FW V06.XX/HAFM SW V08.02.00 HP StorageWorks SAN High Availability Planning Guide (AA-RS2DD-TE, July 2004)
Table Of Contents
- SAN HA Planning Guide
- Contents
- About this Guide
- Introduction to HP Fibre Channel Products
- Product Management
- Planning Considerations for Fibre Channel Topologies
- Fibre Channel Topologies
- Planning for Point-to-Point Connectivity
- Characteristics of Arbitrated Loop Operation
- Planning for Private Arbitrated Loop Connectivity
- Planning for Fabric-Attached Loop Connectivity
- Planning for Multi-Switch Fabric Support
- Fabric Topologies
- Planning a Fibre Channel Fabric Topology
- Fabric Topology Design Considerations
- FICON Cascading
- Physical Planning Considerations
- Port Connectivity and Fiber-Optic Cabling
- HAFM Appliance, LAN, and Remote Access Support
- Inband Management Access (Optional)
- Security Provisions
- Optional Features
- Configuration Planning Tasks
- Task 1: Prepare a Site Plan
- Task 2: Plan Fibre Channel Cable Routing
- Task 3: Consider Interoperability with Fabric Elements and End Devices
- Task 4: Plan Console Management Support
- Task 5: Plan Ethernet Access
- Task 6: Plan Network Addresses
- Task 7: Plan SNMP Support (Optional)
- Task 8: Plan E-Mail Notification (Optional)
- Task 9: Establish Product and HAFM Appliance Security Measures
- Task 10: Plan Phone Connections
- Task 11: Diagram the Planned Configuration
- Task 12: Assign Port Names and Nicknames
- Task 13: Complete the Planning Worksheet
- Task 14: Plan AC Power
- Task 15: Plan a Multi-Switch Fabric (Optional)
- Task 16: Plan Zone Sets for Multiple Products (Optional)
- Index
Planning Considerations for Fibre Channel Topologies
122 SAN High Availability Planning Guide
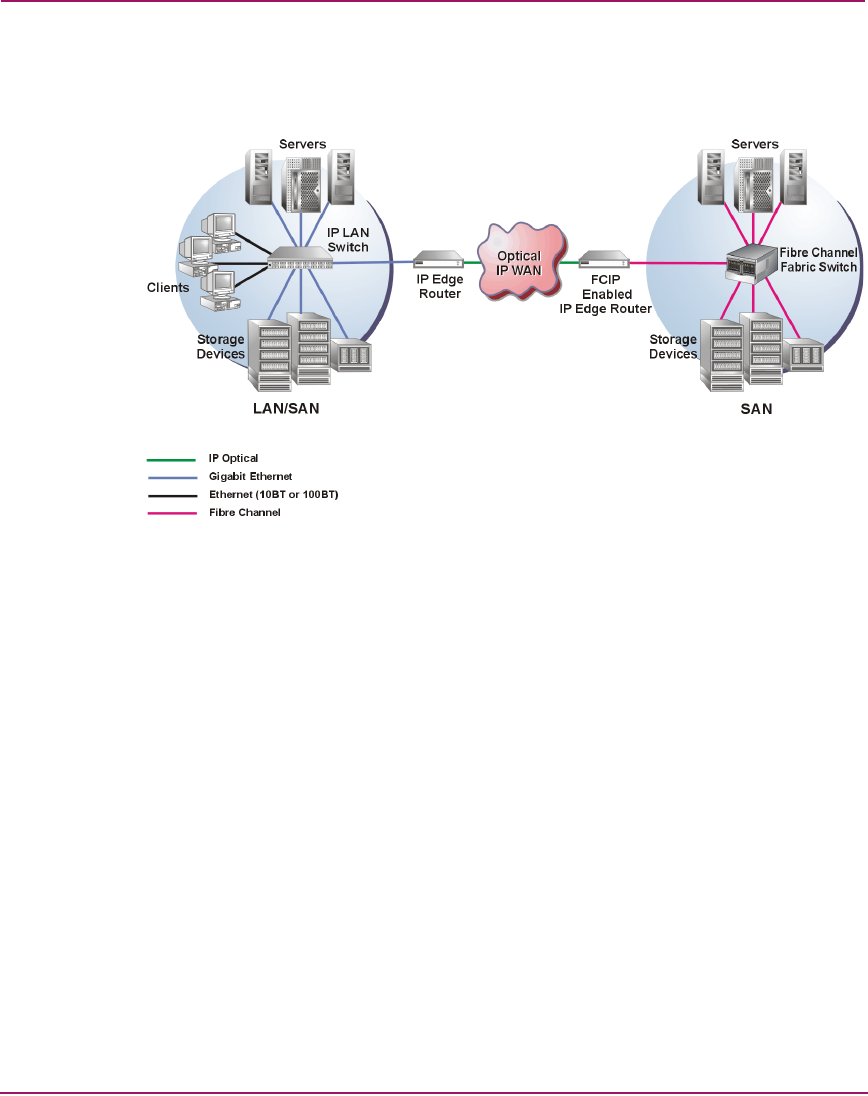
iFCP, each connected SAN fabric is maintained separately from the others, while
the IP network provides connectivity, congestion control, error detection, and
error recovery. Figure 48 illustrates iFCP WAN extension.
Figure 48: iFCP WAN Extension
iSCSI Protocol
iSCSI is a TCP/IP-based protocol for establishing and managing connections
between IP-based storage devices, hosts, and clients. iSCSI operates on top of
TCP, moving block data (iSCSI packets) over an IP Ethernet network. This
protocol consolidates SANs into a single IP network for data and storage traffic,
using Ethernet (not Fibre Channel) for the SAN and IP for the WAN. iSCSI
requires equipping both server and storage systems with iSCSI components,
resulting in additional capital costs and higher server overhead associated with
TCP processing. Applications include storage access where performance is not
critical. Figure 49 illustrates iSCSI WAN extension.










