting alternate paths by selecting multiple external LUs (Delete Paths)
- Checking an external LU’s status (LDEV Information)
- Disconnecting external arrays or LUs
- Checking the connection status and resuming external LU operations (Check Paths & Restore Vol.)
- Restoring external LUs (LDEV Restore)
- Stopping the use of paths to an external LU by specifying an external array’s WWN (Disconnect Paths)
- Restoring paths to an external LU by specifying an external array’s WWN (Check Paths)
- Changing an external array’s port setting
- Stopping the use of paths to an external LU by specifying a local array’s port (Disconnect Paths)
- Restoring paths to an external LU by specifying a local array’s port (Check Paths)
- Deleting external LU mappings (Delete LU)
- 6 Troubleshooting NAS Blade systems that include external arrays
- 7 Remote command devices
- 8 Troubleshooting External Storage XP
- A Notes on connecting external arrays
- Connecting Thunder 9500V subsystems
- System parameters for connecting Thunder 9500V subsystems
- Relationship between serial numbers in the Device list on the LU Operation pane and Thunder 9500V subsystem models
- Relationship between the WWN of the port on the Thunder 9500V subsystem and the controller
- Path status and examples of recovery procedures (Thunder 9500V subsystems)
- Connecting TagmaStore AMS and TagmaStore WMS subsystems
- System parameters for connecting TagmaStore AMS and TagmaStore WMS subsystems
- Relationship between serial numbers in the Device list on the LU Operation pane and TagmaStore AMS and TagmaStore WMS subsystem models
- Relationship between the WWN of the port on the TagmaStore AMS or TagmaStore WMS subsystem and the controller
- Path status and examples of recovery procedures (TagmaStore AMS and TagmaStore WMS subsystems)
- Connecting XP12000/XP10000 Disk Arrays
- Connecting XP1024/XP128 Disk Arrays
- Connecting XP512/XP48 Disk Arrays
- Connecting HP 200 Storage Virtualization System as external storage
- Connecting EVA arrays
- Connecting Thunder 9500V subsystems
- B Required volume capacity for emulation types
- C Adjusting volume capacity for copy pair setting
- D Using an XP12000/XP10000/SVS200 with an EVA3000/5000 external storage
- E Configuring MSA1000/1500 as external arrays
- Index
External Storage XP user guide 39
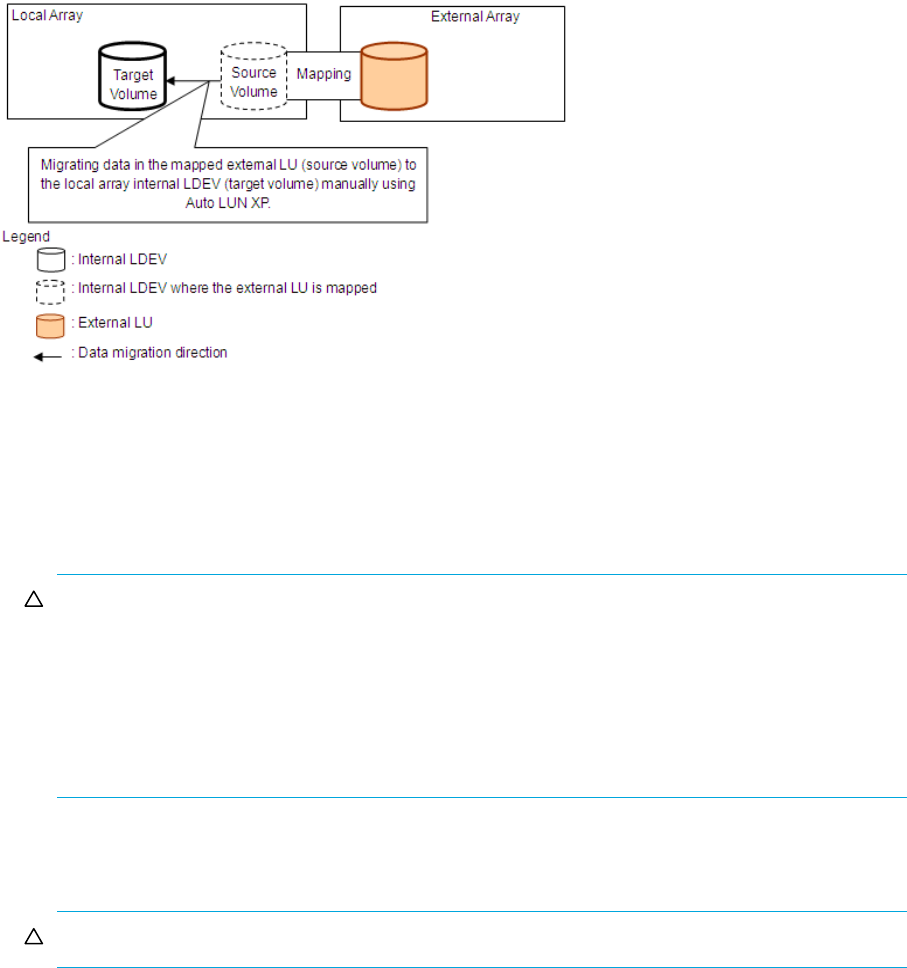
Using external LUs for Auto LUN XP operations
Figure 14 shows an example of using an external LU for Auto LUN XP operations. The mapped external
LU is set as the source volume, and the local array internal LDEV is set as the target volume. Existing data
in the external LU is (in effect) manually migrated to the internal LDEV on the local array using Auto LUN
XP. For more information, see the HP StorageWorks Auto LUN XP user guide for the
XP12000/XP10000/SVS200.
Figure 14 Example of Auto LUN XP operations
1. Use External Storage XP to map a volume in the external array to an internal LDEV of the local array.
For this example, set the following attributes for the mapped LU:
• Emulation type: OPEN-V
• IO Suppression mode: Disable
For more information, see ”Mapping external LUs (Add LU)” on page 73.
CAUTION: To migrate existing data in the mapped external LU to a local array volume using Auto
LUN XP or Business Copy XP, as shown in Figure 14, set the local array’s emulation type to
OPEN-V when mapping the LU. Only OPEN-V emulation can be used to read existing data in the
external LU from the local array side.
To copy existing data in the mapped external LU using HP StorageWorks software products, such
as Continuous Access XP and Business Copy XP, the mapped external LU’s emulation type must
also be OPEN-V.
2. Prepare a local array internal LDEV with the same capacity as the mapped external LU. Use Volume
Manager to adjust the internal LDEV’s capacity as required. For instructions, see the HP StorageWorks
LUN Configuration and Security Manager XP user guide for the XP12000/XP10000/SVS200.
CAUTION: The emulation type of the local array’s prepared internal LDEV must be OPEN-V.
3. Set the mapped external LU as the source volume, and set the local array internal LDEV as the target
volume.
4. Use Auto LUN XP to manually migrate existing data in the mapped external LU to the local array
internal LDEV (without changing the associated LDEV/LU).
Using external LUs for Continuous Access XP operations
Figure 15 shows an example of using an external LU for Continuous Access XP operations. The mapped
external LU is set as the Continuous Access XP pair’s S-VOL, and the volume in the local array that is
connected as the MCU is set as the Continuous Access XP pair’s P VOL. For more information about










