Neoview Workload Management Services Guide (R2.5)
Behavior Without Aggregation
Without query statistics aggregation, the execution of repetitive, short-running queries can
overload system resources and inundate the Repository with unnecessary records. Consider
what happens when query statistics aggregation is not enabled for a query that is prepared once
and executed repeatedly. Each time the query executes, the NDCS server sends a “would like to
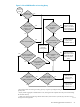
execute” request to WMS. See Figure 1-7.
Figure 1-7 Query Statistics Aggregation Disabled for a Repetitive Query
VST020.vsd
Repository
Database
Query prepare
Query execution
SQL Compiler
or Executor
Begin message
End message
Would like to execute
Query execution
Begin message
End message
Query finished
Query finished
Would like to execute
WMS
Process
NDCS
Server
When the query is executed repeatedly, numerous “would like to execute” requests are made
to WMS. The “would like to execute” requests can increase the query elapsed time.
After each “would like to execute” request, the NDCS server sends begin and end messages to
the Repository as it writes the query statistics to the Repository. The overhead involved in writing
a record to the Repository can be as much as the query itself.
When many repetitive, short-running queries are running simultaneously in the system, the
processing nodes (CPUs) become overloaded with requests and messages, causing the CPU
usage to increase. High CPU usage diminishes system performance.
Behavior With Aggregation
Enabling query statistics aggregation reduces the number of “would like to execute” requests
and begin/end messages for queries that are prepared once and executed repeatedly. See Figure 1-8
(page 29).
28 Introduction