HP StorageWorks Auto LUN XP user guide for the XP128/XP1024 (December 2005)
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Auto LUN XP for the XP128/XP1024
- Auto LUN XP features
- Auto LUN XP tasks
- Reserve volumes
- Volume migration
- Estimating usage rates
- Automatic migration
- Manual migration
- Requirements and restrictions
- Starting Auto LUN XP
- Creating and executing migration plans
- Troubleshooting Auto LUN XP
- Auto LUN/Performance Control Base Monitor for the XP128/XP1024
- Auto LUN statistics
- Usage statistics
- Collecting usage statistics about disk array resources
- Viewing parity group usage statistics
- Viewing logical volume usage statistics
- Viewing channel adapter (CHA) usage statistics
- Viewing channel processor (CHP) usage statistics
- Viewing disk adapter (DKA) usage statistics
- Viewing disk processor (DKP) usage statistics
- Viewing data recovery and reconstruction processor (DRR) usage statistics
- Viewing write pending rates
- Viewing access path usage statistics
- Workload and traffic statistics
- Index
Auto LUN XP user guide for the XP128/XP1024 15
4. Analyze monitor data to confirm tuning results.
Manual migration
Use manual migration to select and migrate logical volumes under direct, manual control. The manual
migration function displays estimated results of proposed migration operations, which you can use to
determine expected performance improvements prior to the actual migration.
While auto migration operations are based on disk usage and hierarchy of parity groups, you can use
manual migration operations to address back-end processor usage (DKPs and DRRs) and volume and
parity group usage. If monitoring shows high or unbalanced processor usage, use manual migration
operations to tune the processor performance of the XP128/XP1024.
Requirements and restrictions
Logical volumes
Source and target volumes must be in the same XP128/XP1024 and have the same emulation type and
capacity.
NOTE: For users in the StorageAdmins group, the function you can use are limited. For more information
about these limitations, see the HP StorageWorks Command View XP User Guide for XP Disk Arrays or the
HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console User Guide for XP1024/XP128.
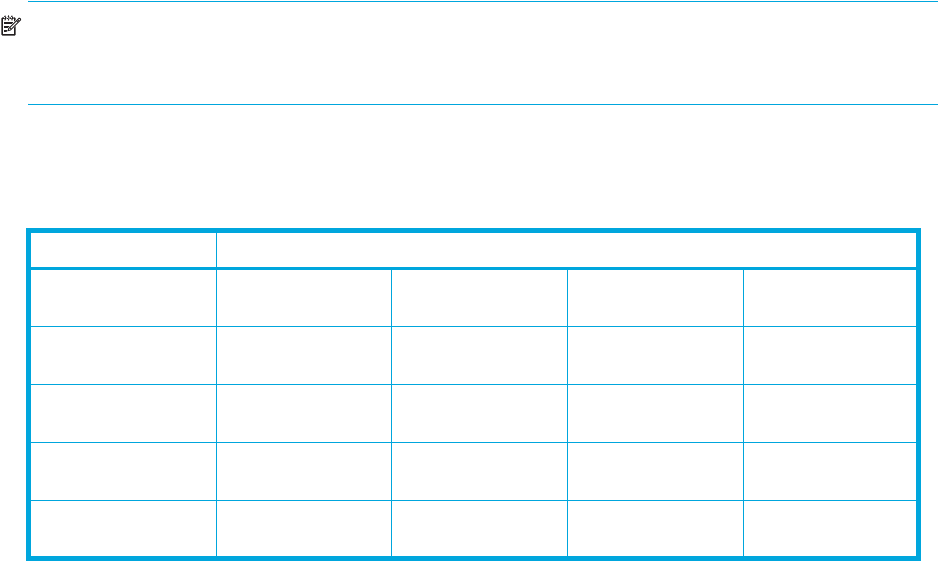
Whether you can or cannot perform volume migration with a pair consisting of customized volumes (CVs)
and normal volumes depends on the volumes’ emulation type. For details, see Table 3.
You cannot make pairs of the volumes.
Source volumes
The following describes whether volumes can be used as source volumes:
• Volumes set as command devices (reserved for use by hosts) cannot be used as source volumes.
• Volumes in an abnormal or inaccessible condition (for example, fenced) cannot be used as source
volumes.
• Volumes with Cache LUN data stored in cache cannot be used as source volumes.
• iSCSI volumes (volumes to which paths are defined from iSCSI ports) cannot be used as source
volumes.
• Volumes that HP StorageWorks Continuous Access XP Journal or Universal Replicator for z/OS uses as
a data or journal volume cannot be used as source volumes.
• Volumes reserved by a migration program other than Volume Migration cannot be used as source
volumes.
Table 3 Movability of volumes in pairs consisting of CV and normal values
Source volume Target volume
Normal volume
(not OPEN-V)
Normal volume
(OPEN-V)
CV
(not OPEN-V)
CV
(OPEN-V)
Normal volume
(not OPEN-V)
Movable — Not movable —
Normal volume
(OPEN-V)
— Movable — Movable
CV
(not OPEN_V)
Not movable — Movable —
CV
(OPEN-V)
— Movable — Movable










