HP Virtualization Manager 6.0 Software with Logical Server Management User Guide
Table Of Contents
- HP Insight Virtualization Manager 6.0 Software with Logical Server Management: User Guide
- Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Getting started with Virtualization Manager
- 3 Working with logical servers
- Using logical servers in Virtualization Manager
- New features in logical servers
- Understanding logical servers as they appear in visualization perspectives
- Logical server operations
- Authorizations, requirements, and configuration
- Logical server requirements
- Configuring and registering VMware vCenter
- Configuring VMware vSphere client settings for browsing datastore
- Configuring HP SIM with Onboard Administrator credentials
- Configuring HP SIM for SAN storage validation
- Configuring Extensible Server & Storage Adapter (ESA)
- Configuring Storage Provisioning Manager (SPM)
- LSMUTIL database utility
- 4 Defining storage for logical servers
- 5 Troubleshooting
- Navigation tips
- User preferences tips
- Performance tips
- Problems with meters collecting data
- Search button displays error page
- Displaying empty, hidden resource pools
- Errors accessing single sign-on iLO or Onboard Administrator
- Recovery after logical server operation failures
- Troubleshooting an inoperable logical server
- Correcting problems powering on a logical server
- Logical server operations cannot be cancelled
- Logical Server Automation service fails to start if TCP layer ports are in use
- Use portable WWNs and MAC addresses for Virtual Connect domain groups
- Do not use valid host name as logical server name
- Oversubscribing the number of networks
- Insufficient NICs error when activating or moving logical servers (Virtual Connect Flex-10 support)
- Use caution when renaming or moving a Virtual Connect domain group
- Deactivate or move logical servers before replacing blade
- Unmanaging a logical server using a storage pool entry may result in an inconsistent state
- Synchronize clocks on the CMS, managed systems, and VMware vCenter
- Ensure VM Hosts use fully qualified host names
- VM Hosts must be in same vCenter for ESX virtual machine logical server moves
- VM displayed without association in Virtualization Manager perspectives after deactivation
- Moving logical servers when the CMS and vCenter are in different network domains
- Changing the IP address of a VM Host after logical server discovery prevents the VM Host from appearing as an activation and move target
- Creating and managing logical servers on Microsoft Windows Hyper-V Server 2008
- 6 Advanced features
- 7 Support and other resources
- Index
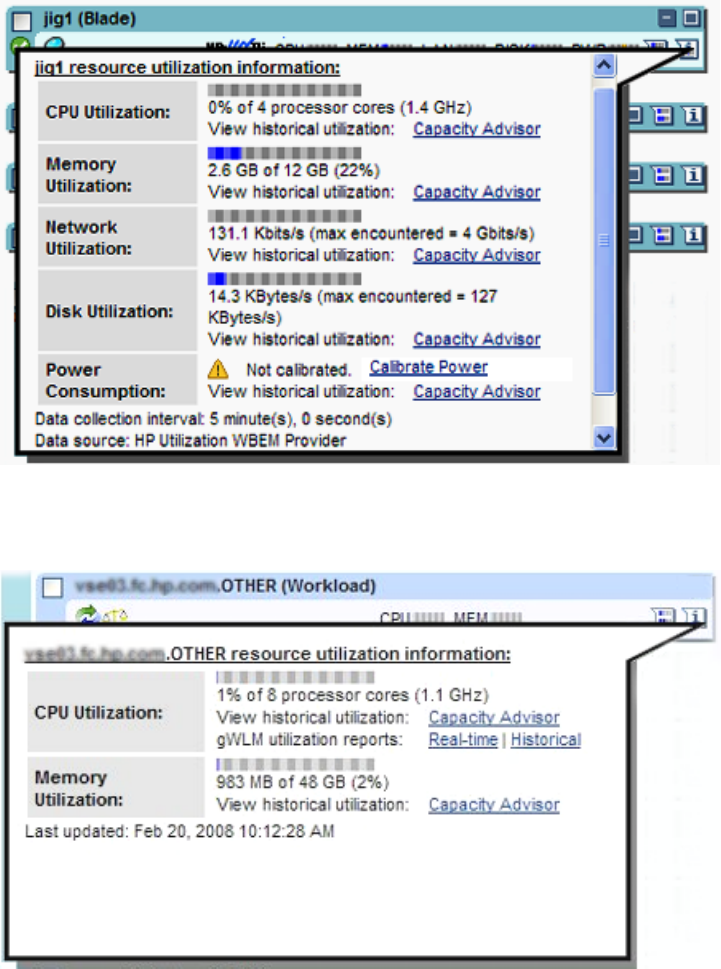
Meter callout information
Meter callouts exist only on the Visualization tab. Meter callout information includes:
• Current utilization data for CPU, memory, network, and disk; plus the ability to view
historical data, for example, by linking to Capacity Advisor to display a profile page.
• Information about power consumption for any physical server, including standalone servers,
nPartitions, or server blades.
• Collection interval; which is typically in 5 minute intervals for WBEM/VMM data, but can
vary for agentless data collection.
• Source of the meter data, indicating whether the data comes from the utilization WBEM
provider, VMM, or via agentless data collection.
• Last-updated time of the data collection.
• Error messages (for example, if there was a problem collecting utilization data from the
server), a suggested resolution, and an optional Retry link.
The following figure shows meter callout information for a server blade running on HP-UX.
If the compartment shows a managed workload, links appear that let you view real time and
historical information from the Global Workload Manager (gWLM). For example:
94 Advanced features










