Hitachi HPAV for z/OS user guide (HITA737-96006, June 2008)
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Compatible PAV Function for the XP1024/XP128/XP12000/XP10000
- Overview of Compatible PAV Operations
- Preparing for Compatible PAV Operations
- Performing Compatible PAV Operations
- Monitoring Compatible PAV Activities
- Additional MVS Commands
- GTF I/O Tracing
- Figure 13 Sample Output of Display Command - Compatible PAV Base Device with 5 Aliases
- Figure 14 Sample Output of Display Command - Compatible Hyper PAV with 16 Aliases
- Figure 15 DEVSERV DISPLAY PATHS Command
- Figure 16 Sample DEVSERV QPAV Command (Compatible PAV)
- Figure 17 Sample DEVSERV QPAV Command (Compatible Hyper PAV)
- Figure 18 Sample Output of DEVSERV QPAV,SSID=xxxx Command (Compatible PAV)
- Figure 19 Sample Output of DEVSERV QPAV,SSID=xxxx Command (Compatible Hyper PAV)
- Figure 20 Sample Output of DS QP,xxxx,VOLUME Command (Compatible PAV)
- Figure 21 Sample Output of DS QP,xxxx,VOLUME Command (Compatible Hyper PAV)
- Figure 22 Sample Output of D IOS,HYPERPAV Command
- Using HCD to Define and View XP1024/XP128/XP12000/XP10000 LCUs and Compatible PAV Devices
- Using HCD to Define an XP1024/XP12000/XP10000 LCU and the Base and Alias Devices
- Figure 23 Basic HCD Panel
- Figure 24 Define, Modify, Or View Configuration Data
- Figure 25 Add Control Unit Panel
- Figure 26 Selecting the Operating System
- Figure 27 Select, Change Option
- Figure 28 Control Unit Chpid, CUADD, and Device Address Range Addressing
- Figure 29 Define, Modify, Or View Configuration Data
- Figure 30 I/O Device List
- Figure 31 Add Device
- Figure 32 Device / Processor Definition Panel - Selecting the Processor ID
- Figure 33 Define Device / Processor Panel
- Figure 34 Define Device to OS Configuration Window - Selecting the OS Configuration
- Figure 35 Select / Disconnect Option
- Figure 36 Define Device Parameters / Features
- Displaying Compatible PAV Device Parameters
- Using HCD to Define an XP1024/XP12000/XP10000 LCU and the Base and Alias Devices
- Checking the WLM PAV Settings
- Settings about Compatible Hyper PAV
- Index
HPAV for z/OS user guide for the XP128/XP1024/XP12000/XP10000 21
• The unused device addresses in the XP1024/XP128/XP12000/XP10000 are used as alias devices.
If you use most of the unused device addresses for aliases, you will only have a small amount of free
devices available. If you determine that a large number of aliases will be required, consider adding
more disks to ensure that storage will be available when needed.
• Compatible PAV may not provide good results for devices that are always shared and used by
multiple host systems. For access by multiple hosts, use the Multiple Allegiance (MA) host software
function supported by the XP1024/XP128/XP12000/XP10000.
• If dynamic Compatible PAV can be used in all systems, expect good results if you assign eight to
sixteen (8-16) aliases to each CU image.
• The recommended ratio of base devices to alias devices is 1:3. Table 4 shows examples of
calculating the number of base and alias devices for a CU image with 256 devices. If you know the
types of jobs and/or the expected host access rates for the base devices, determine the number of
aliases for each base device to meet your requirements for each base device.
• Up to 255 alias devices can be assigned to one base device for an XP12000/XP10000. For an XP
1024, 128 up to 15. In this case, however, the desired effect will not be achieved because I/O
conflicts can occur with the base device and the alias devices. Therefore, the devices may be
unable to receive the I/Os.
• For Compatible Hyper PAV
• During assignment of aliases to base devices via Command View or Remote Console. Do not assign
more than three aliases to a single base device address.
• The number of alias devices assigned to each base device should be kept as equal as possible. For
example, a CU with 10 aliases could have three aliases each assigned to the first to third base
addresses, one alias to the fourth base address, and no alias assignments to the remaining base
addresses or you could assign one alias to each of the 10 addresses, as needed.
• Hyper PAV does not use WLM to calculate the number of aliases.
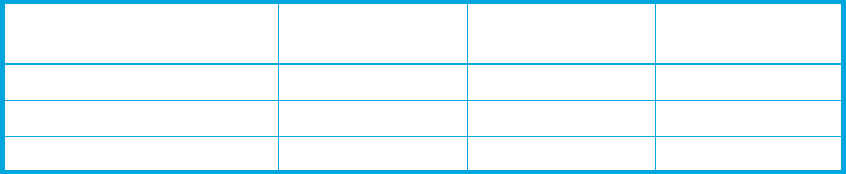
Table 4 Ratio of base devices to alias devices
Ratio
(base devices : alias devices)
Number of Base
Devices
Number of Alias
Devices
Total Devices
1:3 (recommended) 64 192 256 (64+192)
1:2 85 171 (85+86) 256 (85+171)
1:1 128 128 256 (128+128)










