FW V06.XX/HAFM SW V08.02.00 HP StorageWorks SAN High Availability Planning Guide (AA-RS2DD-TE, July 2004)
Table Of Contents
- SAN HA Planning Guide
- Contents
- About this Guide
- Introduction to HP Fibre Channel Products
- Product Management
- Planning Considerations for Fibre Channel Topologies
- Fibre Channel Topologies
- Planning for Point-to-Point Connectivity
- Characteristics of Arbitrated Loop Operation
- Planning for Private Arbitrated Loop Connectivity
- Planning for Fabric-Attached Loop Connectivity
- Planning for Multi-Switch Fabric Support
- Fabric Topologies
- Planning a Fibre Channel Fabric Topology
- Fabric Topology Design Considerations
- FICON Cascading
- Physical Planning Considerations
- Port Connectivity and Fiber-Optic Cabling
- HAFM Appliance, LAN, and Remote Access Support
- Inband Management Access (Optional)
- Security Provisions
- Optional Features
- Configuration Planning Tasks
- Task 1: Prepare a Site Plan
- Task 2: Plan Fibre Channel Cable Routing
- Task 3: Consider Interoperability with Fabric Elements and End Devices
- Task 4: Plan Console Management Support
- Task 5: Plan Ethernet Access
- Task 6: Plan Network Addresses
- Task 7: Plan SNMP Support (Optional)
- Task 8: Plan E-Mail Notification (Optional)
- Task 9: Establish Product and HAFM Appliance Security Measures
- Task 10: Plan Phone Connections
- Task 11: Diagram the Planned Configuration
- Task 12: Assign Port Names and Nicknames
- Task 13: Complete the Planning Worksheet
- Task 14: Plan AC Power
- Task 15: Plan a Multi-Switch Fabric (Optional)
- Task 16: Plan Zone Sets for Multiple Products (Optional)
- Index
Planning Considerations for Fibre Channel Topologies
93SAN High Availability Planning Guide
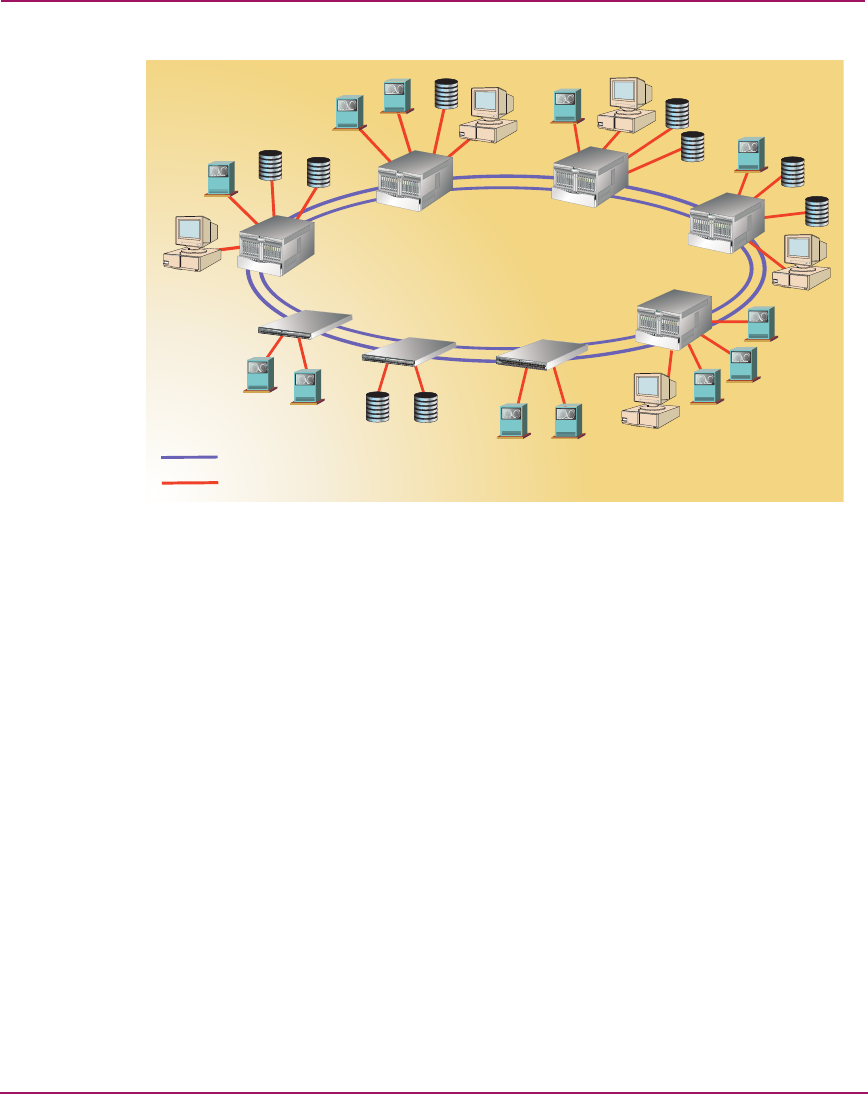
Figure 37: Ring fabric
Ring fabrics are generally more expensive than cascaded fabrics, are also easy to
deploy, provide a simple solution to add additional fabric devices, and can solve
hop-count problems inherent to cascaded fabrics. Ring fabrics also have increased
reliability because traffic can route around a single ISL, director, or switch failure
(subject to hop count limitations).
Like cascaded fabrics, ring fabrics are well suited for applications where data
access is local, but not for applications that require any-to-any connectivity. In
addition, ring fabrics are useful when connecting SANs over a MAN or WAN.
These networks typically use a ring topology.
Mesh Fabric
There are two types of mesh fabrics: full mesh and modified (or partial) mesh. In a
full-mesh topology, every director or switch is directly connected to all directors
and switches in the fabric. The maximum hop count between fabric-attached
devices is one hop. Figure 38 illustrates a full-mesh fabric topology.
T
M
TM
TM
T
M
T
M
E
R
R
P
W
R
RS
T
1
0
/
1
0
0
T
M
E
R
R
P
W
R
RS
T
1
0
/1
0
0
T
M
P
W
R
E
R
R
1
0
2
4
6
8
1
0
1
2
1
4
1
6
1
8
2
0
2
2
2
4
2
6
2
8
3
0
3
5
7
9
11
1
3
1
5
1
7
1
9
2
1
2
3
2
5
2
7
2
9
3
1
R
S
T
1
0
/
1
0
0
T
M
Interswitch Link
Fabric Connection










