HP StoreAll Storage Network Best Practices Guide
Table Of Contents
- HP StoreAll Storage Network Best Practices Guide
- Contents
- 1 Overview of HP StoreAll Storage networking
- 2 StoreAll 9730 platform networking
- 3 StoreAll 93xx/8x00 platform networking
- 4 Expanding an existing cluster
- 5 Support and other resources
- 6 Documentation feedback
- A BOND modes
- B StoreAll 93xx 10 GbE bonding modes and switch interconnection
- C Install and the default Virtual Connect configuration
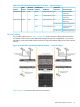
3. The bond driver determines which of its two underlying physical interfaces are up and
functioning correctly. If both interfaces are available, the packet is sent out over the last working
interface, otherwise it is routed to the working interface. For illustration, assume that the eth1
interface was chosen for transmission to the VC via the enclosure midplane.
4. The VC module in bay 1 receives the packet from the enclosure midplane and determines that
it is meant for the external network. It forwards the packet out the X5 connector (or one of the
other LACP trunked connectors) to the customer network via the customer edge switch.
5. Packet routing from this switch to the file client is completed within the customer’s network.
Packet traversing from node to node:
1. The packet is created in the application layer of StoreAll node (bay 1) and is destined for
StoreAll node (bay 2).
2. The operating system determines by IP address that StoreAll node (bay 2) can be reached
through the bond1 interface and queues the packet for that interface.
3. The bond driver determines which of its two underlying physical interfaces to use. For
illustration, assume that the eth2 interface was chosen for transmission to the VC via the
enclosure midplane.
4. The VC module in StoreAll node (bay 2) receives the packet from the enclosure midplane and
determines that it is meant for another server in the same enclosure. It forwards the packet via
the enclosure midplane to the eth2 interface of StoreAll node (bay 2).
5. The StoreAll node (bay 2) eth2 physical interface receives the packet from the enclosure
midplane. Since eth2 is a member of bond1, the packet is forwarded to the bond driver for
routing to the application layer.
6. The application layer on StoreAll node (bay 2) receives the packet from the bond1 interface.
Packet traversing from StoreAll node to management network:
1. The packet is created in the application layer of the node and is destined for the management
interface of one of the enclosure's SAS interconnect modules.
2. The operating system determines by IP address that the management network can be reached
through the bond0 interface and queues the packet for that interface.
3. The bond driver determines which of its two underlying physical interfaces should be used to
transmit the packet. For illustration, assume that the eth0 interface was chosen for transmission
to the VC via the enclosure midplane.
4. The VC module in StoreAll node (bay 1) receives the packet from the enclosure midplane and
determines that it should be routed through the external network. It forwards the packet out
the X6 connector, to the customer’s management network via the customer edge switch.
5. The packet is routed through the customer’s network to the edge switch connected to the
enclosure's active OA module.
6. The OA determines that the packet needs to be routed to the enclosure's SAS interconnect. It
forwards the packet via the enclosure midplane to the management interface on the target
SAS interconnect.
7. The embedded system on the SAS interconnect module receives and processes the packet.
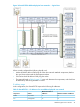
StoreAll node physical hardware mapping
Table 8 (page 43) shows the mapping of the logical networks to the server blade and VC
interconnect hardware.
42 StoreAll 9730 platform networking