HP Device Manager 4.6 - Deployment Guide
Table Of Contents
Huge scale deployments
Device number: >50,000
Deployment: Because one HPDM Server supports up to 50,000 devices with verified performance, deployments of greater
than 50,000 devices require multiple instances of HPDM. You mighte view it as multiple Normal scale deployments to
deploy.
Optimizing HPDM configurations
HPDM manages devices remotely with tasks. Configuring the most suitable parameters for tasks can help improve
performance.
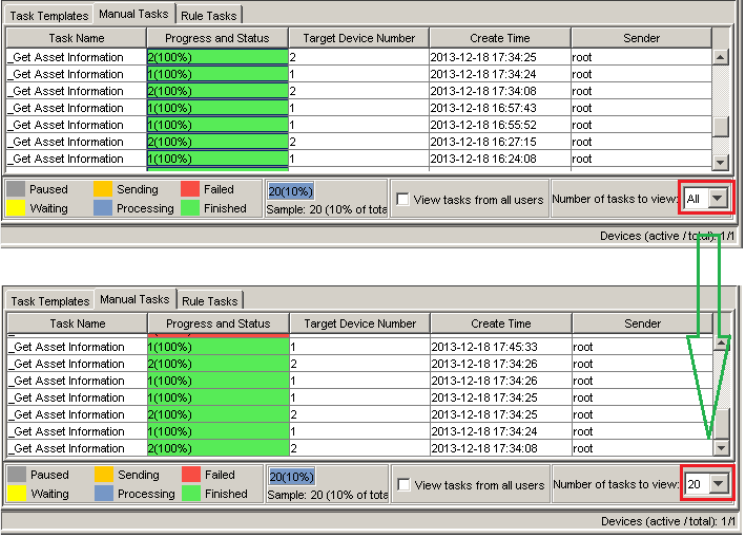
Reducing the visible task amount
The following tip increases the speed of the startup process of the HPDM Console. The HPDM Console takes time to render
task summaries when initializing. Before closing the HPDM Console, open the Manual Tasks tab and select a smaller
number under Number of tasks to view. Then, change the setting in the Rule Tasks tab.
Figure 5. Setting the number of tasks to view
Batch tasks
Batch Control is an optional task parameter that can be used when deploying images or other tasks with a payload to a
large number of devices. The batch settings control how many devices are sent the task at a time, which gives you some
control over the amount of network traffic that HPDM generates.
The continued write speed of current devices is around 3.5 MBps (megabytes per second). Use that number to decide how
many imaging tasks you can send in one batch for each repository and how long the interval between batches should be.
For example, suppose you are deploying a 4 GB image to your devices. The network is a high-quality, 1000 Mbps Ethernet,
which means it can provide continuous theoretical bandwidth. Many of the latest 7200 rpm hard drives have higher
continuous read speeds than that, and those using RAID even higher. Assuming that the network is the bottleneck, we have
the following:
1000 Mbps ÷ 8 bits per byte ÷ 3.5 MBps ≈ 35 concurrent imaging tasks in a batch
9










