Neoview Workload Management Services Guide (R2.5)
6. If the query is allowed to finish executing, Neoview SQL returns the results of the query to
the NDCS server. The NDCS server sends the query results back to the client application.
7. If the query is cancelled, WMS terminates the query without stopping the NDCS server, and
the NDCS server returns an SQL error message (8007) to the client application that issued
the query. The client application remains connected to the Neoview platform. For more
information, see “Cancel a Query” (page 145).
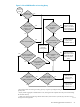
Figure 1-6 How WMS Handles an Executing Query
vst113.vsd
Yes
No
Yes
Has the condition of
an execution rule
been met?
No
Executing
query
Are there execution
rules associated with
the service?
WMS cancels the
query, and the NDCS
server returns an SQL
error message (8007).
WMS sets and
saves the
warning level.
No
Has the query
execution time
expired?
No
Yes
Is the execution rule
action = CANCEL?
Yes
The query continues to
execute.
For information on execution rules, see “Execution Rules” (page 98).
Query Statistics Aggregation
In Neoview Release 2.5 and later releases, you have the option of enabling query statistics
aggregation for repetitive, short-running queries. Repetitive, short-running queries are INSERT,
UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT statements that are prepared once and executed many times.
The queries in many load jobs and in some reports behave in this manner—they are prepared
once and executed repeatedly.
Benefits of Query Statistics Aggregation
When enabled, query statistics aggregation:
• Improves system performance by reducing the overhead for repetitive, short-running queries.
• Reduces the number of records in the Repository, causing reports to run more quickly and
making it easier for you to analyze historical data. Fewer records also allow more historical
data to be stored in the Repository.
• Provides visibility for unique queries (that is, queries that access only one row of data) in
WMS, allowing you to track those queries' progress in real time.
Query Statistics Aggregation 27