HP Remote Graphics Software 5.4.8 User Guide
Using RGS in Normal Mode
Normal Mode is one of the two RGS operating modes—see RGS operating modes on page 26.
Normal Mode is the simplest means of establishing a connection—you enter the IP address or hostname
of the Remote Computer in the Local Computer Receiver Control Panel, and click Connect.
NOTE: The second RGS operating mode, Directory Mode, is described in Using Directory Mode
on page 170 .
NOTE: The RGS Sender listens on TCP/IP port 42966. The port used by the RGS Receiver is
assigned by the Local Computer OS and can vary.
Before attempting to connect to a particular Remote Computer for the first time, HP recommends that
you verify that the Remote and Local Computers satisfy the
Pre-connection checklist on page 91 . The
Pre-connection checklist on page 91 can also be used as a troubleshooting aid if a connection attempt
fails. After verifying the preconnection checklist, start the Receiver on the Local Computer. This can be
done from the start menu or from the command line (see
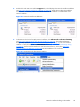
Figure 5-1 Starting the Receiver on Windows
on page 101).
Figure 5-1 Starting the Receiver on Windows
The RGS Receiver supports the following command line options for the Windows executable,
rgreceiver.exe, and the Linux executable, rgreceiver.sh:
[-config [filename]]
[-directory [file]]
[-nosplash]
[-v | -ver | -version]
[-h | -help | -?]
-Rgreceiver.propertyname=value
-config filename—Specifies the name of a RGS Receiver configuration file to use.
-directory [file]—Starts the Receiver in Directory Mode. If the optional file path is specified, the
file is opened and used to look up the Remote Computers assigned to the user. If a file is not specified,
the user is prompted to enter a path to the directory file. For information on Directory Mode, see
Using
Directory Mode on page 170.
-nosplash—Disables display of the splash screen when the Receiver starts.
[-v | -ver | -version]—Displays the Receiver version information.
Using RGS in Normal Mode
101