HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document - Application Notes - Best Practices for Enabling Microsoft Windows with SAN/iQ®
Table Of Contents
- Application Notes Best Practices for Enabling Microsoft Windows with SANiQ
- Contents
- 1 Chapter: Enabling LeftHand SAN volumes with the Microsoft™ iSCSI 2.0x Initiator
- 2 Chapter: Finding the iSCSI Initiator Version
- 3 Chapter: LeftHand Networks and Microsoft™ MPIO Support
- 4 Chapter: Expanding a Windows Volume on the SAN
- 5 Chapter: Shrinking a Windows Volume on the SAN
- 6 Chapter: Setting the Windows Disk Partition Offset for Optimal Performance
- 7 Chapter: Ensure That Application Resources on iSCSI Volumes Come Online After a Server Reboot
- 8 Chapter: Microsoft™ iSCSI Initiator Session Timeout Setting
- 9 Chapter: Measuring Performance in a Windows Environment
- Overview
- Using Windows Performance Monitor to Measure SAN Performance
- Setting up Windows Performance Monitor
- Saving a Performance Monitor Log for Analysis
- Monitoring More Than One Server Simultaneously
- Scheduling Performance Data Collection
- Using IOMeter as a SAN Benchmark Tool
- Configuring the ISCSI Volume
- Configuring IOMeter
- Configuring IOMeter Access Specification for each Test
- Running the Test
- Interpreting Results
- Access Specifications to Run
- 10 Chapter: Frequently Asked Questions
69
Monitoring More Than One Server Simultaneously
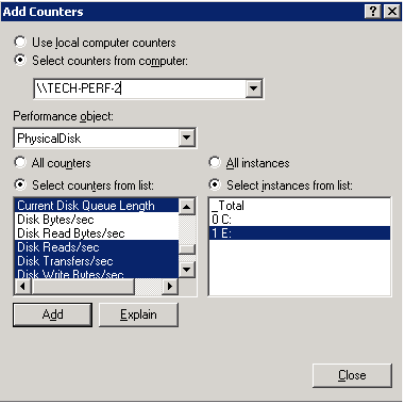
When collecting data from multiple servers, you can collect all data from a
single perfmon instance by changing the server name in the “Select counters
from computer:” box. The appropriate physical drives will show up for
that server.
Scheduling Performance Data Collection
Data collection can be scheduled using the Performance Monitor tool.
To enable scheduling, right-click on a log that has been created, and select
“Properties”. Go to the “Schedule” tab to set up the start and stop time for the
performance data logging. The most value comes from a schedule that
encompasses typical workloads, so it is suggested that the schedule be set to
include times with peak loads, such as backups, end-of-week batch processing
jobs, or other times when the SAN is heavily utilized. Depending on the
individual environment, this schedule could last for 24 hours to one week.
Typically, logging of less than 24 hours does not represent a comprehensive
workload.