HP StorageWorks Continuous Access XP user guide for the XP10000/XP12000 (December 2005)
54 Continuous Access XP for the XP10000/XP12000
• CU#: CU number selected on the tree.
• Type: MCU or RCU.
• S/N and SSID: Serial number and SSID of the other CU of the pair.
• Paired CU#: CU number of the other CU of the pair.
• M-R Path: Path channel type (Fibre or Serial) between the other CU of the pair.
• Status: Normal indicates no failure path between the RCU. Failed indicates there are failure paths
between the RCU. This column is blank when the pair CU is MCU.
• Num. of Path: Number of paths. This column is blank when the pair CU is MCU.
Port tree and Port list
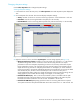
Click Port in the Switch Display box to display the Port tree and Port list. The Port tree displays channel
adapters (fibre: )and port types (Target: , RCU Target: , Initiator: , External: ). Only ports
that can be selected for remote copy operations are displayed.
Figure 25 RCU Operation pane with the Port option button selected
• Port: Cluster and port number (1A - 2R).
When the speed mode is standard, two port numbers are displayed in a row, and the speed mode can
be modified on a two- port basis.
When the speed mode is high, the port number is displayed on a package basis, and the speed mode
can be modified on a package basis.
• Attribute: Port type (Initiator, Target, RCU Target, External, RCP, or LCP).
• PCB Mode: Speed mode of the port (only for the fibre packages): standard, high-speed, or high-speed
(2 port).
• CU: Range of CU images (00-0F or 10-1F), which is displayed only for serial ports.
In the Port tree, port type can be selected to display specified information in the Port list. For example,
when Initiator is selected in the Port tree, the system looks for ports of Initiator from all ports entered, and
lists Initiator ports in the Port list. Only one port type can be selected in the tree.
Asynchronous Operation pane
The Asynchronous Operation pane displays consistency group information for the connected disk array
and provides access to the Continuous Access XP Asynchronous pair operation (see ”Continuous Access
XP Asynchronous operations” on page 75).