HP Scripting Toolkit 9.10 for Linux User Guide
Table Of Contents
- HP Scripting Toolkit for Linux User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Deployment using the Scripting Toolkit
- 3 Booting and OS installation
- 4 Scripting Toolkit utilities
- Native package formats
- Syntax conventions
- Utility online help
- Using Scripting Toolkit utilities
- Using REBOOT
- Using SETBOOTORDER
- Using STATEMGR
- Using RBSURESET
- Using BOOTEXTRACT
- Using HPDISCOVERY
- Using IFHW
- Using HWQUERY
- Using CONREP
- CONREP command-line syntax
- CONREP command line arguments
- CONREP return codes
- CONREP screen output
- CONREP -s (Store to Data file) Example usage for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- CONREP –l (Load from Data File) Example Usage for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- CONREP Data File Sample Contents for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- CONREP command file contents for HP ProLiant servers not using the Oxx ROM family
- Using HPRCU
- Using HPACUSCRIPTING
- Using HPLPCFG
- Using LO100CFG
- Using HPQLAREP
- Using HPONCFG
- 5 Troubleshooting
- 6 Support and other resources
- 7 Documentation feedback
- Acronyms and abbreviations
- Index
insmod /opt/hp/hp-ilo/bin/`uname -r`/hp_ilo.ko
6. Mount the network share:
mkdir /mnt/toolkit_share
7. Capture a hardware discovery report using the HPDISCOVERY utility:
cd /mnt/toolkit_share/utilities
8. Capture the system BIOS configuration using the CONREP utility:
cd /mnt/toolkit_share/utilities
./conrep -s -f/mnt/toolkit_share/data_files/conrep.dat
9. Capture the Smart Array configuration using the ACU utility:
cd /mnt/toolkit_share/utilities/hpacuscripting
./hpacuscripting -c /mnt/toolkit_share/data_files/hpacuscripting.dat
10. Capture the iLO configuration using the HPONCFG utility:
cd /mnt/toolkit_share/utilities
./hponcfg -w /mnt/toolkit_share/data_files/hponcfg.dat
11. Edit the iLO configuration report to create an iLO configuration script:
vi /mnt/toolkit_share/data_files/hponcfg.dat
Unmount the network share
umount /mnt/toolkit_share
12. Reboot the source server, and then eject the Toolkit CD.
Creating an ISO image to be written to media
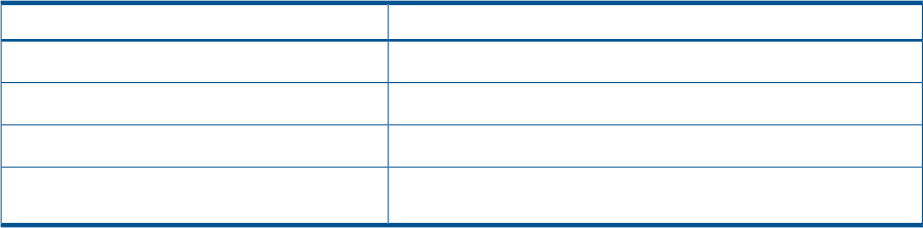
The mkisofs command is used to create an ISO image. The following table describes the arguments
used with this command.
DescriptionArgument
This argument is the output of the mkisofs command, the ISO file.
-o linuxbootCD.iso
This argument sets isolinux.bin as the bootloader.
-b isolinux/isolinux.bin
This argument sets the volume label of the CD.
-V LinuxBootCD
This argument specifies the target directory that will be the root of
the CD.
./linuxbootCD
To create the ISO image, execute the following command at the shell prompt:
mkisofs -J -iso-level 3 -R -L -o linuxbootCD.iso \
-b isolinux/isolinux.bin -c isolinux/boot.cat \
-V LinuxBootCD \
-no-emul-boot -boot-load-size 4 \
-boot-info-table \
./linuxbootCD
Now, the ISO file can be written to a CD.
Configuring the target server
1. At the target server, boot the media that contains the custom Scripting Toolkit for Linux image.
2. At the boot prompt, type bash and then press Enter. When the process is complete, a command
prompt appears.
10 Deployment using the Scripting Toolkit










