Zero Downtime Backup of MaxDB database with HP Data Protector
Non-archive log mode
By default, the log area can be overwritten only if the appropriate log entries have been backed up.
You must therefore make regular log backups.
The log entries of the log area and the log backups are then available if you need to recover the
database. If these entries and the data backups are complete and available without gaps, you can
recover the database up to any point in time.
Archive log mode
The log area is overwritten cyclically, even if you do not perform any log backups.
This interrupts the log backup history. Only the log entries in the log area are available if you need to
recover the database. This usually means that you can recover your database instance only to the
state it had at the time of the last data backup; you cannot restore it up to the last COMMIT before the
crash, or to any other time.
You can only restore the database to a time of your choice if all the log entries written after the data
backup exist in the log area (which means that the log area has not been overwritten since the data
backup).
A transaction log backup consists of two distinct steps. Initially, the entries are exported from the log
volumes to an archivelog area in the filesystem. From there, they can be backed up by Data Protector.
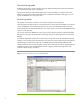
The following screenshot shows properties of a MaxDB instance inside MaxDB’s DBM GUI. The
instance MaxDB is online and among others, the GUI shows data and log volumes configured to exist
on different volumes. Note that although the instance is logging, because Auto Log mode is Off,
automatic redo-archiving is not active.
Figure 5. Properties of a MaxDB instance inside MaxDB’s DBM GUI
10