Neoview ODBC Drivers Manual (R2.2 SP1)
Table Of Contents
- HP Neoview ODBC Drivers Manual
- Table of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 HP Neoview ODBC Driver Overview for Windows
- 2 HP Neoview ODBC Drivers Overview for Linux, HP-UX, IBM AIX®, and Sun Solaris
- 3 Installing the HP Neoview ODBC Drivers
- Installing ODBC Client Software
- Avoiding Driver-Platform Version Incompatibility
- Installing the HP Neoview ODBC Driver for Windows
- Reinstalling the HP Neoview ODBC Driver for Windows
- Uninstalling the HP Neoview ODBC Driver for Windows
- Setting Up the Client Environment
- Troubleshooting
- Getting the Version of the Driver
- ODBC API Reference
- Installing or Reinstalling HP Neoview ODBC Drivers for Linux, HP-UX, IBM AIX®, and Sun Solaris
- Setting Up the Client Environment
- Running the Sample Program
- Troubleshooting
- Debugging
- Getting the Version of the Driver
- ODBC API Reference
- 4 Configuring Client Data Sources
- 5 HP Neoview ODBC Drivers Conformance
- 6 HP Neoview ODBC Drivers Messages
- Index
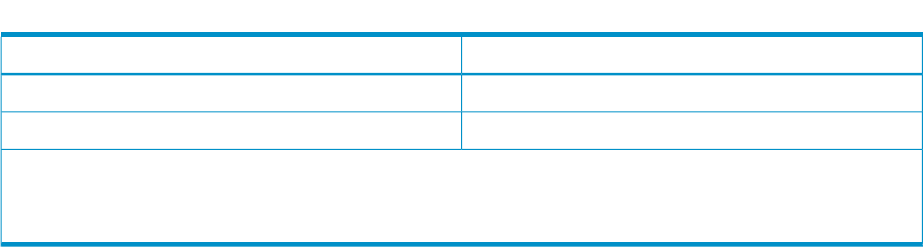
Table 5-17 Microsoft Escape Clauses (continued)
SQL EquivalentMicrosoft Escape Clause
Not supported in the current release.
{ escape 'escape-character' }
Not supported in the current release.
{ [?=]call procedure-name... }
1. ODBC syntax does not include nested joins, while SQL does. HP Neoview ODBC extends the Microsoft syntax
for an outer join.
2. Functions are controlled by SQLGetInfo. Only SQL native functions are supported.
Stored Procedures
The HP Neoview ODBC driver supports stored procedures, including results sets. Pointer to
cursors and returning codes are not supported.
Transactions and Cursor Behavior with Multiple Statements
AUTOCOMMIT is a connection-level attribute describing the semantics of transaction
demarcation. AUTOCOMMIT ON defines the semantics where the underlying system
automatically commits the current transaction at statement completion. COMMIT has secondary
effects on open cursors, SELECT statements in an OPEN state, having position in a result set.
AUTOCOMMIT occurs when the connection attribute is ON and any of these secondary actions
occur:
• An UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE statement forces a COMMIT before returning control to the
application.
• A cursor fetch (SELECT) detecting end-of-data, SQL_NO_DATA, is set to the CLOSED state
and becomes unpositioned.
• The statement is directly closed. For example: SQLFreeStatement (..., SQL_CLOSE)
These secondary actions do not result in an AUTOCOMMIT when there is a superior or outer
cursor to this statement. These actions allow an outer cursor to hold position until all rows of
the cursor have been processed, while allowing updates or other cursor operations to occur.
SQL Conformance Level 61










