hot plug RAID memory technology for fault tolerance and scalability
hot plug RAID memory technology for fault tolerance and scalability
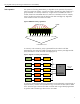
figure 5: diagram of a memory read transaction for one of the four data paths
RAID Memory
Logic
MUX
Parity
Compare
Good
Data
Miscompare
= NMI, if
ECC did not
report it
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
MC1
MC2
MC3
MCP
MC4
SDRAM
SDRAM
SDRAM
SDRAM
SDRAM
During every read transaction, the ECC logic also passes data to a RAID memory logic
circuit where a RAID algorithm simultaneously regenerates each data word using the
data words from the other three memory controllers and the parity controller. For
example, as shown in figure 5, the RAID memory logic uses the data words from memory
controllers 2, 3, 4, and P to regenerate the data word for memory controller 1 (MC1).
Each regenerated data word from the RAID memory logic is then passed to a separate
MUX (figure 6).
figure 6: RAID memory architecture
RAID Memory
Logic
MUX 1
PC1
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
ECC Logic
MC1
MC2
MC3
MCP
MC4
SDRAM
SDRAM
SDRAM
SDRAM
SDRAM
MUX 2
PC2
MUX 3
PC3
MUX 4
PC4
If the signal from the ECC logic to the MUX indicates the data is good, the MUX sends
the original data to the processor. If the signal from the ECC logic to the MUX indicates
the data has an error, the MUX sends the regenerated data from the RAID memory logic.
At this point, the error detected by the ECC logic has been eliminated and only good
data has been transmitted.
7