Linux Best Management Practices for HP ProLiant Gen8 Servers and Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Technical white paper | Linux Best Management Practices: HP ProLiant Gen8 Servers and Red Hat Enterprise Linux
The iLO 4 Agentless Management SNMP service supports the widely-used SNMP v1 protocol. The service generates SNMP v1 traps
(messages about the status of monitored subsystems) and directs them to trap destinations (such as HP SIM). Trap destinations are
specified in the iLO 4 GUI AdministrationManagement configuration page. For a list of traps generated, see “Appendix B: Traps
generated by iLO 4 Agentless Management and AMS”. For security reasons, the iLO 4 SNMP service does not support SNMP set
operations.
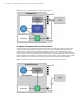
Networking interface considerations
Standard management practice recommends having a dedicated (and isolated) Management LAN (MLAN). When legacy agents are
being used, the MLAN needs to be connected to both the iLO and one of the host NICs (on a single LAN segment or VLAN). This allows
you to access the iLO remote console, Web interface, and iLO SSH, and to access the host SNMP from the MLAN.
Agentless Management on HP ProLiant Gen8 Servers provides a single MLAN interface, without having to shuffle data repeatedly
between the OS and the iLO 4. By allowing the iLO 4 to access and process the data locally, you get up to 85% reduction in memory
usage and 95% fewer processor cycles consumed than you would using the legacy agents.
Installing HP AMS for Red Hat Enterprise Linux
You can install HP AMS for Linux by using any of the following methods:
• Obtain the hp-ams RPM from the HP Service Pack for ProLiant (SPP) ISO image and install it using the rpm command:
# rpm –ivh hp-ams-*.rpm
This is the simplest and recommended method.
• Add the HP ProLiant Linux Software Delivery Repository (SDR)
1
to the local yum repository configuration, and enter the yum
command:
# yum install hp-ams
This method automatically satisfies all dependencies; however, this is not necessary because the Linux hp-ams dependencies are
part of the base OS installation.
• Obtain and install the latest Service Pack for Proliant. HP recommends that you do not install hp-snmp-agents when installing
hp-ams. This method is simple but installs everything, including hp-snmp-agents, which might not be desirable.
HP also introduces Intelligent Provisioning, an essential single-server deployment tool embedded in HP ProLiant Gen8 servers.
Intelligent Provisioning simplifies HP ProLiant server setup, providing a reliable and consistent way to deploy HP ProLiant server
configurations. More information is available at the following web address:
http://www.hp.com/go/intelligentprovisioning
User-configurable options for hp-ams startup
When starting up the hp-ams helper daemon hpHelper, you can use several user-configurable options. These options are
documented in the hpHelper manpage that is installed with the hp-ams package. The hpHelper daemon runs with the following
default:
OPTIONS="-I0"
2
You can add or change the options by adding the following line to the /etc/sysconfig/hp-ams file (this file is not created
automatically when you install the hp-ams package):
OPTIONS="-I1"
This gives the –I parameter the value of 1 when the hpHelper daemon starts. For information about hpHelper command-line
options, see “hpHelper options”.
hpHelper options
The following command-line options are available for hp-ams (see the hpHelper manpage):
1
http://downloads.linux.hp.com/SDR
2
The “-I” option changes the interval that memory usage, cpu usage, and performance counters are logged to the Active Health Service: 0 = at startup, 1 = 1 minute, 2 = 10
minutes, 3 = 1 hour.
5