HP Scripting Toolkit 9.10 for Linux User Guide
Table Of Contents
- HP Scripting Toolkit for Linux User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Deployment using the Scripting Toolkit
- 3 Booting and OS installation
- 4 Scripting Toolkit utilities
- Native package formats
- Syntax conventions
- Utility online help
- Using Scripting Toolkit utilities
- Using REBOOT
- Using SETBOOTORDER
- Using STATEMGR
- Using RBSURESET
- Using BOOTEXTRACT
- Using HPDISCOVERY
- Using IFHW
- Using HWQUERY
- Using CONREP
- CONREP command-line syntax
- CONREP command line arguments
- CONREP return codes
- CONREP screen output
- CONREP -s (Store to Data file) Example usage for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- CONREP –l (Load from Data File) Example Usage for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- CONREP Data File Sample Contents for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- CONREP command file contents for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- Using HPRCU
- Using HPACUSCRIPTING
- Using HPLPCFG
- Using LO100CFG
- Using HPQLAREP
- Using HPONCFG
- 5 Troubleshooting
- 6 Support and other resources
- 7 Documentation feedback
- Acronyms and abbreviations
- Index
NOTE: For a complete list of all command-line parameters, execute the /? utility.
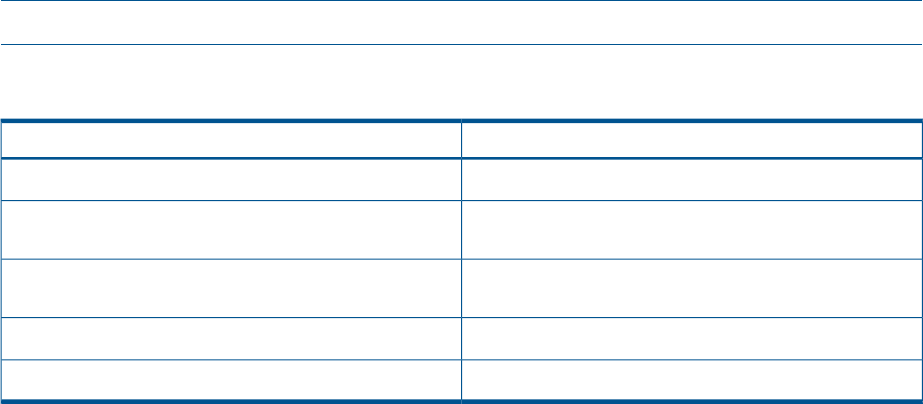
HPONCFG return codes
MeaningValue
The script was sent successfully to the device.
0
The script could not be sent to the device. There is an error
in xml.
1
The Management processor is not present, or the driver is
not running.
2
The iLO flash is still in progress.
3
The script is unable to create an output file.
255
If the script itself fails, errors are reported in the log file created by HPONCFG.
HPONCFG command file contents
HPONCFG can be used to perform the following tasks:
• Obtain an entire configuration
• Obtain a specific configuration
• Set a configuration
Obtaining an entire configuration
HPONCFG can be used to obtain an entire configuration from iLO. In this case, the utility executes
from the command line without specification of an input file. The name of the output file is given
on the command line. For example:
hponcfg -w config.xml
In this example, the utility indicates that it obtained the data successfully and wrote it to the output
file as requested. The following is a typical example of the contents of the output file:
<HPONCFG VERSION = "1.1">
<!--- Generated 04/15/04 15:20:36 --->
<MOD_DIR_CONFIG>
<DIR_AUTHENTICATION_ENABLED VALUE = "N"/>
<DIR_LOCAL_USER_ACCT VALUE = "Y"/>
<DIR_SERVER_ADDRESS VALUE = ""/>
<DIR_SERVER_PORT VALUE = "25"/>
<DIR_OBJECT_DN VALUE = " "/>
<DIR_OBJECT_PASSWORD VALUE = ""/>
<DIR_USER_CONTEXT_1 VALUE = ""/>
<DIR_USER_CONTEXT_2 VALUE = "_"/>
<DIR_USER_CONTEXT_3 VALUE = ""/>
</MOD_DIR_CONFIG>
<MOD_NETWORK_SETTINGS>
<SPEED_AUTOSELECT VALUE = "Y"/>
<NIC_SPEED VALUE = "100"/>
<FULL_DUPLEX VALUE = "Y"/>
<IP_ADDRESS VALUE = "16.100.241.229"/>
Using HPONCFG 57










