HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI Reference Guide Part number: TK981-96014 First edition: April 2014
Legal and notice information © Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
Contents Preface ................................................................................................ 9 1 Extended commands ........................................................................ 11 Overview of extended commands ............................................................................................... List of extended commands ..................................................................................................
2 Basic commands .............................................................................. 79 List of basic commands .............................................................................................................. 79 Before reading the basic command descriptions ........................................................................... 81 Basic command path ..........................................................................................................
Contacting HP ........................................................................................................................ HP technical support ......................................................................................................... Subscription service .......................................................................................................... Documentation feedback ...................................................................................................
Figures 1 drmsqlrecovertool dialog box .................................................................................
Tables 1 List of extended commands (File system backups) ......................................................... 12 2 List of extended commands (Common commands) ....................................................... 12 3 List of extended commands (Tape-related commands) .................................................. 12 4 List of extended commands (SQL Server database backups) .......................................... 13 5 List of extended commands (Exchange database backups) .......................
31 Cluster software parameters ................................................................................... 108 32 Items displayed by the drmdevctl -sigview command .................................................. 116 33 Partition styles and corresponding disk signatures to be specified ................................ 117 34 Host information displayed by the drmhostinfo command ........................................... 120 35 Backup information displayed by the drmtapecat command ...............
Preface This guide describes how to manage HP XP7 Replication Manager.
Preface
1 Extended commands This chapter describes the extended commands provided by Application Agent. Overview of extended commands An extended command is used to reduce the effort required to perform data protection operations, such as backup or restoration. You can use extended commands to automatically perform backup and restoration, without needing to specify further complicated operations. For example, suppose that you want to back up data to a tape device by using Application Agent commands.
List of extended commands The following tables display the extended commands provided by Application Agent and provide a general explanation for each command. Table 1 List of extended commands (File system backups) Extended command name Explanation EX_DRM_FS_BACKUP Backs up a file system. EX_DRM_FS_DEF_CHECK Checks the contents of an operation definition file and automatically creates a temporary directory. EX_DRM_FS_RESTORE Restores a file system from its backup to the primary volume.
Extended command name Explanation EX_DRM_UMOUNT Unmounts a secondary volume. Table 4 List of extended commands (SQL Server database backups) Extended command name Explanation EX_DRM_SQL_BACKUP Backs up an SQL Server database. EX_DRM_SQL_DEF_CHECK Checks the contents of an operation definition file and automatically creates a temporary directory. EX_DRM_SQL_RESTORE Restores the SQL Server database from its backup to the primary volume.
Extended command formats All arguments that can be specified are described in this section. If multiple argument conditions exist, the formats are described separately for each condition. Do not mix separate formats. Viewing the format To display the extended command format, execute an extended command by specifying the -h option after the extended command name.
Extended command specifications (File system backups) This section explains the extended command specifications that apply to file system backup and restore operations.
Description This extended command backs up a file system from the primary volume to the secondary volume; the file system has the operation ID specified by executing the drmfsbackup command. At this time, the EX_DRM_FS_BACKUP command generates a backup ID. Prerequisites The prerequisite for executing this extended command is as follows: • An operation definition file linked to the specified operation ID has been provided.
• The value is case sensitive. • When a reserved character or a one-byte space character is used, the entire value must be enclosed in double quotation marks ("). • If the value contains a reserved character, but is not enclosed in double quotation marks, the reserved character is not correctly interpreted as a part of the backup comment, and is parsed as a reserved character.
Specify this option to execute a user script. Specify user-script-file-name as an absolute path. The conditions for specifying the value in the user-script-file-name parameter are as follows: • • • • The value must be 255 bytes or less. The value can include alphanumeric, one-byte space, and multi-byte characters. The value is case sensitive. If the value contains space characters, the entire value must be enclosed in double quotation marks (").
or restoration failures. The items, volumes, and conditions to be checked are described in the following table. Table 7 Status check of a secondary volume Check item A secondary volume is hidden from a backup server Volume to be checked All secondary volumes defined for a backup-target primary volume Check condition Checked when a primary volume is defined in pairs with secondary volumes of multiple generations and any of the following items is applicable: • A primary volume is a cluster resource.
EX_DRM_FS_BACKUP operation01 -mode cold • In this example, the extended command is used to back up the file system specified by the operation ID operation01 to the secondary volume, using the VSS backup method: EX_DRM_FS_BACKUP operation01 -mode vss EX_DRM_FS_DEF_CHECK (Checks the contents of an operation definition file and automatically creates a temporary directory) Formats To check the contents of an operation definition file for a file server: EX_DRM_FS_DEF_CHECK operation-ID -db To check the content
Item name Details to be checked • The mount point directory specified in INSTANCE_NAME must exist. INSTANCE_NAME • If a mount point list file is specified, both the specified file and the mount point’s directory defined in it must exist. TARGET_NAME Do not specify a value for this item by specifying TARGET_NAME=. FTP_HOME_DIR • The specified directory must exist.#1, #2 • The absolute path must be specified. • The specified directory name must not contain a delimiter character (\).
A character string that uniquely identifies the operation to be performed. Information in the operation definition file corresponding to the specified operation ID is used when executing the extended command. -db Specify this option to check the contents of an operation definition file for a file server. -bk Specify this operation to check the contents of an operation definition file for a backup server.
Prerequisites The prerequisites for executing this extended command are as follows: • An operation definition file linked to the specified operation ID has been provided. • EX_DRM_BACKUPID_SET or EX_DRM_DB_IMPORT has been executed, and the backup ID has been stored in the backup ID record file. Arguments operation-ID A character string that uniquely identifies the operation to be performed.
You can create a copy parameter definition file by using a name of your choice. Specify the file name by using an alphanumeric character string that is 64 bytes or less. You must save the copy parameter definition file to the following location: Application-Agent-installation-directory\DRM\conf\raid NOTE: • The backup information in the backup catalog is managed by using a copy group as a key.
Extended command specifications (Common commands) EX_DRM_BACKUPID_SET (Generates a backup ID file) Format EX_DRM_BACKUPID_SET operation-ID -backup_id backup-ID Description This extended command is used to generate a backup ID file that contains the specified backup ID. The command stores the file in the temporary directory for extended commands. Execute this extended command as preparation for restoring the backed up file system or the database to the primary volume.
• The system cannot acquire information from the operation definition file linked to the operation ID. • The backup ID cannot be recorded in the backup ID file. • A command executed inside the extended command encounters an error. • Information cannot be acquired from the host environment settings file. • No storage directory for extended-command temporary files is specified in the operation definition file. • The command fails to obtain the name of the directory where dictionary map files are stored.
Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • • • • An invalid option is specified. The file specified in the argument does not exist, or the system cannot access the file. An error is detected in the copy-group list file. A command executed inside the extended command encounters an error. Example • In this example, the extended command is used to check the copy-group list file C:\WORK\CGDEF.txt: EX_DRM_CG_DEF_CHECK -cg_file C:\WORK\CGDEF.
Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • An invalid option is specified. • The system cannot acquire information from the operation definition file linked to the operation ID. • Information cannot be acquired from the host environment settings file. • No storage directory for extended-command temporary files is specified in the operation definition file.
A character string that uniquely identifies the operation to be performed. Information in the operation definition file corresponding to the specified operation ID is used when executing the extended command. Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • An invalid option is specified.
• An operation definition file linked to the specified operation ID has been provided. • This extended command is executed on the FTP client. • The files that this extended command will transmit have already been generated by executing the EX_DRM_DB_EXPORT extended command. • The EX_DRM_FS_DEF_CHECK command has been executed to create a directory on the FTP server that will contain the transferred files.
Example • In this example, the extended command is used to transfer files from the FTP server to the FTP client, based on the settings in the operation definition file operation01.
-password FTP-password For FTP-password, specify the FTP user password used when connecting to the FTP server. Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • An invalid option is specified. • The system cannot acquire information from the operation definition file linked to the operation ID. • A connection to the FTP server or file transmission fails.
that the contents of the HOST_ROLE and MAX_LOG_LINES entries in the host environment settings file are set as described in the table below. Table 10 Items checked in the host environment settings file Item Items checked • Both the name and value of the item are specified. • Only one item is specified. • The length of the value in characters does not exceed the maximum value. HOST_ROLE • If the -db argument is specified in the extended command, DB is specified as the item.
Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • An invalid option is specified. • The file specified in the argument does not exist, or the system cannot access the file. • The check of the contents of the file for setting up the host environment detects an abnormality. Examples • In this example, the extended command is used to check the contents of the host environment settings file C:\Program Files\drm\SCRIPT\conf\host.
If all copy groups have been used for backup processing, the command specifies the oldest copy group used for backup processing. Prerequisites The prerequisites for executing this extended command are as follows: • The operation definition file corresponding to the specified operation ID has been created. • The copy-group list file has already been created when copy groups are resynchronized by using the copy-group list file.
Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • An invalid option is specified. • The system cannot acquire information from the operation definition file linked to the operation ID. • Information cannot be acquired from the backup ID file (when no copy group is specified). • Information cannot be acquired from the copy-group list file (when the file is specified).
To clear the cache of the secondary volume when usual operation is in the split state: EX_DRM_CACHE_PURGE operation-ID { -cg copy-group | -cg_file copy-group-list-file } Description This extended command sequentially executes the drmmount and drmumount commands to clear the cache of the secondary volume.
NOTE: Before you attempt to back up the file system or the database to a secondary volume, execute this extended command for all secondary volumes of resources to be backed up. If you back up data without clearing the cache of the secondary volume, when you mount the secondary volume, the existing cache is overwritten to the secondary volume, and the backup data might be lost.
EX_DRM_MOUNT (Mounts a secondary volume) Formats To mount a volume in a basic disk configuration: EX_DRM_MOUNT operation-ID [ -copy_group copy-group-name | -force ] [ -mount_pt mount-point-directory-name ] To mount a volume in a dynamic disk configuration: EX_DRM_MOUNT operation-ID [ -mount_pt mount-point-directory-name ] [ -force ] [ -conf ] Description The EX_DRM_MOUNT command mounts a secondary volume and locks the appropriate copy group.
-copy_group copy-group-name Specifies the name of the copy group to be mounted. You must clear the system cache before backing up data. When doing so, specify a copy group from the backup server and mount the secondary volume. Then, when you unmount the secondary volume with the EX_DRM_UMOUNT command, the system cache is cleared.
Application-Agent-installation-directory\DRM\conf\vm\CG_MP.
-exopt Specify this option when you want to use extended functions. You must specify -exopt to specify another option. However, you can omit -exopt if you specify neither the -force nor -bup_env options. -mount_pt mount-point-directory-name Specify the name of the mount point directory on which the secondary volume is to be mounted. The secondary volume is mounted at the specified mount point, and data is backed up from the secondary volume to a tape device.
If you omit this option, the extended command terminates with an error without mounting if the following condition also holds: the copy group name, LDEV number, and SERIAL number of the primary volume, which were obtained when the file server or database server was backed up, do not match the information on the file server or database server. Specify this option when you need to forcibly mount a secondary volume using only the copy group name of the primary volume as a key.
• In this example, the extended command is used to forcibly mount the secondary volume identified by the operation ID operation01 and execute a tape device backup: EX_DRM_TAPE_BACKUP operation01 -exopt -backup -force EX_DRM_TAPE_RESTORE (Restores data from backup tape to the secondary volume) Formats EX_DRM_TAPE_RESTORE operation-ID -backup_id backup-ID [ -exopt [ -mount_pt mount-point-directory-name][ -raw ] [ -force ] [ -bup_env configuration-definition-file-name] ] The command can also be executed in t
• The backup ID to be specified in this extended command has already been determined by executing the drmtapecat command. • The mount point directory has been created. Take the command retry period into consideration when you execute more than one EX_DRM_TAPE_RESTORE command concurrently. For details about the settings, see the notes on command execution in the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide.
Any drive not being used when the extended command is executed. -raw Specify this option when the data to be restored was backed up to a tape device as raw device data. If the target data has been backed up by the EX_DRM_TAPE_BACKUP extended command with the -raw option specified, this extended command executes restore processing normally even when this option is omitted.
• An invalid option is specified. • The system cannot acquire information from the definition file linked to the operation ID. • A specified Application Agent command option cannot be specified as an extended command option. • The system cannot acquire information from the backup ID file. • A command executed inside the extended command encounters an error. • The command fails to obtain the name of the directory where dictionary map files are stored.
• EX_DRM_TAPE_RESTORE If you cannot unmount the secondary volume by using the EX_DRM_UMOUNT command, unlock the copy group by using the drmcgctl command, and then unmount the secondary volume by using the following: • The unmount function provided by RAID Manager Arguments operation-ID A character string that uniquely identifies the operation to be performed. -copy_group copy-group-name Specifies the name of the copy group (mounted by the EX_DRM_MOUNT command) to be unmounted.
Description This extended command executes the drmsqlbackup command to back up the SQL Server database of the instance that was specified by the operation ID from the primary volume to the secondary volume. When this extended command performs a backup, a backup ID is generated. If the data files, databases, and other objects of the resolved instance exist on multiple volumes, all primary volumes will be backed up to the secondary volumes.
Database of interest#1 Storage destination for backup files File type of interest Backup file name Metafile#2 Varies depending on the VDI metafile storage directory specified with the -drmsqlinit command#3 #1: If you do not specify the –system option, only the user database is backed up. #2: This file is created when the drmsqlbackup command is executed. #3: If you registered a VDI metafile storage directory by using the drmsqlinit command, the backup file is stored in the registered directory.
A hyphen (-) cannot appear as the first character in the backup comment. If you specify two consecutive double quotation marks ("") after the -comment option, no backup comment will be registered in the backup catalog. -rc name-identifying-the-generation Use this option to specify the name identifying the generation of the copy group to be backed up. Execute the drmsqldisplay command with the -cf option specified, and then specify a value for the displayed GEN-NAME. For single volumes, a hyphen (-) appears.
Specify this option to automatically transfer a backup catalog to a backup server after backing up a volume. You must specify this option together with the -s option. -auto_mount mount-point-directory-name Specify this option to automatically mount a secondary volume on a backup server after backing up a volume. You must specify this option together with the -s and -auto_import options. Specify the mount-point-directory-name parameter by using a character string that is 64 bytes or less.
• An invalid option is specified. • The system cannot acquire information from the operation definition file linked to the operation ID. • A specified Application Agent command option cannot be specified as an extended command option. • The system fails to record a backup ID in the backup ID record file. • A command executed inside the extended command encounters an error. • The command fails to obtain the name of the directory where dictionary map files are stored.
• The specified item appears only once. • The number of characters does not exceed the maximum allowable for the item. In addition, the command checks the contents of the operation definition file for the items listed in the following table.
The table below lists the directories that are automatically created by the checking tool.
Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • An invalid option is specified. • The file specified in the argument does not exist, or the system cannot access the file. • The system cannot access the database server (when the -db option is specified). • The system detects an error in the results of the file check. • The command fails to create a temporary directory.
To apply only metafiles to the primary volume: EX_DRM_SQL_RESTORE operation-ID -no_resync [ -undo ] [ -nochk_host ] [ -target database-name | -f database-list-file ] Description This extended command executes the drmsqlrestore command to restore backup data from the secondary volume to the primary volume for a specified database. Prerequisites The prerequisites for executing this extended command are as follows: • An operation definition file linked to the specified operation ID has been provided.
Specify this option to restore the database to standby mode. When you specify this option, the database can be used in the read-only mode after restoration. A temporary file is created for each database in the undo-log file storage directory registered by using the drmsqlinit command. If you do not specify this option, this extended command performs normal restoration. Immediately after normal restoration, the database will be placed in the loading status, in which you cannot use the database.
NOTE: • The backup information in the backup catalog is managed based on the use of a copy group as a key. Depending on the backup method, you might not be able to perform restoration, even though the backup data exists on the secondary volume. For further information, see the notes on running Application Agent in the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide. • If ONLINE is set in CLU_MSCS_RESTORE in the Application Agent configuration definition file (init.
Description This extended command executes the drmsqllogbackup command to back up the SQL Server's transaction log linked to the specified operation ID. Prerequisites The prerequisite for executing this extended command is as follows: • An operation definition file linked to the specified operation ID has been provided. • None of the transaction log backup functions provided by SQL Server (such as BACKUP LOG and the log distribution function) are being used.
Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • • • • An invalid option is specified. The system cannot acquire information from the definition file linked to the operation ID. A command executed inside the extended command encounters an error. The command fails to obtain the name of the directory where dictionary map files are stored.
Arguments operation-ID A character string that uniquely identifies the operation to be performed. Information in the operation definition file corresponding to the specified operation ID is used when executing the extended command. Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • An invalid option is specified.
Prerequisites The prerequisites for executing this extended command are as follows: • An operation definition file linked to the specified operation ID has been provided. • The temporary folder for extended commands has been created. Arguments operation-ID A character string that uniquely identifies the operation to be performed. Information in the operation definition file corresponding to the specified operation ID is used when executing the extended command.
[ [ [ [ -pf copy-parameter-definition-file ] -vf VSS-definition-file-name ] -script user-script-file-name ] -s backup-server-name [ -auto_import [ -auto_mount [ mount-point-directory-name ]] ] [ -svol_check] ] Description This extended command executes the drmexgbackup command, which backs up the Exchange database that is in the storage group or Information Store specified by the operation ID from the primary volume to the secondary volume.
-transact_log_del Specify this option to delete a committed transaction log file. By deleting the transaction log file, you can increase the amount of unused drive capacity. If you delete a transaction log file, you will no longer be able to use the -recovery option to restore any previous backups. Specify this option when you want to restore data other than the most recent backup data without specifying the -recovery option.
A hyphen (-) cannot appear as the first character in the backup comment. If you specify two consecutive double quotation marks ("") after the -comment option, no backup comment will be registered in the backup catalog. -rc name-identifying-the-generation Use this option to specify the name identifying the generation of the copy group to be backed up. Execute the drmexgdisplay command with the -cf option specified, and then specify a value for the displayed GEN-NAME. For single volumes, a hyphen (-) appears.
For details about creating user script files, see the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide. If you specify LOCATION=REMOTE in the user script file, you must also specify the -s option. -s backup-server-name Specify this option to connect to a remote backup server to perform a backup. Specify the backup-server-name parameter by using the host name or the IP address of the backup server. Specify the host name by using a character string that is 255 bytes or less.
NOTE: Each piece of backup information in the backup catalog is managed by using a copy group as a key. Depending on the backup method, you might not be able to perform restoration, even though the backup data exists on the secondary volume. For details, see the notes on running Application Agent in the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide.
EX_DRM_EXG_DEF_CHECK operation-ID -bk To check the contents of an operation definition file for a database server by specifying a definition file: EX_DRM_EXG_DEF_CHECK -db -f definition-file-name To check the contents of an operation definition file for a backup server by specifying a definition file: EX_DRM_EXG_DEF_CHECK -bk -f definition-file-name Description This extended command checks the contents of an operation definition file, and if no problem is found, automatically creates a temporary directory
#1 Specification of the folder name is not case sensitive. #2 This item is checked only if the -bk option is specified. The table below lists the directories that are automatically created by the checking tool.
Conditions Causing an Error This extended command fails in the following cases: • • • • • An invalid option is specified. The file specified in the argument does not exist, or the system cannot access the file. An irregularity is detected in the contents of the operation definition file. The command fails to create a temporary directory. The command fails to obtain the name of the directory where dictionary map files are stored.
[ -force ][ -pf copy-parameter-definition-file] [ -vf VSS-definition-file-name ] [ -ef Exchange-environment-setting-file ] To restore an Information Store (Exchange Server 2010 or Exchange Server 2013): EX_DRM_EXG_RESTORE operation-ID -resync [ -target Information-Store-name ] [ -f target-definition-file-name ] [ -force ] [ -recovery ] [ -pf copy-parameter-definition-file ] [ -vf VSS-definition-file-name ] [ -ef Exchange-environment-setting-file ] Description This extended command executes the drmexgresto
Specify this option if you use Exchange Server 2007 to perform restoration on a specific Information Store from backup data obtained by using VSS. Specify the Information-Store-name parameter after the storage-group-name parameter by separating the two parameters with a backslash (\ ). If you specify the Information-Store-name parameter for backup data other than backup data that was obtained by using VSS, an error occurs.
If you omit this option, the value of the RAID Manager-linkage definition file (DEFAULT.dat) is used. The values in the RAID Manager-linkage definition file (DEFAULT.dat) are used for any parameters that are not included in the copy parameter definition file. You can create a copy parameter definition file by using a name of your choice. Specify the file name by using an alphanumeric character string that is 64 bytes or less.
NOTE: • Note the following when you use Exchange Server 2007 to perform restoration in units of Information Stores from backup data obtained by using VSS: • When performing restoration in units of Information Stores, if you specify both an Information Store name and a storage group name at the same time, the following occurs: - If you specify both an Information Store and a storage group of the same storage group, an error will occur.
EX_DRM_EXG_RESTORE operation01 -resync • In this example, the extended command is used to restore Information Store IS12 of storage group SG1, based on the settings specified in the operation definition file operation01: EX_DRM_EXG_RESTORE operation01 -resync -recovery -target SG1\IS12 EX_DRM_EXG_VERIFY (Verifies the consistency of an Exchange database) Format EX_DRM_EXG_VERIFY operation-ID [ -mount_pt mount-point-directory-name ] [ -force ] Description The EX_DRM_EXG_VERIFY extended command executes the
The mount point directory name must satisfy the following: • Maximum number of characters: Path lengths to be specified must comply with the specifications of the mount and unmount functions provided by RAID Manager. • Available characters: Characters that can be used in a directory name in Windows (excluding space characters).
EX_DRM_EXG_VERIFY operation01 78 Extended commands
2 Basic commands This chapter describes the basic commands provided by Application Agent. List of basic commands The table below lists the basic commands that Application Agent provides. Table 19 List of basic commands (file system backups) Basic command name Function summary drmfsbackup Backs up a file system to a secondary volume. drmfscat Displays a list of the backup information for a file system. • Displays a list of file system information. drmfsdisplay • Updates the dictionary map files.
Basic command name Function summary drmmediarestore Restores backup data from a tape device. drmmount Mounts a secondary volume. drmtapecat Displays a list of backup information for a tape device. drmtapeinit Registers the parameters for a backup management product. drmumount Unmounts a secondary volume. Table 22 List of basic commands (utility commands) Basic command name Function summary drmdbsetup Creates or deletes a Protection Manager database.
Before reading the basic command descriptions Note the following before reading the basic command descriptions: Do not forcibly terminate a basic command that is being executed. If you do so, the pair status of the copy group or the backup catalog might enter an unexpected status. For further information, see the description of permissions for command execution in the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide.
File name Use alphanumeric characters to specify the file name. File contents The contents of the file must adhere to the following conventions: • Each parameter (file name, directory name, SQL Server database name, storage group name, or Information Store name) must be specified on one line. • Lines beginning with a hash mark (#) are assumed to be comment lines.
# Protection Manager 3.5 # Log Backup Files [SQLDB001] C:\MSSQL\BackupLog\SQLDBLog001.bak C:\MSSQL\BackupLog\SQLDBLog002.bak C:\MSSQL\BackupLog\SQLDBLog003.bak [SQLDB002] C:\MSSQL\BackupLog\SQLDB2Log001.bak C:\MSSQL\BackupLog\SQLDB2Log002.bak C:\MSSQL\BackupLog\SQLDB2Log003.bak Correspondence with Replication Manager GUI terms Some terms used in the Application Agent command line interface have different meanings from those used in the Replication Manager GUI.
Basic command specifications (File system backups) drmfsbackup (Backs up a file system to a secondary volume) Formats To perform an online backup: drmfsbackup { mount-point-directory-name | mount-point-directory-target-definition-file-name } [ -mode online ] [ -rc [ name-identifying-the-generation ]] [ -pf copy-parameter-definition-file ] [ -comment backup-comment ] [ -script user-script-file-name ] [ -s backup-server-name [ -auto_import [ -auto_mount [ mount-point-directory-name ]] ] [ -svol_check ] ] To
When the drmfsbackup command is executed on the local site and the pair status is SMPL, the command does not automatically create a pair. In this case, if the PAIR_CREATE parameter in the RAID Manager-linkage definition file (DEFAULT.dat) is set to ENABLE, the command automatically creates a pair.
If you omit this option, online backup is assumed. -mode vss Specify this option to perform a VSS backup. To use this option, the Protection Manager service must be running on the backup server. -rc name-identifying-the-generation Use this option to specify the name identifying the generation of the copy group to be backed up. Execute the drmfsdisplay command with the -cf option, and specify the displayed GEN-NAME value. In a single volume, a hyphen (-) appears.
The following special characters cannot be used in backup comments: \ / ` | < > " * ? & ; ( ) $ Note that the first character must not be a hyphen (-). If you specify two double quotation marks after the -comment option, as in -comment "", no backup comment will be registered in the backup catalog. -vf VSS-definition-file-name Specify this option to switch the settings to be used for each VSS backup. You can use this option only when using VSS for backup.
Execute the drmumount command to unmount the mounted secondary volume. In the argument of the drmumount command, specify the backup ID. -svol_check Specify this option to check the status of a secondary volume on a backup server. This option must be specified concurrently with the -s option. Checking the status of a secondary volume prevents backup or restoration failures. The items, volumes, and conditions to be checked are described in the following table.
The location of the mount point directory target definition file: Application-Agent-installation-directory\DRM\conf\fs\APP1 Contents of the mount point directory target definition file: D: E: F:\MNT • In this example, the command is used to perform an online backup to a remote site: PROMPT> drmfsbackup F: -rc remote_0 • In this example, the command is used to back up by using VSS: PROMPT> drmfsbackup H: -mode vss KAVX0001-I The drmfsbackup command will now start. KAVX0019-I Copying file(s) now...
Displayed item Description ORIGINAL-ID Original backup ID obtained by the drmfsbackup command START-TIME Start time of a snapshot backup END-TIME End time of a snapshot backup HOSTNAME Server name where the snapshot backup was performed Object type T (F, which means file, is always displayed.
Displayed item Description BACKUP-COMMENT Backup comment #1 If this command is executed with the -device option, DEVICE will be displayed after T. #2 This information is displayed when the command is executed with the -v option. A hyphen (-) is displayed for any item that cannot be displayed. If no items can be displayed, an error message is displayed. Each item is separated by a space.
Specify this option to display backup information for specific files or directories on the file system specified by the mount-point-directory-name argument. Create a target definition file that contains a list of absolute paths of the mount point directories, drives, or volume mount points for which you want to display information. By specifying the target definition file name, you can collectively specify all of the targets for which you want to display information.
character but is not enclosed in double quotation marks, the special character is not properly handled as a part of the backup-comment string and is parsed as a special character. If you specify -comment "*", the command will display all backup catalogs. If two double quotation marks are specified after the -comment option (as in -comment ""), a message is displayed indicating that no backup data exists.
PROMPT> drmfscat D: -hostname FILESERV1 INSTANCE: D: BACKUP-ID:0000000001 BACKUP-MODE: COLD INSTANCE: D: ORIGINAL-ID:0000000001 START-TIME:2002/06/01 10:00:00 END-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:03:00 HOSTNAME: FILESERV1 T FILE FS DG DEVICE COPY-GROUP F D: Harddisk1 VG01,dev01 F VG01,dev01 • In this example, the command is used to display backup information for the file system of the D drive and management information for the backup catalog: PROMPT> drmfscat D: -v VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME: host1 DB-PATH: D:\Program Files\CV
drmfsdisplay (Displays or updates file system information) Formats To display file system information: drmfsdisplay [ mount-point-directory-name ] [ -target file-or-directory-names | -f target-definition-file-name ] [ -device device-file-name ][ -l ] [ -v ][ -cf ] To update the information in the dictionary map files: drmfsdisplay -refresh Description The drmfsdisplay command performs the following three functions: 1. 2. 3.
Displayed item Description PORT# Port name on the server host side TID# Target ID on the server host side LUN# Logical unit number on the server host side MU# Pair identifier LDEV# Logical device number across RAID devices Letter identifying whether the volume is primary or secondary: P: Primary volume of a pair P/S S: Secondary volume of a pair -: A volume that is not part of a pair SERIAL# Serial number across RAID devices Copy type COPY-FUNC Copy type: The name of the copy type varies de
Specify the drive letter of the file system for which you want to display information, or specify its absolute path starting with the drive letter. Do not specify a backslash (\) at the end of the path. If this argument is not specified, the command targets all file systems. -target file-or-directory-names Specify this option to display information about specific files or directories. Use absolute paths to specify the file names or directory names.
If the disk configuration has changed, always update the dictionary map files. NOTE: When specifying on the command line a file name or directory name containing space characters for the -target option or the -f option, you must enclose the file name in double quotation marks ("). Note that enclosing with double quotation marks is not necessary for target paths specified in batch definition files.
PROMPT> drmfsdisplay D: -v VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME: host1 DB-PATH: D:\Program Files\CVXPAE\DRM\db2 INSTANCE: D: CORE-MAPFILE-UPDATE-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:00:00 APP.
2. 3. The command confirms that the file system has been unmounted, and then resynchronizes the disks by restoring the backup data from the secondary volume to the primary volume. The command mounts the file system again. The following explains the command processing for restoration in a cluster configuration: 1. The command automatically takes the disk resource offline when the disk resource in the file system to be restored is brought online.
Before a backup After a backup Primary volume Primary volume Command execution result Secondary volume GPT disk Command status Error message (DRM-10337) Before resynchronizing#2 MBR disk Error message (KAVX5171-E or KAVX5137-E) GPT disk Normal termination GPT disk After resynchronizing#1 #1 The error message is displayed after resynchronizing. #2 The error message is displayed before resynchronizing. Arguments backup-ID Specify the backup ID of the backup data you want to use for restoration.
containing space characters, enclose the directory name in double quotation marks ("). You cannot specify a backslash (\) at the end of the path. If you omit both this option and the -f option, the entire file system registered in the backup catalog will be restored. -f target-definition-file-name Specify this option to restore the file system that contains the specific file or directory. Use the file or directory name registered in the backup catalog specified by the backup ID.
Examples • In this example, the command is used to restore data from the secondary volume to the primary volume, which resynchronizes the disks. The backup data used for restoration is identified by the backup ID 0000000001. PROMPT> drmfsrestore 0000000001 -resync • In this example, the command is used to restore data from the secondary volume to the primary volume, which resynchronizes the disks. The backup data used for restoration is identified by the backup ID 0000000001.
Displayed item Description BACKUP-MODE Backup mode HOSTNAME#2 Name of the server where the snapshot backup was performed BACKUP-OBJECT Snapshot backup object type INSTANCE#2, #3 • The name of the instance of the backup target (for a database) • The name of the mount point directory (for a file system) START-TIME Start time of a snapshot backup END-TIME End time of a snapshot backup VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME Virtual server name (value of the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable) DB-PATH Name of the di
• Virtual server name (value of the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable) If the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable has not been set, a hyphen (-) appears. -comment backup-comment Specify this option to display only information on a specific backup comment. The backup-comment value is not case sensitive. You can use an asterisk (*) to specify a wildcard in backup-comment.
2003/10/02 18:59:37 PROMPT> • In this example, the command is used to display the backup catalog list and backup catalog management information, with backup comments: PROMPT> drmappcat -v -comment "Comment*" VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME: host1 DB-PATH: D:\Program Files\CVXPAE\DRM BACKUP-COMMENT BACKUP-ID BACKUP-MODE BACKUP-OBJECT START-TIME END-TIME Comment1 0000000162 ONLINE FILESYSTEM 2003/10/02 18:24:35 2003/10/02 18:59:37 Comment2 0000000251 ONLINE MSSQL 2003/10/03 18:55:15 2003/10/03 18:59:37 PROMPT> • In this
Arguments -copy_group copy-group-name Specify the name of the copy group you want to lock or unlock. You can confirm that the logical volumes are the same by executing the drmfsdisplay command and checking the items listed for LVM-DEVICE. In environments where one logical volume group comprises multiple copy groups, if the multiple generation backup function is used, the number of generations of all copy groups comprising the logical volume group must match.
PROMPT> drmcgctl -copy_group VG01,dev01 -mode unlock • In this example, the command is used to lock the copy groups used for the backup identified by the backup ID 0000000001: PROMPT> drmcgctl -backup_id 0000000001 -mode lock • In this example, the command is used to unlock the copy groups used for the backup identified by the backup ID 0000000001: PROMPT> drmcgctl -backup_id 0000000001 -mode unlock drmclusinit (Registers the parameters for the cluster software) Formats To register the parameters for the
Registered item Description Enter the disk resource name. You do not need to enter the service resource name. Resource name • For an environment with Veritas Storage Foundation: Enter the cluster resource name for mount-point (logical volume)#1 and disk-group#2. Enter the following information, based on the resource name: • When mount-point is specified: Disk name (required when D has been specified for the resource type) Enter a mount point (such as D:).
NOTE: Execute the drmclusinit command before performing backup. If you have changed the cluster configuration, execute the drmclusinit command to re-specify the cluster information. Execute the drmclusinit command on both the active server and standby server. The resource information to be registered by using the drmclusinit command must completely match the information registered in the cluster software.
Examples • In this example, the command is used to register, for a disk configuration that uses Veritas Storage Foundation, the parameters for controlling the cluster software (for Exchange Server). This example is based on the configuration below. For SQL Server, the storage group portion is the SQL instance. Virtual server name: VHOST1 Service group name: ServiceGroup-Exc Disk configuration: See the following table.
Storage group Mount point Disk group Physical disk F: (resource name is MountV-F) DG2 (resource name is VMDG-2) Harddisk3 F:\mnt (resource name is MountV-F-mnt) DG3 (resource name is VMDG-3) Harddisk4 PROMPT> drmclusinit VCS KAVX0313-I Enter the virtual host name: VHOST1 KAVX0310-I Enter the resource group name: ServiceGroup-FS KAVX0317-I Enter the instance name: KAVX0311-I Enter the resource name: MountV-E KAVX0314-I Enter the resource type (S for service.
• When the backup is of a file system, use the drmfscat command. • When the backup is of an SQL Server database, use the drmsqlcat command. • When the backup is of an Exchange database, use the drmexgcat command. -f export-destination-file-name Use an absolute path to specify the file to which you want to export the backup information. Use a maximum of 511 bytes for a file name. If the specified export destination file already exists, the existing file is overwritten.
Example • In this example, the command is used to import the backup information from the file D:\tmp\ 0000000001.drm: PROMPT> drmdbimport -f D:\temp\0000000001.
Description This command conceals or reveals physical volumes of storage system devices connected to the server. By concealing physical volumes from the server and controlling access, you can prevent errors caused by user operations. In addition, you can conceal physical volumes and obtain backups either in Veritas Storage Foundation environments or by using Fast Snap or Snapshot, and then store multiple generations of these backups on secondary volumes.
-sigview Displays the disk signatures of the physical volumes. Use this option to restore operation when the KAVX5137-E message is output and the restoration command terminates with an error. • When a backup ID is specified with the -sigview option: The disk signature recorded when the backup was made is displayed. You can use this to compare the value of the current disk signature with the value at the time the backup was created.
• When the -sigset option and the -copy_group copy-group-name are specified at the same time, the current disk signature is updated in accordance with the specified disk signature that follows the -sigset option. In this case, a disk signature must always be specified. The disk signature to be specified differs depending on the partition style. The following table lists partition styles and corresponding disk signatures to be specified.
NOTE: A backup ID and the -copy_group option cannot be specified at the same time. If neither the backup-ID option nor the -copy_group option is specified, the secondary volumes of all copy groups managed by Application Agent will be targeted. The RAID Manager instance used by Application Agent is specified in the RAID Manager-linkage definition file (DEFAULT.dat) as HORCMINST=n.
Examples • In this example, the command conceals the secondary volumes of all copy groups, and performs a drive rescan: PROMPT> drmdevctl -detach • In this example, the command conceals the secondary volumes of the copy groups registered in the backup catalog, and performs a drive rescan: PROMPT> drmdevctl 0000000002 -detach • In this example, the command is used to execute multiple conceal operations for the secondary volumes of copy groups, and to perform a drive rescan at the end: PROMPT> PROMPT> PROMP
PROMPT> drmdevctl 0000000002 COPY_GROUP DEVICE TYPE VG01,dev01 Harddisk10 MBR VG01,dev02 Harddisk11 MBR -sigview CUR_DISKID BKU_DISKID ABCDEF01 ABCDEF00 ABCDEF02 ABCDEF03 • In this example, the command is used to display the current disk signature of the local volume for the copy group VG01,dev01: PROMPT> drmdevctl -copy_group VG01,dev01 -sigview COPY_GROUP DEVICE TYPE CUR_DISKID BKU_DISKID VG01,dev01 Harddisk10 MBR ABCDEF01 -------- • In this example, for the copy group recorded in the backup catalog th
Displayed item Description Product version. If this option is not specified, the information is displayed in the format VV.R.r.AASS(VV-Rr-as#1)#2. The following are examples: HP StorageWorks P9000 Replication Manager Application Agent Copy Controller 7.0.0-00: 07.0.0.0000(07-00) HP StorageWorks P9000 Replication Manager Application Agent Copy Controller 7.0.0-01: VERSION 07.0.0.0001(07-00-01) If the -i option is specified, the information is displayed in the format VV.R.r.AASS#2.
Examples The following are examples of using Application Agent version 7.0. • In this example, the drmhostinfo command is used to display host information: PROMPT> drmhostinfo PRODUCT VERSION HP StorageWorks P9000 Replication Manager Application Agent Copy Controller 07.0.0.0000(07-00) HP StorageWorks P9000 Replication Manager Application Agent for SQL 07.0.0.
command when the PAIR_CREATE parameter in the RAID Manager-linkage definition file (DEFAULT.dat) is set to ENABLE. Arguments -copy_group copy-group-name Specify the name of the copy group you want to resynchronize. To check the copy group name, execute either of the following commands according to what was backed up: • When the backup is of a file system, use the drmfscat command. • When the backup is of an SQL Server database, use the drmsqlcat command.
Examples • In this example, the command is used to resynchronize the copy group VG01,dev01: PROMPT> drmresync -copy_group VG01,dev01 • In this example, the command is used to lock the copy groups used in the backup identified by the backup ID 0000000001: PROMPT> drmresync -backup_id 0000000001 Basic command specifications (Tape-related commands) drmmediabackup (Backs up data from a secondary volume to a tape device) Format drmmediabackup backup-ID [ -raw ] [ -bkdir backup-file-directory ] [ -bup_env confi
Arguments backup-ID Specify the backup ID for the secondary volume that contains the backup data to be copied to a tape device. A backup ID uniquely identifies backup data and is registered in the backup catalog during backup. To check backup IDs, execute one of the following commands according to what was backed up: • When the backup is of a file system, use the drmfscat command. • When the backup is of an SQL Server database, use the drmsqlcat command.
The conditions for specifying a configuration definition file name are as follows: Maximum number of characters (total length of the directory name and file name): 255 bytes Specifiable characters: Those characters specifiable for file names in Windows NOTE: - will be displayed unless the NetBackup master server, media server, and client server are all configured on the host where the drmmediabackup command is executed. Refer to the NetBackup image catalog to check the media label name.
• YES (normal termination) • NO (termination with an error) • CANCEL (operation canceled) After restoration with Backup Exec finishes, enter the correct keyword. Before executing the drmmediarestore command, confirm the following: • The backup management product has been linked. • The drmmount command has been executed with a backup ID specified and the secondary volume to be backed up has been mounted. • The secondary volume is not in the mirror status.
Create a configuration definition file in the directory containing the default configuration definition file. For further information, see the description of configuration definition file creation in the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide. NOTE: The value of NBU_MASTER_SERVER in the configuration definition file must be the same as the value that was used during the backup.
If the copy group mount definition file exists, the mount point specified in this file is used as the mount point for the secondary volume. For details about the copy group mount definition file, see the settings for mounting a secondary volume in the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide. When a backup ID is specified, the copy group corresponding to the specified backup ID is locked.
absolute-path-specified-for-mount-point-directory-name When mounting the secondary volume by specifying the backup ID: absolute-path-specified-for-mount-point-directory-name\ primary-volume-drive-letter\primary-volume-mount-point If a path does not end with a backslash (\), the command assumes a backslash at the end of the path. For example, D: and D:\ are assumed to be the same drive. D:\MOUNTDIR and D:\MOUNTDIR\ are assumed to be the same directory.
Examples • In this example, the command is used to mount the secondary volume identified by the backup ID 0000000001 to D:: PROMPT> drmmount 0000000001 -mount_pt D: If several secondary volumes have been backed up with the backup ID 0000000001, the command searches for an unused drive in alphabetical order beginning from the D drive, and mounts the secondary volume to the first found drive.
Description The drmtapecat command lists the backup information about tape backups, which is stored in the backup catalog on the server where the command was executed. The backup catalog displayed is that created with the drmmediabackup command. By checking the backup information, you can confirm information about the objects corresponding to the backup ID, and hence confirm the backup ID to be used for restoration.
- will be displayed unless the NetBackup master server, media server, and client server are all configured on the host where a tape backup is executed. Refer to the NetBackup image catalog to check the media label name. #4 When the -bkdir option is specified, this information is displayed. #5 When the -v option is specified, this information is displayed. #6 When the -v and -o options are specified, this information is displayed. A hyphen (-) is displayed for any item that cannot be displayed.
For each backup ID, displays the time when the backup catalog was created. This information is displayed only when the -o option is specified. -o FILESYSTEM Specify this option to display the information for a backup from a primary volume to a secondary volume, and the type of backup object is a file system. -o MSSQL Displays detailed information for the backup that was registered when a snapshot backup was performed for the backup information about the instance for the backup object type.
• -hostname drmexgcat-command-options You can specify the following options for the drmexgcat command. For details about the functions of the options, see the description of the drmexgcat command. • -target • -f • -device • -transact_log • -datafile • -l • -v • -backup_id • -hostname -delete Specify this option to delete the backup information for the backup catalog.
PROMPT> drmtapecat BACKUP-ID BACKUP-OBJECT BACKUP-MEDIA 0000000002 FILESYSTEM MEDIA3 0000000003 FILESYSTEM MEDIA4 SNAPSHOT TIME EXPIRATION TIME 2002/02/01 11:00:00 2002/05/01 11:00:00 2002/02/01 11:30:00 2002/05/01 11:30:00 • In this example, the command is used to display the backup information of the backup ID 0000000002: PROMPT> drmtapecat -backup_id 0000000002 BACKUP-ID BACKUP-OBJECT SNAPSHOT TIME BACKUP-MEDIA 0000000002 FILESYSTEM 2002/02/01 10:30:00 MEDIA2 EXPIRATION TIME 2002/05/01 10:30:00
DB-PATH: D:\Program Files\CVXPAE\DRM\DB2 KAVX0024-E The specified backup data does not exist.
PROMPT> drmtapecat -comment "SQL-DB*" BACKUP-COMMENT BACKUP-ID BACKUP-OBJECT SNAPSHOT SQL-DB-1 0000000002 MSSQL 2003/09/05 C:\NBU_BACKUP\stdg11_1070608229_C1_F1 SQL-DB-2 0000000002 MSSQL 2003/09/05 C:\NBU_BACKUP\stdg11_1070608250_C1_F1 SQL-DB-3 0000000008 MSSQL 2003/09/06 C:\NBU_BACKUP\stdg11_1070608251_C1_F1 SQL-DB-4 0000000008 MSSQL 2003/09/06 C:\NBU_BACKUP\stdg11_1070608252_C1_F1 TIME EXPIRATION TIME 15:50:54 2003/12/05 15:50:54 BACKUP-MEDIA 15:50:54 2003/12/05 15:50:54 15:50:54 2003/12/06 15:50:54 15
Arguments -v Specify this option to display the settings of the parameters currently registered. NOTE: • If you specify a storage period for backup information that is longer than the protection period for the backup management product media, you cannot use the drmmediarestore command to restore data from a tape device because the media information in the backup management product will have been deleted.
• In this example, the command is used to display the parameters for linking with Backup Exec: PROMPT> drmtapeinit -v Backup application name: BEWS Days to keep the backup catalog: 1 PROMPT> drmumount (Unmounts secondary volumes) Formats To unmount a secondary volume by specifying the name of a copy group: drmumount -copy_group copy-group-name To unmount a secondary volume by specifying the name of a backup ID: drmumount backup-ID Description The drmumount command unmounts a secondary volume that has b
the backup server to mount the secondary volume, and then unmount the secondary volume by using the drmumount command to clear the system cache. To check the name of a copy group, execute either the drmfscat command or the drmfsdisplay command. backup-ID Specify the backup ID associated with the copy groups you want to unmount. When multiple copy groups were used for the backup identified by the specified backup ID, the secondary volumes of all the copy groups are unmounted.
Description The drmdbsetup command creates and deletes the contents of the dictionary map files. Dictionary map files for creation and deletion are stored as defined by the path information in DRM_DB_PATH, in the Application Agent configuration definition file (init.conf). For details about the Application Agent configuration definition file, see the description of Application Agent operation settings in the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide.
Description The drmsqlbackup command takes the volume that contains the specified instance in memory, and backs it up to the secondary volume. If the instance's objects (such as data files and various databases) exist across several volumes, all primary volumes will be backed up to secondary volumes. When SQL Server instances are backed up, an online backup will be performed. If instances that are not running are specified when executing a command, a command error occurs.
One execution of the command can back up a maximum of 64 databases. If you want to back up 65 or more databases, execute the command more than once. Backups can only be performed for files described in the following table.
This file is created when the drmsqlbackup command is executed. #3: If you registered a VDI metafile storage directory by using the drmsqlinit command, the backup file is stored in the registered directory. The file name is backup-ID_database-ID.dmp. If you did not register a VDI metafile storage directory by using the drmsqlinit command, the backup file is stored in the directory that contains the file with the smallest management number (file_id) value for SQL Server in the database file.
When you omit name-identifying-the-generation, the secondary volume that has the smallest value among the generation numbers on the remote-side becomes the backup destination. In this case, the generation number is remote_n, where n is the smallest generation number. -pf copy-parameter-definition-file Specify this option when using the number of retries and the retry interval defined in the copy parameter definition file. Specify only the file name, without specifying the path.
Specify this option to automatically mount a secondary volume on a backup server after backing up a volume. This option must be specified concurrently with the -s and -auto_import options. Specify mount-point-directory-name by using a character string of up to 64 bytes. If you omit the mount-point-directory-name parameter, a mount destination for a secondary volume is automatically determined. This destination is determined in the same way as when using the drmmount command without specifying a mount point.
NOTE: If you use the -target or -f option, specify all the databases that are contained in the same logical volume. If this is option is not specified, a command error occurs. The backup information in the backup catalog is managed based on using the copy group as a key. Depending on the backup method, you might not be able to perform restoration, even though the backup data exists on the secondary volume.
KAVX0086-I The backup information has been assigned as follows: Backup ID = 0000000001 KAVX0002-I drmsqlbackup command will now end. • To create backups in the local and remote destinations using the script: PROMPT> drmsqlbackup default -script C:\Uscript.txt KAVX0001-I The drmsqlbackup command will now start. KAVX1017-I SQL Server information is being collected now. KAVX1207-I Backing up the database... KAVX0210-I The user script will now start.
End code = 0 KAVX0211-I Execution of the user script has finished. KAVX0210-I The user script will now start. Procedure section = SPLIT_PROC KAVX0212-I A command from the user script will now execute. Command line = C:\HORCM\etc\pairsplit.exe -g TC01 -d sql01 -FBC 0 KAVX0213-I A command from the user script has ended. End code = 0 KAVX0212-I A command from the user script will now execute. Command line = C:\HORCM\etc\pairsplit.exe -g TC01 -d sql02 -FBC 0 KAVX0213-I A command from the user script has ended.
Displayed item Meaning Object type: T D: Data file T: Transaction log M: Metafile DB SQL Server database name SQL Server object name: OBJECT DATAFILE: Data file name TRANSACT: Transaction file name METAFILE: VDI metafile name FILE File name CHECKPOINT-LSN Log sequence number for the starting point of database recovery when a transaction log backup file is restored.
Displayed item Meaning VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME#3 Virtual server name (value of the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable) DB-PATH#3 Name of the directory storing the backup catalog CATALOG-UPDATE-TIME#3 Time when the backup catalog was created BACKUP-COMMENT Backup comment #1 A hyphen (-) is displayed if OBJECT is something other than DATAFILE. A hyphen (-) is displayed for a backup catalog created by a version earlier than Application Agent 6.3.0-00.
file. If you specify a database name containing a space character, enclose the database name in double quotation marks ("). When both this option and the -target option are omitted, all information about the instance specified by the instance name will be displayed. -transact_log Specifies that only information relating to the transaction log file will be displayed.
Displays the path that is set in DRM_DB_PATH in the Application Agent configuration definition file (init.conf). If DRM_DB_PATH has not been set, the default storage directory for the dictionary map files, which are created automatically during installation, is displayed. • Virtual server name (value of the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable) If the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable has not been set, a hyphen (-) appears.
Return Values 0: Normal termination Any value other than 0: Termination with an error Examples • In this example, the command is used to display information about the SQL Server database specified in instance SQL1: PROMPT> drmsqlcat SQL1 INSTANCE: SQL1 BACKUP-ID: 0000000001 BACKUP-MODE: ONLINE INSTANCE: SQL1 ORIGINAL-ID: 0000000001 START-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:00:00 END-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:03:00 HOSTNAME: DB_SVR1 T DB OBJECT FILE FS DG DEVICE COPY-GROUP M DB1 METAFILE C:\METADIR\Meta1 C: D DB1 DATAFILE D:\SQL
DEVICE COPY-GROUP PORT# TID# LUN# MU# LDEV# P/S SERIAL# M DB1 METAFILE C:\METADIR\Meta1 C: NTFS \\?\Volume{df66a5b0-5583-12d5-a410-806d6172696f}\ Harddisk1 VG11,dev01 CLI-A 2 10 0 10010 P 15044 D DB1 DATAFILE D:\SQL\data1.mdf D: NTFS \\?\Volume{df67a5b0-5583-11d5-a410-806d6172696f}\ Harddisk2 VG12,dev02 CLI-A 2 20 0 10020 P 15044 - - VG12,dev02 CLI-A 2 21 0 10021 S T DB1 TRANSACT D:\SQL\tlog1.
• In this example, the command is used to display information about the SQL Server database specified by the instance SQL1 and management information for the backup catalog: PROMPT> drmsqlcat SQL1 -v VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME: DB_SVR1 DB-PATH: D:\Program Files\CVXPAE\DRM\db2 INSTANCE: SQL1 BACKUP-ID: 0000000001 BACKUP-MODE: ONLINE INSTANCE: SQL1 ORIGINAL-ID: 0000000001 START-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:00:00 END-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:03:00 HOSTNAME: DB_SVR1 CATALOG-UPDATE-TIME: 2002/06/01 11:00:00 T DB OBJECT FILE FS DG DEV
T UserDB1 TRANSACT O: Harddisk4 - - SI01,sql01 O:\UserDB1_Log.
Description The drmsqldisplay command does the following: 1. 2. 3. Displays the resource information of the SQL Server database on the server on which the command was executed. Displays resource information pertaining to optional instances for the system on which the command was executed. Updates the SQL Server database information of the dictionary map files. Execute this command before performing a backup. The items displayed in 1 and 2 are shown in the table below.
Displayed item Meaning LUN# The logical unit number on the host server MU# Paired ID LDEV# The logical device number within the RAID setup A letter to distinguish the primary volume from the secondary volume: P: Primary volume P/S S: Secondary volume -: A volume that is not part of a pair SERIAL# The serial number within the RAID device Copy type COPY-FUNC Copy type: The name of the copy type varies depending on the DKC software product (storage system unit) and microcode version.
-target database-names Displays the information regarding specific databases of the instance instance-name. To display or update information for more than one database, separate the database names using commas. If you specify a database name containing a space character, enclose the database name in double quotation marks ("). -f target-definition-file-name Displays the information regarding specific databases of the instance instance-name.
Specifies the SQL Server database information that will be displayed in the long format. -v Specify this option to display management information about the dictionary map files. The following information is displayed: • Name of the directory storing the backup catalog Displays the path that is set in DRM_DB_PATH in the Application Agent configuration definition file (init.conf).
Specify this option to display information with linking for copy groups for both the local site and all remote sites. NOTE: When specifying on the command line a file name or directory name containing space characters for the -target or -f option, you must enclose the file name in double quotation marks ("). Note that enclosing with double quotation marks is not necessary for target paths specified in batch definition files.
VG01,dev01 CLI-A 2 20 0 10020 S T DB1 TRANSACT D:\SQL\tlog1.ldf D: NTFS \\?\Volume{df67a5b0-5583-11d5-a410-806d6172696f}\ Harddisk1 VG01,dev01 CLI-A 2 10 0 10000 P - - - 15044 VG01,dev01 CLI-A 2 20 0 10020 S T DB1 TRANSACT D:\SQL\tlog2.ldf D: NTFS \\?\Volume{df67a5b0-5583-11d5-a410-806d6172696f}\ Harddisk1 VG01,dev01 CLI-A 2 10 0 10000 P - - - 15044 VG01,dev01 CLI-A 2 20 0 10020 S D DB2 DATAFILE E:\SQL\data1.
PROMPT> drmsqldisplay SQL1 -v VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME: host1 DB-PATH: D:\Program Files\CVXPAE\DRM\db2 INSTANCE: SQL1 CORE-MAPFILE-UPDATE-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:00:00 APP.-MAPFILE-UPDATE-TIME: 2002/06/01 10:00:00 T DB OBJECT FILE FS DG DEVICE D DB1 DATAFILE D:\SQL\data1.mdf D: Harddisk1 - T DB1 TRANSACT D:\SQL\tlog1.ldf D: Harddisk1 - D DB2 DATAFILE E:\SQL\data2.mdf E: Harddisk2 - T DB2 TRANSACT E:\SQL\tlog2.
Description The drmsqlinit command provides an interactive interface that lets you register the SQL Server parameters necessary to back up an SQL Server database. You can register parameters for each instance. This command registers the following information. Table 41 Parameters for the SQL Server Setting Description Use an absolute path to specify the name of the directory for storing a VDI metafile. An existing directory must be specified.
Whether the directories can be specified depends on how to specify the directories. The following table lists whether the directories can be specified.
KAVX1107-I Enter the name of the storage directory for the backup-log files: D:\MSSQL\tlog KAVX1103-I SQL Server information has been updated.
drmsqllogbackup instance-name -d [ -s log-backup-ID ] [ -e log-backup-ID ] To display the detailed information of transaction log files in the log backup catalog: drmsqllogbackup instance-name -lsn Description The drmsqllogbackup command backs up the transaction log file of a SQL server database that was backed up by using the drmsqlbackup command. Use the drmsqlinit command to set the directory to which this file is to be backed up.
-v Specify this option to display a list of the transaction log files that were backed up. Information on the backups of the transaction log files acquired after the backup ID specified together will be displayed. You can take the information displayed by this option, and use it as a transaction log target definition file. BACKUP-ID Specify BACKUP-ID to display the backup IDs of the backups for the specified instance.
-e log-backup-ID Specify this option to set the end of the range of the transaction log backup files to be deleted or displayed. Use this option with the -s option to specify the start and end of this range. Specifying the -e option alone sets the range from the first log backup ID to the log backup ID specified with the -e option. Possible log backup ID values are 0001 through 9999. -lsn Specify this option to display the detailed information of the transaction log files in the log backup catalog.
NOTE: This command cannot be applied to the system databases (master, msdb, model, tempdb, and distribution). After a database has been restored, the log backup for different recovery paths are mixed and displayed. For the instance that is the target of this command, if the drmsqlbackup command of Application Agent 6.3.0-00 or later has been executed for the instance, you can back up the transaction logs entries associated with a backup ID, regardless of whether the backup catalog exists.
PROMPT> drmsqllogbackup 0000000020 -v -s 0001 -e 0003 [userDB1] C:\LogBackup\userDB1_20021106010101_0001.bk C:\LogBackup\userDB1_20021106050101_0002.bk C:\LogBackup\userDB1_20021106090101_0003.bk [userDB2] C:\LogBackup\userDB2_20021106010101_0001.bk C:\LogBackup\userDB2_20021106050101_0002.bk C:\LogBackup\userDB2_20021106090101_0003.
PROMPT> drmsqllogbackup -no_cat -v # ORIGINAL-ID:BACKUP-ID:[UserDB3] C:\MSSQL\FLORA4\default\tlog\UserDB3_20040116163638_0001.bk C:\MSSQL\FLORA4\default\tlog\UserDB3_20040116163640_0002.bk # ORIGINAL-ID:BACKUP-ID:[UserDB2] C:\MSSQL\FLORA4\default\tlog\UserDB2_20040116163637_0001.bk C:\MSSQL\FLORA4\default\tlog\UserDB2_20040116163640_0002.bk # ORIGINAL-ID:BACKUP-ID:[UserDB1] C:\MSSQL\FLORA4\default\tlog\UserDB1_20040116163637_0001.bk C:\MSSQL\FLORA4\default\tlog\UserDB1_20040116163640_0002.
During command execution, from another computer such as an application server, you should not connect to the database that was restored. If another server connects to the database during command execution, the command might fail. Arguments instance-name Specify the database instance to be recovered. If the instance to be recovered is the default, specify DEFAULT. -target database-names Specify this option to recover specific databases.
When the -loading option is specified, because no temporary files are created as with the -undo option, you do not need to create the temporary file storage directory beforehand. If both the -undo option and -loading option are omitted, the database can be fully accessed after recovery, but any subsequent transaction logs are not applied.
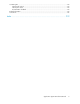
Figure 1 drmsqlrecovertool dialog box INSTANCE Displays the instance name specified for the drmsqlrecovertool command. The command will recover this instance. To change the instance, close the drmsqlrecovertool dialog box, and then re-execute the drmsqlrecovertool command. Transaction log backup list Displays a list of transaction log backup files that apply to the database selected in Target database. Use the Add button to add a file to this list. Use the Delete button to delete a file.
Roll forward? Select whether or not to perform a roll-forward during recovery. If No is selected, the Transaction log backup list becomes inactive. Recovery takes place without a roll forward, even when transaction log backup files are displayed. Add button Choose this button to add a transaction log file to be applied. This button adds the selected file to the files selected in Transaction log backup list. The files are sorted by name (not including file extensions and paths) and added.
drmsqlrestore backup-ID -resync [ -force ][ -undo ][ -nochk_host ] [ -instance name-of-the-SQL-Server-instance ] [ -target database-name | -f target-definition-file-name ] [ -pf copy-parameter-definition-file ] To apply only the metafile to the primary volume: drmsqlrestore backup-ID -no_resync [ -undo ][ -nochk_host ] [ -instance name-of-the-SQL-Server-instance ] [ -target database-name | -f target-definition-file-name ] To restore backup data on the remote site by resynchronization: drmsqlrestore backup
2. 3. The command performs disk resynchronization to restore the backup data from a secondary volume to the primary volume. The command brings the disk resource online, and then brings the cluster resource, including databases, online. If ONLINE is set in CLU_MSCS_RESTORE in the Application Agent configuration definition file (init.conf), you can perform restoration of a user database while the cluster resources are online by specifying the -resync option.
Before a backup After a backup Primary volume Primary volume Command execution result Secondary volume MBR disk Command status Error (DRM-10337 message) Before resynchronizing#2 MBR disk GPT disk GPT disk Error (DRM-10337 message) Before resynchronizing#2 MBR disk Error (KAVX5171-E or KAVX5137-E message) GPT disk Normal termination GPT disk After resynchronizing#1 #1 The error message is displayed after resynchronizing. #2 The error message is displayed before resynchronizing.
appears, indicating that no parameters are set for the drmsqlinit command. Specify the UNDO file storage directory using the drmsqlinit command. When this option is omitted, a regular restoration is performed. In this case, the database will be placed in loading status after the restoration has finished, and will not be usable. -nochk_host Specify this option to restore the data to a host other than the one specified in the drmsqlbackup command.
-template Specify this option to perform restore operations by using a backup catalog that was created by executing the drmsqlbackup command with the -template option specified. The START-TIME and END-TIME of a template catalog specified with the -template option are the times at which creation of the template catalog started and finished. -pf copy-parameter-definition-file Specify this option when using the number of retries and the retry interval defined in the copy parameter definition file.
PROMPT> drmsqlrestore 0000000001 -resync • In this example, the command, using the template catalog, is used to restore the backup data identified with backup ID 0000000002: PROMPT> drmsqlrestore 0000000002 -resync -nochk_host -template KAVX0001-I drmsqlrestore command will now start. KAVX1316-I Performing restore pre-processing... KAVX1000-I Logged on to the SQL Server system. KAVX1300-I Restore processing will now start. KAVX1000-I Logged on to the SQL Server system.
] [ -svol_check ] ] To perform a backup by using VSS with a cascade configuration (Exchange Server 2007): drmexgbackup -mode vss -cascade [ -target storage-group-name | -f target-definition-file-name ] [ -transact_log_del | -noverify | -noverify_log_del ] [ -event_check ][ -rc name-identifying-the-generation ] [ -comment backup-comment ] [ -vf VSS-definition-file-name ] [ -script user-script-file-name ] [ -auto_import [ -auto_mount [ mount-point-directory-name ] ] ] Description The drmexgbackup command ba
Option Database to be backed up The target file type is fixed Exchange Server Information Store File to be backed up Data files *.edb Transaction log files *.log Checkpoint files *.chk Arguments -mode vss Specify this option to perform a backup by using VSS. To use this option, the Protection Manager service must be running on the backup server. -target storage-group-names Specify this option to back up the database resources containing the specific storage group.
Always specify this option when backing up from a primary volume to a secondary volume on the remote side. If this option is omitted, the secondary volume on the local side is backed up. If you omit name-identifying-the-generation, the secondary volume that has the smallest value among the generation numbers on the remote-side becomes the backup destination. In this case, the generation number is remote_n, where n is the smallest generation number.
in double quotation marks ("). If the backup-comment string contains a special character but is not enclosed in double quotation marks, the special character is not properly handled as a part of the backup-comment string and is parsed as a special character. The following special characters cannot be used for backup comments: \ / ` | < > " * ? & ; ( ) $ Note that the first character must not be a hyphen (-).
When you specify the -cascade option, a backup catalog is automatically transferred to a backup server defined in the cascade configuration information definition file. The backup catalog is transferred to a backup server on both the local site and the remote site. -auto_mount mount-point-directory-name Specify this option to automatically mount a secondary volume on a backup server after backing up a volume.
If you specify the -rc option concurrently with this option, and the generation identifier specified in the -rc option and the generation number at the remote side are different, an error occurs. If you specify the -script option concurrently with this option, a user script file specified in the -script option needs to exist on both the local site and remote site.
Storage-group-name = STR3 KAVX0002-I The drmexgbackup command will now end. • In this example, the command is used to use VSS for backup: PROMPT> drmexgbackup -mode vss KAVX0001-I Starting the drmexgbackup command. KAVX0256-I Connecting to the Protection Manager Service is performed. Host name = BackupServer KAVX1600-I Backup processing will now start. KAVX1610-I Verification of the database on the backup server will now be performed.
• To perform an online backup using VSS in an Exchange Server 2010 configuration: PROMPT> drmexgbackup –mode vss KAVX0001-I The drmexgbackup command will now start. KAVX0256-I A connection to the Protection Manager service will now be established. Host name = BackupServer1 KAVX1600-I Backup processing will now start. KAVX5108-I Resynchronizing a copy group. Copy group name = EXG001,B001 KAVX5108-I Resynchronizing a copy group. Copy group name = EXG001,B002 KAVX5108-I Resynchronizing a copy group.
Displayed item Meaning BACKUP-ID Backup ID BACKUP-MODE Backup mode ORIGINAL-ID Original backup ID obtained by the drmexgbackup command START-TIME Start time of a backup END-TIME End time of a backup HOSTNAME Name of the server where the snapshot backup was performed Object type: M: Mailbox store T P: Public folder store T: Transaction log file C: Checkpoint file A type of Exchange Server object and its name: MAILBOXSTORE: Mailbox store name PUBLICSTORE: Public folder store name OBJECT TRANS
Displayed item Meaning LDEV# Logical device number inside the RAID device A letter identifying the primary or secondary volume: P: Primary volume P/S S: Secondary volume SERIAL# Serial number inside the RAID device VIRTUAL-SERVERNAME#3 Virtual server name (value of the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable) DB-PATH#3 Name of the directory storing the backup catalog CATALOG-UPDATE-TIME#3 Time when the backup catalog was created #1 The display format of information about transaction log files (*.
storage groups or Information Stores for which information is to be displayed. The target definition file containing the list of storage groups or Information Stores must be created before you use this option. Use an absolute path to specify the target definition file. -transact_log Specifies that only information relating to the transaction log file that will be displayed.
• Virtual server name (value of the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable) If the DRM_HOSTNAME environment variable has not been set, a hyphen (-) appears. • Time when the backup catalog was created For each backup ID, displays the time when the backup catalog was created. -backup_id backup-ID Specify this option to display only the backup information of a specific backup ID. A backup ID uniquely identifies backup data and is registered in the backup catalog during backup processing.
M T C MAILBOXSTORE TRANSACT CHECKPOINT mail - N:\data\mail.edb M:\log\E01*.log M:\log\E01.
C CHECKPOINT VG01,VG01_000 Mail2 Harddisk2 VG01,VG01_000 - VG01,VG01_000 P PUBLICSTORE Pub Harddisk5 - T TRANSACT VG01,VG01_003 VG01,VG01_003 Pub Harddisk4 VG01,VG01_002 - VG01,VG01_002 C CHECKPOINT Pub Harddisk4 - - VG01,VG01_002 VG01,VG01_002 M:\mount\VG01\000\Mail2\E01.chk M:\mount\VG01\000 - - M:\mount\VG01\003\Pub\pub.edb M:\mount\VG01\003 - - M:\mount\VG01\002\Pub\E02*.log M:\mount\VG01\002 - - M:\mount\VG01\002\Pub\E02.
To update the dictionary map files to the latest status (Exchange Server 2010 or Exchange Server 2013): drmexgdisplay [ Information-Store-name ] -refresh [ -coremap ] Description The drmexgdisplay command does the following: 1. 2. 3. Displays resource information for the Exchange database or Information Stores on the server on which the command was executed. Displays resource information for the specified Exchange database in the system in which the command was executed.
Displayed item Meaning LVM-DEVICE A logical device file name (when using a logical volume manager) or a GUID (when logical volume manager has not been implemented) DEVICE#2 Harddiskn (where n is an integer) COPY-GROUP The copy group name, displayed as follows: RAID-Manager-volume-group-name,paired-volume-name PORT# Port name on the host server TID# Target-ID on the host server LUN# Logical unit number on host server MU# Pair ID LDEV# Logical device number inside the RAID device A letter ide
The display format of information about transaction log files (*.log) depends on the Exchange Server version. Exchange Server 2007: Information for all files is displayed together in the following format: mount-point-directory-name\storage-group-name\E00*.log. Exchange Server 2010 or Exchange Server 2013: Information for all files is displayed together in the following format: mount-point-directory-name\Information-Store-name\E00*.log.
When you specify this option with the -target option or -f option, only information pertaining to the transaction log of the specified storage group or Information Store will be displayed when this option is specified. If either the -target or the -f option is omitted, information pertaining to all transaction logs of all storage groups or Information Stores will be displayed. -datafile Specifies that only information relating to the data file will be displayed.
Information-Store-name Use this option with the -refresh option to specify the Information Store for which the dictionary map files are to be updated. -refresh Specify this option to update the dictionary map files. If you specify this option with storage-group-name or Information-Store-name, only the information about the specified storage group or Information Store in the application map file will be updated.
T TRANSACT Harddisk16 - C CHECKPOINT Harddisk16 - - EXG,EXG_001 EXG,EXG_001 EXG,EXG_001 EXG,EXG_001 D:\mount\EXG_002\log1\E00*.log D:\mount\EXG_002 - - - - D:\mount\EXG_002\system1\E00.
T C - - - TRANSACT Harddisk4 CHECKPOINT Harddisk4 Harddisk6 Harddisk7 - VG01,VG01_003 Pub VG01,VG01_002 VG01,VG01_002 Pub VG01,VG01_002 VG01,VG01_002 VG01,VG01_004 VG01,VG01_004 VG01,VG01_005 VG01,VG01_005 - - M:\mount\VG01\002\Pub\E02*.log M:\mount\VG01\002 - - M:\mount\VG01\002\Pub\E02.
To restore backup data in units of Information Stores (Exchange Server 2010 or Exchange Server 2013): drmexgrestore backup-ID -resync [ -target Information-Store-name,… | -f target-definition-file-name ] [ -force ] [ -recovery ] [ -pf copy-parameter-definition-file ] [ -vf VSS-definition-file-name] [ -ef Exchange-environment-setting-file-name ] Description The drmexgrestore command performs from the secondary volume, use disk resynchronization to restore the backup data specified by the backup ID to the pr
Arguments backup-ID Specify the backup ID of the backup data to be restored. The backup ID is used to uniquely identify backup data, and is registered in the backup catalog during backup. To check a backup ID, execute the drmexgcat command. -resync Specify this option to resynchronize the primary and secondary volumes for restoration. Backup data on the secondary volume is synchronized to the primary volume.
With this option, forced resynchronization is performed if the copy group name of the primary volume obtained when backup processing was performed on the database server matches the information on the database server, even though the LDEV and SERIAL numbers do not match the LDEV and SERIAL numbers when backup processing was performed. Specify this option only if restoration by resynchronization could not be performed with the -resync option, such as when the LDEV number changes when the volume is replaced.
The specified Exchange environment settings file must be stored in the following folder: Application-Agent-installation-folder\conf\exchange If this option is omitted, the default value is used. For details about the Exchange environment settings file, see the HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI User Guide. NOTE: The backup information in the backup catalog is managed based on using the copy group as a key.
KAVX1806-I The information store will now be mounted. Storage group name = STR1 KAVX0002-I The drmexgrestore command will now end. • In this example, the command is used to restore, by disk resynchronization, the backup data identified by the backup ID 0000000003, and then performs roll-forward recovery: PROMPT> drmexgrestore 0000000003 -resync -recovery KAVX0001-I The drmexgrestore command will now start. KAVX1805-I The information store will now be dismounted.
KAVX1734-I The replication function of Exchange Server has resumed. Storage group name = STR2 KAVX0002-I The drmexgrestore command will now end. PROMPT> • In this example, the command is used to restore, by disk resynchronization, the backup data identified by the backup ID 0000000005 (backup is created for Mail01 and Mail02) with the seed function enabled in a Exchange Server 2010 DAG configuration. It then performs a pointin-time recovery: PROMPT> drmexgrestore 0000000005 –resync –ef exchange.
KAVX1755-I The replication function of Exchange Server has resumed. Exchange Server name = DatabaseServer2 Information store name = Mail01 KAVX1757-I Seed processing will now start. Exchange Server name = DatabaseServer2 Information store name = Mail02 KAVX1758-I Seed processing has finished. Exchange Server name = DatabaseServer2 Information store name = Mail02 KAVX1755-I The replication function of Exchange Server has resumed.
Example • In this example, the command is used to verify the backup data whose backup ID is 0000000001: PROMPT> drmexgverify 0000000001 KAVX0001-I The drmexgverify command will now start. KAVX0076-I The checksum of the Exchange database file was confirmed. Storage group name = STR1 KAVX0002-I The drmexgverify command will now end.
Basic commands
3 Support and other resources Numerous support options are available. Contacting HP HP technical support For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website: http://www.hp.
Conventions This guide follows the conventions shown in Table 49 to refer to HP XP7 products.
Product reference Full name or meaning This abbreviation is used when it is not necessary to distinguish the following products: • Continuous Access Synchronous Continuous Access Synchronous • Continuous Access XP Synchronous • P9000 Continuous Access Synchronous • XP Continuous Access Synchronous • XP7 Continuous Access Synchronous This abbreviation is used when it is not necessary to distinguish the following products: Data Retention Utility • Data Retention Utility • LUN Security XP Extension • XP D
Product reference Full name or meaning This abbreviation is used when it is not necessary to distinguish the following products: • LUN Configuration and Security Manager XP (Virtual LVI) Open Volume Management • Open Volume Management • Security Manager XP • XP Data Shredder • XP Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) This abbreviation is used when it is not necessary to distinguish the following products: • RAID Manager RAID Manager • RAID Manager XP • XP RAID Manager • XP7 RAID Manager This abbreviation is used when
Index B basic command functionality concealing and revealing physical volume, 115 create and delete Application Agent database, 142 basic command path , 81 basic commands drmappcat, 103 drmcgctl, 106 drmclusinit, 108 drmdbexport, 112 drmdbimport, 113 drmdbsetup, 141 drmdevctl, 114 drmexgbackup, 184 drmexgcat, 192 drmexgdisplay, 198 drmexgrestore, 205 drmexgverify, 212 drmfsbackup, 84 drmfscat, 89 drmfsdisplay, 95 drmfsrestore, 99 drmhostinfo, 120 drmmediabackup, 124 drmmediarestore, 126 drmmount, 128 drmre
C check tool EX_DRM_EXG_DEF_CHECK, 69 EX_DRM_FS_DEF_CHECK, 20 EX_DRM_SQL_DEF_CHECK, 53 coding rules for creating transaction log target definition file, 82 common commands basic command specifications, 103 extended command specifications, 25 conceal and reveal physical volume , conventions for creating target definition file, 81 create and delete Application Agent database , 141 D data file (for SQL Server database), 49, 144 displaying information for Information Store, 198 displaying information for stora
extended commands EX_DRM_BACKUPID_SET, 25 EX_DRM_CACHE_PURGE, 36 EX_DRM_CG_DEF_CHECK, 26 EX_DRM_DB_EXPORT, 27 EX_DRM_DB_IMPORT, 28 EX_DRM_EXG_BACKUP, 63 EX_DRM_EXG_DEF_CHECK, 68 EX_DRM_EXG_RESTORE, 71 EX_DRM_EXG_VERIFY, 76 EX_DRM_FS_BACKUP, 15 EX_DRM_FS_DEF_CHECK, 20 EX_DRM_FS_RESTORE, 22 EX_DRM_FTP_GET, 29 EX_DRM_FTP_PUT, 31 EX_DRM_HOST_DEF_CHECK, 32 EX_DRM_MOUNT, 39 EX_DRM_RESYNC, 34 EX_DRM_SQL_BACKUP, 48 EX_DRM_SQL_DEF_CHECK, 53 EX_DRM_SQL_RESTORE, 56 EX_DRM_SQL_TLOG_BACKUP, 59 EX_DRM_SQLFILE_EXTRACT, 61