Hitachi HPAV for z/OS user guide (HITA737-96006, June 2008)
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Compatible PAV Function for the XP1024/XP128/XP12000/XP10000
- Overview of Compatible PAV Operations
- Preparing for Compatible PAV Operations
- Performing Compatible PAV Operations
- Monitoring Compatible PAV Activities
- Additional MVS Commands
- GTF I/O Tracing
- Figure 13 Sample Output of Display Command - Compatible PAV Base Device with 5 Aliases
- Figure 14 Sample Output of Display Command - Compatible Hyper PAV with 16 Aliases
- Figure 15 DEVSERV DISPLAY PATHS Command
- Figure 16 Sample DEVSERV QPAV Command (Compatible PAV)
- Figure 17 Sample DEVSERV QPAV Command (Compatible Hyper PAV)
- Figure 18 Sample Output of DEVSERV QPAV,SSID=xxxx Command (Compatible PAV)
- Figure 19 Sample Output of DEVSERV QPAV,SSID=xxxx Command (Compatible Hyper PAV)
- Figure 20 Sample Output of DS QP,xxxx,VOLUME Command (Compatible PAV)
- Figure 21 Sample Output of DS QP,xxxx,VOLUME Command (Compatible Hyper PAV)
- Figure 22 Sample Output of D IOS,HYPERPAV Command
- Using HCD to Define and View XP1024/XP128/XP12000/XP10000 LCUs and Compatible PAV Devices
- Using HCD to Define an XP1024/XP12000/XP10000 LCU and the Base and Alias Devices
- Figure 23 Basic HCD Panel
- Figure 24 Define, Modify, Or View Configuration Data
- Figure 25 Add Control Unit Panel
- Figure 26 Selecting the Operating System
- Figure 27 Select, Change Option
- Figure 28 Control Unit Chpid, CUADD, and Device Address Range Addressing
- Figure 29 Define, Modify, Or View Configuration Data
- Figure 30 I/O Device List
- Figure 31 Add Device
- Figure 32 Device / Processor Definition Panel - Selecting the Processor ID
- Figure 33 Define Device / Processor Panel
- Figure 34 Define Device to OS Configuration Window - Selecting the OS Configuration
- Figure 35 Select / Disconnect Option
- Figure 36 Define Device Parameters / Features
- Displaying Compatible PAV Device Parameters
- Using HCD to Define an XP1024/XP12000/XP10000 LCU and the Base and Alias Devices
- Checking the WLM PAV Settings
- Settings about Compatible Hyper PAV
- Index
HPAV for z/OS user guide for the XP128/XP1024/XP12000/XP10000 17
XP1024/XP128/XP12000/XP10000. WLM compatibility mode provides static Compatible PAV
functionality and WLM goal mode provides dynamic Compatible PAV functionality. WLM must be in
“GOAL” mode to support “Dynamic Alias Management” Compatible PAV functionality.Support for
Dynamic Alias Management by the Workload Manager (WLM) is dependent on the following three
parameter settings:
• WLM Goal Mode setting
• WLM “Dynamic alias management” setting in the Service Coefficients/Service Definitions window.
• WLMPAV setting of each base device as defined in the “Define Device Parameters / Features” HCD
definition window.
Static and Dynamic Compatible PAV Operations
Static or dynamic Compatible PAV operation is determined by the combination of the following parameter
settings:
• The ‘WLMPAV=xxx’ parameter setting for each device defined to the z/OS and OS/390 host through
the HCD. The default setting of this parameter is ‘WLMPAV=YES’ for 3390B or 3390A devices defined
through the HCD.
• The ‘Dynamic Alias Support’ parameter setting for WLM.
• Static Compatible PAV is implemented when the WLM feature for ‘Dynamic Alias Support’ is set to NO
and the appropriate aliases are assigned to the base devices using Command View XP or XP Remote
Web Console. The setting of the ‘WLMPAV=xxx’ parameter defined for each 3390B or 3390A device
is ignored. In addition, the ‘I/O Priority Management’ setting for WLM is ignored (Table 2 on
page 17).
• Dynamic Compatible PAV is implemented when ‘Dynamic Alias Support’ is set to YES and the
appropriate aliases are assigned to the base devices using Command View XP or XP Remote Web
Console. The setting of the ‘WLMPAV=xxx’ parameter defined for each 3390B or 3390A device must
be set to ‘YES’ if WLM is to manage the alias device address assignments. In addition, the ‘I/O Priority
Management’ setting for WLM determines the dynamic alias algorithm to be used for meeting the
Performance Index of the workloads under the control of WLM using the Compatible PAV feature (see
• Table 2 on page 17).
NOTE: When ‘Dynamic Alias Support’ is enabled, the alias-to-base assignments are managed by the
WLM component of the z/OS and OS/390 system as needed in response to changes in I/O activity.
Static Compatible PAV
When static Compatible PAV is used, the number of aliases specified for each base device does not
change, even when the number of I/O requests to each device changes. When dynamic Compatible PAV
is used, the number of aliases for each base device is likely to change as the number of I/O requests
changes.
The following figure shows an example of static Compatible PAV operations. Each of the three base devices
(x10, x11, and x12) has two aliases assigned. If I/O requests converge on base device x10 (shown by the
large arrow), the number of aliases for each base device remains unchanged.
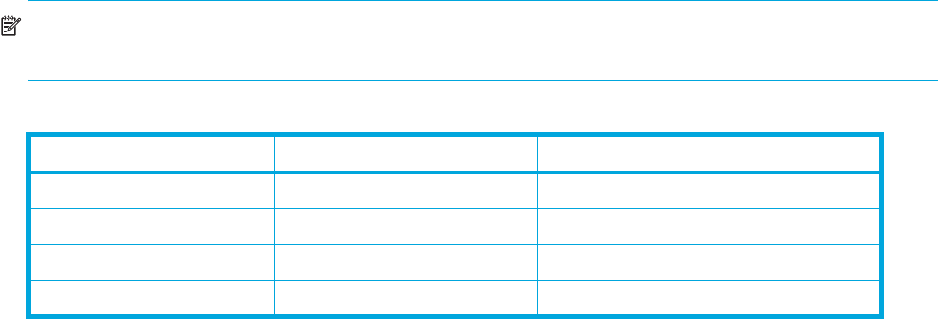
Table 2 HCD settings for static and dynamic Compatible PAV
Dynamic Alias Support I/O Priority Management Dynamic Alias Algorithm in Effect
NO NO None (static Compatible PAV only)
NO YES None (static Compatible PAV only)
YES NO Efficiency only
YES YES Both efficiency and goal










