Neoview Workload Management Services Guide (R2.4)
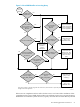
The next section explains how WMS determines which waiting queries are allowed to execute
when system resources become available.
How WMS Determines When to Execute Waiting Queries
When the system resource usage is at its limits, executing queries continue to execute but incoming
queries go into the waiting queue. As queries in each service finish executing, system resources
free up, and WMS starts allowing some of the waiting queries to start executing. While system
resources are free, WMS determines whether to allow waiting queries associated with a service
to start executing based on these criteria:
• Service priority
• Current percentage of executing queries associated with the service
• How the current percentage compares with the expected percentage for the service
The expected percentage of executing queries for each service is based on the service priority,
with higher priority services having a larger expected percentage of executing queries than lower
priority services.
If the percentage of executing queries for a service is greater than the expected percentage, WMS
keeps the queries associated with the service in the waiting queue. If the percentage of executing
queries for a service is equal to or less than the expected percentage, WMS allows waiting queries
associated with the service to start executing. The order in which WMS executes waiting queries
depends on the queries' service priority. For example, WMS executes queries associated with
higher priority services before executing queries associated with lower priority services.
WMS continues the process of dynamically balancing waiting and executing queries based on
the availability of system resources. WMS checks the system resource usage every five seconds.
When the system resource usage reaches its limits, WMS prevents waiting queries from executing
and puts incoming queries into the waiting queue, yet allows executing queries to continue
executing. When the queries finish executing, system resources become available again, and
WMS begins determining which waiting queries to allow to execute.
Configuring the WMS System Configuration
WMS has a built-in system configuration, the SYSTEM service, that defines these thresholds for
the Neoview platform:
Table 3-1 WMS System Thresholds
Default ValueThreshold
100%MAX_CPU_BUSY
85%MAX_MEM_USAGE
0 (no limit)MAX_ROWS_FETCHED
0 (no timeout)EXEC_TIMEOUT
0 (no timeout)WAIT_TIMEOUT
0 (no timeout)HOLD_TIMEOUT
5 secondsSTATS_INTERVAL
60 secondsRULE INTERVAL
Altering the WMS System Configuration
As a database administrator, you can alter the threshold values of the WMS system configuration
(that is, the SYSTEM service) by using the ALTER WMS command.
This ALTER WMS command changes the MAX_CPU_BUSY, MAX_MEM_USAGE, and
MAX_ROWS_FETCHED of the WMS system configuration:
28 Configuring Services