FW V06.XX/HAFM SW V08.02.00 HP StorageWorks SAN High Availability Planning Guide (AA-RS2DD-TE, July 2004)
Table Of Contents
- SAN HA Planning Guide
- Contents
- About this Guide
- Introduction to HP Fibre Channel Products
- Product Management
- Planning Considerations for Fibre Channel Topologies
- Fibre Channel Topologies
- Planning for Point-to-Point Connectivity
- Characteristics of Arbitrated Loop Operation
- Planning for Private Arbitrated Loop Connectivity
- Planning for Fabric-Attached Loop Connectivity
- Planning for Multi-Switch Fabric Support
- Fabric Topologies
- Planning a Fibre Channel Fabric Topology
- Fabric Topology Design Considerations
- FICON Cascading
- Physical Planning Considerations
- Port Connectivity and Fiber-Optic Cabling
- HAFM Appliance, LAN, and Remote Access Support
- Inband Management Access (Optional)
- Security Provisions
- Optional Features
- Configuration Planning Tasks
- Task 1: Prepare a Site Plan
- Task 2: Plan Fibre Channel Cable Routing
- Task 3: Consider Interoperability with Fabric Elements and End Devices
- Task 4: Plan Console Management Support
- Task 5: Plan Ethernet Access
- Task 6: Plan Network Addresses
- Task 7: Plan SNMP Support (Optional)
- Task 8: Plan E-Mail Notification (Optional)
- Task 9: Establish Product and HAFM Appliance Security Measures
- Task 10: Plan Phone Connections
- Task 11: Diagram the Planned Configuration
- Task 12: Assign Port Names and Nicknames
- Task 13: Complete the Planning Worksheet
- Task 14: Plan AC Power
- Task 15: Plan a Multi-Switch Fabric (Optional)
- Task 16: Plan Zone Sets for Multiple Products (Optional)
- Index
Physical Planning Considerations
151SAN High Availability Planning Guide
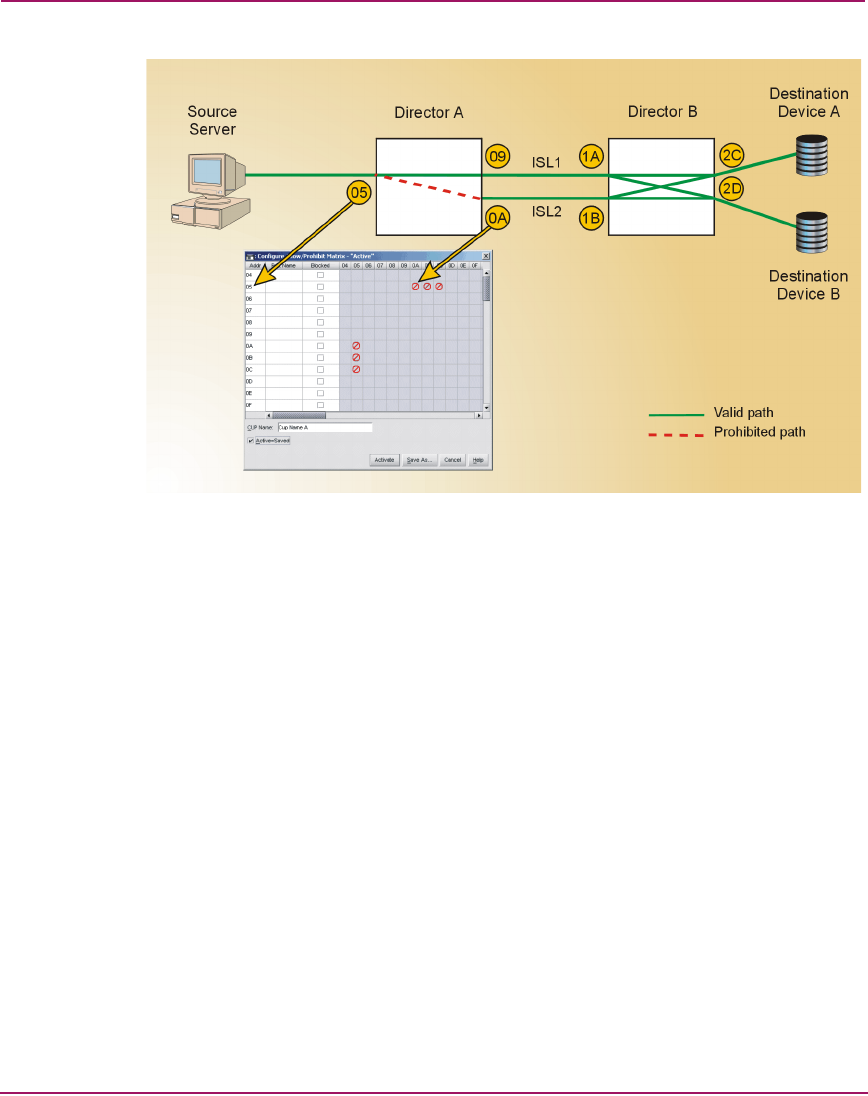
Figure 58: PDCM Array - Example Problem
A PDCM array configured for Director A prohibits logical port address 05 from
communicating with logical port addresses 0A, 0B, and 0C. No PDCM array is
configured for Director B. The PDCM array configured for Director A prohibits
the source server from transmitting or receiving data across ISL 2. However,
internal route tables on both directors indicate a valid server-to-destination device
path across ISL 1.
A problem arises when the source server transmits Class 3 Fibre Channel data to
devices across ISL 1, consuming the ISL bandwidth. Destination devices are
unaware of the PDCM array configured at Director A and transmit frames back to
the server across ISL 2. Because the server is prohibited from communicating
across this ISL, Class 3 Fibre Channel frames are discarded without generating a
busy (BSY) frame, reject (RJT) frame, or otherwise notifying the destination
devices. The server receives no response from destination devices and times out.
Thus, a server or device failure is indicated when in fact the problem is a
user-defined prohibited connection.
Preferred Path
The preferred path option allows a user to specify and configure one or more ISL
data paths between multiple directors or switches in a fabric. At each fabric
element, a preferred path consists of a source port on the director or switch being










