Neoview Character Sets Administrator's Guide (R2.4, R2.5)
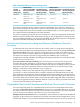
Table 1-2 Default Prefixes for Character String Literals
Non-Default Prefixes for
Character String Literals
(Must Be Specified)
Default Prefix for
Character String Literals
(Does Not Need to Be
Specified)
Non-Default Column
Character Set Definition
(Must Be Specified)
Default Column
Character Set Definition
(Does Not Need to Be
Specified)
Neoview
Character Set
Configuration
_UCS2, N_ISO88591CHARACTER SET
UCS2
CHARACTER SET
ISO88591
ISO88591
_UCS2, N_ISO88591CHARACTER SET
UCS2
CHARACTER SET
ISO88591
SJIS
_ISO88591_UCS2, NCHARACTER SET
ISO88591
CHARACTER SET
UCS2
Unicode
If you do not explicitly specify a column character set definition for a character column in an
SQL statement, the Neoview database assumes it is the default column character set definition
for that configuration. If you do not intend to use the default value, you must explicitly specify
the column character set definition in the SQL statement.
If you do not explicitly specify the character set prefix for a character string literal, the Neoview
database assumes the literal uses the default encoding for that configuration. If the literal does
not use that default encoding, you must explicitly define the encoding in the prefix. The N prefix
represents NCHAR, which maps by default to UCS2 characters.
Client Locale Character Encoding and Neoview Database Character
Encoding
To understand how the Neoview Character Sets feature works, it is important to distinguish
between client locale character encoding and Neoview database character encoding. Client locale
character encoding refers to the character set language that is currently used and active on a
client locale, such as a customer application or client workstation. Table 1-3 (page 17) identifies
the client locale character sets that are supported by the ISO88591, SJIS, and Unicode
configurations. The SQL identifiers and string literals in SQL statements are encoded in the client
locale character set of the client.
Neoview database character encoding refers to the character sets that can be used to store
character data in table columns for a given Neoview character set configuration. Database
character encoding may be different from the client locale character encodings used by customer
applications and client workstations. The rules that govern the use of character data in SQL
language components are described in Chapter 3 (page 23).
For example, assume a Neoview platform using the Unicode configuration has an ODBC
connection to a client workstation that is currently configured for the GBK character set. The
SQL statements issued from this client workstation are encoded in GBK, then converted to the
Neoview database encoding by the Neoview ODBC driver and/or the SQL engine and stored in
user tables. When the stored user data is retrieved by the GBK-configured client workstation or
by a customer application using a different character set, the user data is converted to the client
locale character encoding of the target client.
Compatible Client Locale Characters and Multiple Client Locale Characters
Two other important terms are compatible client locale characters and multiple client locale
characters. Compatible client locale characters refers to use of compatible characters among all
the client locales. Every character used by any one client locale must map to the same code point
value on the Neoview database that it does for every other client locale.
Multiple client locale characters refers to the ability to store and retrieve characters from different
languages on the same Neoview platform. For example, when the Unicode configuration is used,
the Neoview database can store data from different client locale character sets. Every client locale
Client Locale Character Encoding and Neoview Database Character Encoding 15