HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document - Application Notes - Best Practices for Enabling Microsoft Windows with SAN/iQ®
Table Of Contents
- Application Notes Best Practices for Enabling Microsoft Windows with SANiQ
- Contents
- 1 Chapter: Enabling LeftHand SAN volumes with the Microsoft™ iSCSI 2.0x Initiator
- 2 Chapter: Finding the iSCSI Initiator Version
- 3 Chapter: LeftHand Networks and Microsoft™ MPIO Support
- 4 Chapter: Expanding a Windows Volume on the SAN
- 5 Chapter: Shrinking a Windows Volume on the SAN
- 6 Chapter: Setting the Windows Disk Partition Offset for Optimal Performance
- 7 Chapter: Ensure That Application Resources on iSCSI Volumes Come Online After a Server Reboot
- 8 Chapter: Microsoft™ iSCSI Initiator Session Timeout Setting
- 9 Chapter: Measuring Performance in a Windows Environment
- Overview
- Using Windows Performance Monitor to Measure SAN Performance
- Setting up Windows Performance Monitor
- Saving a Performance Monitor Log for Analysis
- Monitoring More Than One Server Simultaneously
- Scheduling Performance Data Collection
- Using IOMeter as a SAN Benchmark Tool
- Configuring the ISCSI Volume
- Configuring IOMeter
- Configuring IOMeter Access Specification for each Test
- Running the Test
- Interpreting Results
- Access Specifications to Run
- 10 Chapter: Frequently Asked Questions
66
Setting up Windows Performance Monitor
1 Open Windows Performance Monitor (Start Menu>Accessories>System
Tools>Performance Monitor, or run the perfmon.exe program).
2 Click the X icon several times to remove any existing counters.
3 Click the + icon or right-click on the graph area to open the Add Counters
function.
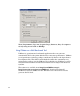
4 Configure the Add Counters window as shown below. Make sure to include
all counters listed above. (To simplify the process, choose “All counters”
from the column on the left to avoid having to individually select
counters). Add the PhysicalDisk counters listed in the table above, and
then click the Add button
5 Make sure to choose the proper physical disks from the section on the
right. Unless directed to do otherwise, select all disk instances and do not
choose the _Total. Selecting all the individual disks allows for a more
detailed analysis of the performance data.
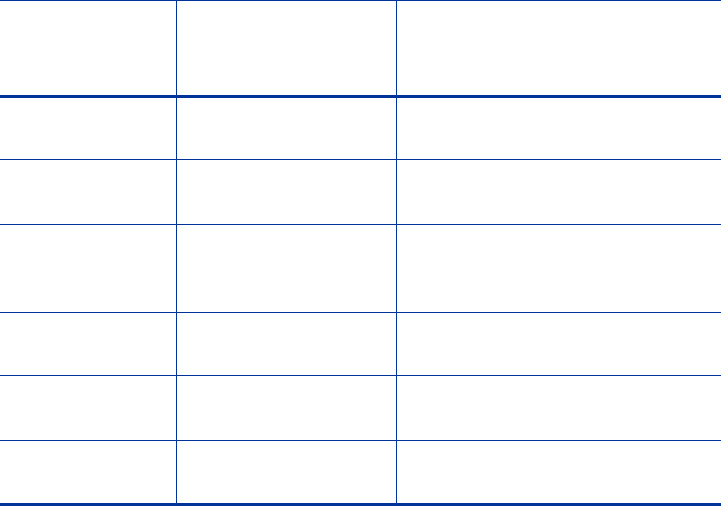
Disk Bytes/sec Total data throughput
for the volume
Measured in Bytes/sec. Typical
values are in Megabytes/sec.
Disk Read Bytes/
sec
Read data throughput
for the volume
Measured in Bytes/sec. Typical
values are in Megabytes/sec.
Disk Write
Bytes/sec
Write data
throughput for
the volume
Measured in Bytes/sec. Typical
values are in Megabytes/sec.
Disk Reads/sec Read IOPS (I/Os / sec)
for the volume
Measured as the raw number.
Disk Writes/sec Write IOPS (I/Os /
sec) for the volume
Measured as the raw number.
Disk Transfers/
sec
Total IOPS (I/Os / sec)
for the volume
Measured as the raw number.
Windows
Performance
Counter SAN Measurement Notes