HP Software File Migration Agent Installation and Administration Guide (September 2009)
Managed Volumes | 57
To view FMA file properties
1. In Windows Explorer, select one or more files or a folder
2. Right-click to display the context menu and select Properties.
3. Click the FMA tab.
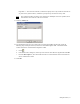
FMA displays the following information:
• Status—The current status of the file
• OFF(n)—Offline
• MOD(n)—Modified
•SAV(n)—Migrated
• INA(n)—Inactive
• DIS(n)—Disabled
(n) indicates the number of valid copies.
• Generations—The number of versions of this file that are archived
• System file ID—The operating system ID number for the file
• File size—The file size in bytes
• Change time—The date and time when this file was last modified
• State—The current status of the file
• Copies—The number of copies of this file that are archived
• Last recall—The last date and time when this file was recalled
• Recalls—The number of times this file has been recalled
To migrate one or more files or a folder
1. In Windows Explorer, select one or more files or a folder
2. Right-click to display the context menu and select Migrate.
3. Select the archive to which FMA should copy the data. If a command takes more than a few seconds,
the Explorer plugin displays a progress bar.
4. In the Processing results dialog box, select OK.
To release one or more files or a folder
1. In Windows Explorer, select one or more files or a folder.
2. Right-click to display the context menu and select Release.
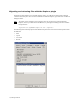
3. If you are releasing a folder, set the following options in the Release options dialog box, as necessary:
• Min number of archive copies—The minimum number of copies that must be migrated to the
archive before the files can be released.
• Modified retention Time—Files that have been modified more than this number of days ago can be
released.
• Accessed retention time—Files that have been accessed more than this number of days ago can be
released.
4. Click OK.