Neoview Workload Management Services Guide (R2.5)
If query statistics aggregation is enabled, WMS manages both non-unique and unique queries.
Non-unique queries access multiple rows of data whereas unique queries access only one row of
data. If query statistics aggregation is disabled, WMS manages only non-unique queries, which
access multiple rows of data, and does not manage unique queries, which access only one row
of data. When query statistics aggregation is disabled, unique queries run directly against the
database without being managed by WMS. If a query accesses multiple rows, even if the query
returns only one row of data, such as in the case of SELECT COUNT(*), WMS manages that
query. For a list of the query types managed by WMS, see Appendix B (page 261).
How WMS Applies Rules and Services
The rules that are associated with services specify conditions for WMS to evaluate and trigger
actions during certain phases of the client session and query execution. There are three phases
of the client session and query execution when WMS applies rules:
• “Connection Phase” (page 22)
• “Compilation Phase” (page 24)
• “Execution Phase” (page 26)
Connection Phase
When a client application connects to an NDCS server, the NDCS server compares the connection
rules in WMS with the client's connection attributes, which are set in ODBC, JDBC, or .NET, to
determine what WMS service to assign to the client session. Each service has one or more
connection rules associated with it.
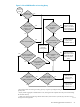
Figure 1-1 shows the sequence of events (designated by the numbers in the diagram) that occur
when a connection rule is applied during the connection phase.
Figure 1-1 How a Connection Rule Is Applied
1
3
vst111.vsd
Neoview Data Warehousing Platform
Neoview
Database
Runtime
Statistics
(RMS)
NDCS Server
Neoview
WMS
Client Application
Requesting a
Connection
Management Tool for
Monitoring WMS
4
5
2
22 Introduction