Disk-Assisted Backup Whitepaper
15
(immediately after the backup, or at a scheduled time) automatically copy the file-based media to a
physical medium such as LTO.
So this becomes a method to perform disk staging of slower backups (for example, over a slow LAN),
followed by high-speed backup to a physical device. And while this is not to a “virtual tape” device, it
does provide file-based backup capability without the need to invest in another physical piece of
hardware.
File Libraries can also be configured on a disk array in a SAN environment allowing backup across a
SAN, as well as LAN.
The file device writes and reads sequentially although disks are random-access media.
The file device is not limited by physical space. HP Data Protector software detects a shortage of disk
space in such a way that users can still close the data segment and write the last catalog segment to
disk. During the file-media formatting, there is an option to allow the pre-allocation of disk space to
avoid out-of-disk-space conditions. The maximum supported file size of the File Library device is
determined by the maximum size supported by the operating system. If no free slot is available, a
new slot will be created.
The free disk space of the file device library is configured per directory. HP Data Protector software
will check for free disk space at the creation of a new file depot and at the start of a backup. The size
of the new file depot will be calculated in such a way that, even if a device becomes full, there will
still be enough space to fulfil the backup requirements. To avoid problems arising when other
applications are writing to the same disk, and using up the disk space so that there is not enough
space available on the disk after a backup is complete, HP Data Protector software should be the
exclusive user of the assigned disk space.
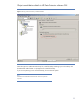
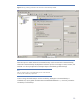
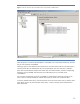
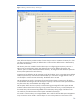
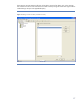
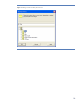
To configure the file device library, select “File Library” as the Device Type (Figure 11).