Open Source Object Storage for Unstructured Data: Ceph on HP ProLiant SL4540 Gen8 Servers
Table Of Contents
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Overview
- Solution components
- Workload testing
- Configuration guidance
- Bill of materials
- Summary
- Appendix A: Sample Reference Ceph Configuration File
- Appendix B: Sample Reference Pool Configuration
- Appendix C: Syntactical Conventions for command samples
- Appendix D: Server Preparation
- Appendix E: Cluster Installation
- Naming Conventions
- Ceph Deploy Setup
- Ceph Node Setup
- Create a Cluster
- Add Object Gateways
- Apache/FastCGI W/100-Continue
- Configure Apache/FastCGI
- Enable SSL
- Install Ceph Object Gateway
- Add gateway configuration to Ceph
- Redeploy Ceph Configuration
- Create Data Directory
- Create Gateway Configuration
- Enable the Configuration
- Add Ceph Object Gateway Script
- Generate Keyring and Key for the Gateway
- Restart Services and Start the Gateway
- Create a Gateway User
- Appendix F: Newer Ceph Features
- Appendix G: Helpful Commands
- Appendix H: Workload Tool Detail
- Glossary
- For more information
Reference Architecture| Ceph on HP ProLiant SL4540 Gen8 Servers
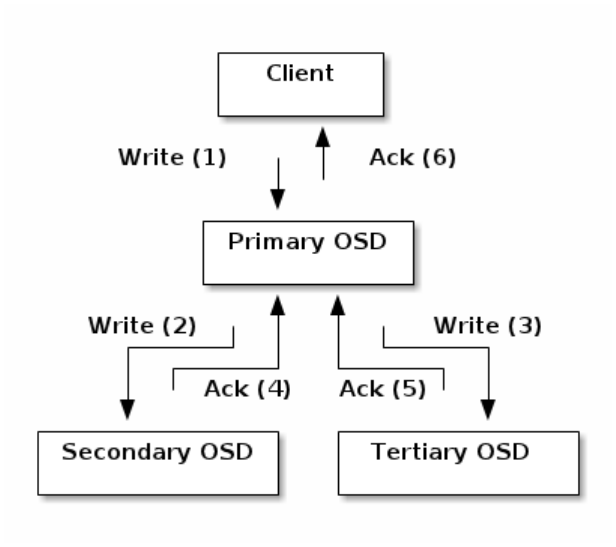
Figure 4: Replication
This model offloads replication to the OSD hosts; the client only has to drive data for the primary write. The picture above is
for the three copies of an object in the sample reference configuration; the Primary OSD will drive as many replicas as are
defined by the target pool.
Peering and Sets:
The Ceph Storage Cluster was designed to store at least two copies of an object, which is the minimum requirement for data
safety. For high availability, a Ceph Storage Cluster should store more than two copies of an object
(e.g., size = 3 and min size = 2) so that it can continue to run in a degraded state while maintaining data safety.
Referring back to the replication diagram, the Ceph OSD Daemons are not specifically named (e.g., osd.0, osd.1, etc.), but
rather referred to as Primary, Secondary, and so forth. By convention, the Primary is the first OSD in the Acting Set, and is
responsible for coordinating the peering process for each placement group where it acts as the Primary, and is
the
ONLY
OSD that that will accept client-initiated writes to objects for a given placement group where it acts as the Primary.
When a series of OSDs are responsible for a placement group, they’re referred to as an Acting Set. An Acting Set may be Ceph
OSD Daemons that are currently responsible for the placement group, or the Ceph OSD Daemons that were responsible for
a particular placement group as of some epoch.
This behavior also applies to removal/failure of an OSD; object copies get remapped from other elements of the Acting Sets
onto free cluster storage.
Rebalancing:
When a Ceph OSD Daemon is added to a Ceph Storage Cluster, the cluster map gets updated with the new
OSD. Consequently, it also changes object placement, because it changes an input for CRUSH map calculations. The process
of redistributing objects across the Ceph cluster is termed rebalancing.
Data Consistency:
Ceph OSDs can compare object metadata in one placement group with its replicas in placement groups
stored on other OSDs. Scrubbing (usually performed daily) catches OSD bugs or file system errors. OSDs can also perform
deeper scrubbing by comparing data in objects bit-for-bit. Deep scrubbing (usually performed weekly) finds bad sectors on a
disk that weren’t apparent in a lighter scrub.
Failure Domain, CRUSH map
: An important element of maintaining fault tolerance is determining where data should be
placed for optimal resiliency. Rather than depend on expensive hardware redundancy for all interconnects, the scale-out
design principle is to assume some components will fail and make the data available by properly partitioning failure
domains.
For a simpler configuration, it’s ok to assume that distributing copies across servers will provide reliability. As clusters scale
out, it will be important to separate replicas across racks, power sources, network switches, or even data centers to reduce
the likelihood a failure event will have untenable impacts. The default CRUSH map generated by ceph-deploy cluster install
10










