ProLiant DL580 Generation 3 Server Maintenance and Service Guide
Table Of Contents
- HP ProLiant DL580 Generation 3 Server Maintenance and Service Guide
- Notice
- Contents
- Illustrated parts catalog
- Removal and replacement procedures
- Required tools
- Safety considerations
- Preparation procedures
- Removing the front bezel
- Removing a media drive blank
- Removing a media drive
- Removing the processor module
- Removing a processor
- Removing a PPM
- Removing a PCI latch
- Removing a PCI retaining clip
- Removing the PCI-X Hot Plug basket
- Removing a non-hot-plug expansion board
- Removing the PCI-X Hot Plug mezzanine option
- Removing the PCI Express mezzanine option
- Recovering data from the BBWC
- Removing the BBWC battery pack
- Removing the BBWC cache module
- Removing the system board
- Removing the system battery
- Removing the media board
- Removing the SCSI backplane
- Removing the power backplane
- Removing the memory backplane
- Removing a hard drive blank
- Removing a hot-plug SCSI hard drive
- Removing a hot-plug SAS hard drive
- Removing the SAS-SATA hard drive cage
- Removing the SAS-SATA backplane
- Removing a PCI-X Hot Plug expansion board
- Removing a power supply blank
- Removing a redundant hot-plug power supply
- Replacing hot-plug fans
- Memory overview
- Diagnostic tools
- SmartStart software
- SmartStart Scripting Toolkit
- HP Instant Support Enterprise Edition
- Option ROM Configuration for Arrays
- HP ROM-Based Setup Utility
- ROMPaq utility
- System Online ROM flash component utility
- Integrated Management Log
- Integrated Lights-Out technology
- Automatic Server Recovery
- HP Systems Insight Manager
- HP Insight Diagnostics
- USB support
- Troubleshooting the system using port 85 codes
- Server component identification
- Front panel components
- Front panel LEDs and buttons
- Memory board components and LEDs
- Processor module LEDs
- Rear panel components
- Rear panel LEDs and buttons
- Power supply LEDs
- System board components
- DIMM slot locations
- SCSI IDs
- Hot-plug SCSI hard drive LEDs
- Hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations
- SATA or SAS IDs
- SATA or SAS hard drive LEDs
- SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations
- Fan locations
- Hot-plug fan LEDs
- BBWC LEDs
- Server cabling
- Specifications
- Acronyms and abbreviations
- Index
Removal and replacement procedures 51
•
DIMMs must be installed in pairs.
• DIMM pairs within a memory bank must contain DIMMs with the same part number.
• Always populate the DIMMs in sequential order per bank: Bank A and then Bank B.
• Always populate the memory boards in sequential order: Board 1, Board 2, Board 3, and Board 4.
Any deviation from this requirement results in the server defaulting to Advanced ECC ("Advanced
ECC memory" on page 51) on the next reboot.
• Dual-rank DIMMs ("Single- and dual-rank DIMMs" on page 51) must be populated before single-rank
DIMMs (dual-rank DIMMs must be in the lower bank).
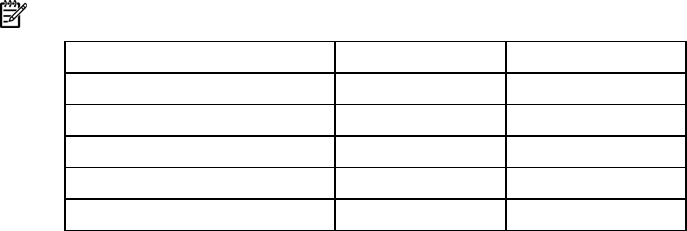
• The following table lists all valid combinations of single- and dual-rank DIMM configurations for a
memory board. "Single" indicates a bank of single-rank DIMMs. "Dual" indicates a bank of dual-
rank DIMMs.
NOTE: A bank contains two DIMMs.
Configuration Bank A Bank B
1 Single —
2 Single Single
3 Dual —
4 Dual Single
5 Dual Dual
• The server can be configured for any AMP mode in RBSU. RBSU displays a warning message if the
selected AMP mode is not supported by the current DIMM configuration. However, if the DIMM
configuration at POST does not match the AMP mode selected in RBSU, the server defaults to
Advanced ECC ("Advanced ECC memory" on page 51). When this occurs, a message displays
during POST and the status LED for the configured AMP mode flashes amber.
• Unpopulated memory boards (those without any installed DIMMs) can be installed in the server for
storing extra memory boards.
• If your server contains more than 4 GB of memory, consult your operating system documentation for
additional requirements.
Single- and dual-rank DIMMs
PC2-3200 DIMMs can either be single- or dual-rank. While it is not normally important for you to
differentiate between these two types of DIMMs, certain DIMM configuration requirements are based on
these classifications.
Certain configuration requirements exist with single- and dual-rank DIMMs that allow the architecture to
optimize performance. A dual-rank DIMM is similar to having two separate DIMMs on the same module.
Although only a single DIMM module, a dual-rank DIMM acts as if it were two separate DIMMs. The
primary reason for the existence of dual-rank DIMMs is to provide the largest capacity DIMM given the
current DIMM technology. If the maximum DIMM technology allows for creating 2-GB single-rank DIMMs,
a dual-rank DIMM using the same technology would be 4-GB.
Advanced ECC memory
Advanced ECC is the default memory protection mode for this server. In Advanced ECC, the server is
protected against correctable memory errors. The server will provide notification if the level of correctable
errors exceeds a predefined threshold rate. The server does not fail because of correctable memory
errors.
Advanced ECC provides additional protection over Standard ECC in that it is possible to correct certain
memory errors that would otherwise be uncorrectable and result in a server failure. Whereas Standard










