HP P9000 Command View Advanced Edition Suite Software 7.3.1-00 Administrator Guide (web)
Table Of Contents
- Administrator Guide (Web Version)
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 System configuration and requirements
- System configuration
- Network security configuration
- Common security risks
- Level 1 security: Setting up a firewall and creating a separate management LAN
- Level 2 security: Placing managed devices behind the firewall and creating a separate management LAN
- Level 3 security: Dual-homed management servers and creating a separate management LAN
- Level 4 security: A flat network
- Management server requirements
- Host requirements
- Related products
- System requirements for managing copy pairs
- System configuration for managing copy pairs
- System configuration for managing copy pairs: Local management
- System configuration for managing copy pairs: Using a pair management server
- System configuration for managing copy pairs: Using a virtual command device server
- System configuration for managing copy pairs: Using an SVP (when defining copy pairs in a configuration definition file)
- System configuration for managing copy pairs: Using an SVP (when defining copy pairs as a device group)
- Device Manager agent requirements for managing copy pairs
- Storage system requirements for managing copy pairs
- Notes on using Device Manager when RAID Manager is already managing copy pairs
- System configuration for managing copy pairs
- 2 Network configuration
- Port settings
- Ports used by P9000 Command View AE Suite products
- Changing ports used by Common Component
- Changing the 23015/tcp port used by Common Component
- Changing the 23016/tcp port used by Common Component
- Changing the 23017/tcp port used by Common Component
- Changing the 23018/tcp port used by Common Component
- Changing the 23025/tcp port used by Common Component
- Changing the 23026/tcp port used by Common Component
- Changing the 23031/tcp port used by Common Component
- Changing the 23032/tcp port used by Common Component
- Registering firewall exceptions
- Network settings for management servers with multiple NICs
- Device Manager settings in IPv6 environments
- Changing the IP address or host name of the management server
- Changing the URL for accessing P9000 Command View AE Suite products
- Port settings
- 3 User account management
- 4 Security
- 5 Configuring Device Manager for use with related products
- 6 Setting up logs and alerts
- 7 Configuring Device Manager for CIM/WBEM
- Device Manager and CIM/WBEM
- CIM/WBEM functions in Device Manager
- Enabling CIM/WBEM functions
- Setting up ports used by CIM/WBEM
- Verifying properties for executing CIM
- Configuring service discovery
- Configuring performance information acquisition
- User account settings for using the CIM/WBEM functions
- 8 Setting up a cluster environment
- Verifying the management server environment
- Setting up a cluster environment
- Installing P9000 Command View AE Suite on cluster management servers (new installation)
- Installing P9000 Command View AE Suite on cluster management servers (upgrade or overwrite)
- Changing the management server environment from a non-cluster environment to a cluster environment
- Removing P9000 Command View AE Suite from a cluster
- 9 Starting and stopping services
- 10 Managing the database
- Managing databases
- Backing up databases
- Restoring databases
- Migrating databases
- 11 Using and maintaining the Device Manager agent
- Before using the Device Manager agent
- When to restart the Device Manager agent service
- Specifying the IP address of the Device Manager agent network adapter
- Applying storage system configuration changes to Device Manager server
- Reinstalling the Device Manager agent after a host OS upgrade
- Device Manager agent in a Windows host environment
- Device Manager agent in an AIX host environment
- Device Manager agent in a Linux host environment
- Setting up the Device Manager agent
- Setting Device Manager server information in Device Manager agent
- Automatically reporting host information to the Device Manager server
- Managing copy pairs
- Changing the Java execution environment
- Changing the user who executes the Device Manager agent service
- Property settings for hosts that manage 100 or more LUs
- Device Manager agent operations
- Configuration definition file for managing copy pairs
- Prerequisites for using a configuration definition file in Device Manager
- Parameters and requirements for the configuration definition file
- Detailed rules for configuration definition files
- Notes about creating a configuration definition file
- Required operations when creating or changing a configuration definition file
- Note about deleting copy pairs
- Device Manager agent commands
- Before using the Device Manager agent
- 12 Setting up Host Data Collector
- Installing Host Data Collector
- Prerequisites for installing Host Data Collector (Windows)
- Installing Host Data Collector (Windows)
- Prerequisites for installing Host Data Collector (Solaris or Linux)
- Installing Host Data Collector (Solaris or Linux)
- Notes on using Host Data Collector computers in a cluster configuration
- Registering a Host Data Collector computer on the management server
- Specifying the Host Data Collector environment settings
- Removing Host Data Collector
- Installing Host Data Collector
- 13 Troubleshooting
- Common problems and solutions
- Maintenance information that must be collected if a failure occurs
- Acquiring maintenance information on the management server
- About acquiring maintenance information on a Host Data Collector computer
- Acquiring maintenance information on a host (for a host managed by Host Data Collector)
- Acquiring maintenance information on a host (for a host managed by Device Manager agent)
- Acquiring a thread dump of the HBase Storage Mgmt Common Service (Windows)
- Acquiring a thread dump of the HCS Device Manager Web Service (Windows)
- Acquiring a thread dump of the HBase Storage Mgmt Common Service (Linux)
- Acquiring a thread dump of the HCS Device Manager Web Service (Linux)
- Checking audit log data
- 14 Support and other resources
- A Device Manager server properties
- Device Manager server property files
- Device Manager server configuration properties (server.properties file)
- server.http.host
- server.http.port
- server.https.port
- server.rmi.port
- server.http.entity.maxLength
- server.base.home
- server.horcmconfigfile.hostname
- server.base.initialsynchro
- server.cim.agent
- server.cim.support
- server.cim.support.job
- server.cim.support.protocol
- server.cim.http.port
- server.cim.https.port
- server.configchange.enabled
- server.logicalview.initialsynchro
- server.mail.enabled
- server.mail.from
- server.mail.smtp.host
- server.mail.smtp.port
- server.mail.smtp.auth
- server.mail.errorsTo
- server.eventNotification.mail.to
- server.mail.alert.type
- server.mail.alert.status
- server.subsystem.ssid.availableValues
- server.smisclient.indication.port
- server.agent.differentialrefresh.manual.enabled
- server.agent.differentialrefresh.periodical.enabled
- Device Manager database properties (database.properties file)
- Device Manager log output properties (logger.properties file)
- Device Manager dispatcher properties (dispatcher.properties file)
- server.dispatcher.message.timeout
- server.dispatcher.message.timeout.in.processing
- server.dispatcher.daemon.pollingPeriod
- server.dispatcher.traps.purgePeriod
- server.dispatcher.daemon.receiveTrap
- server.dispatcher.daemon.configUpdate.detection.interval
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.doRefresh
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.type
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.dayOfWeek
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.startTime
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.interval
- server.dispatcher.daemon.configUpdate.detection.variable.enabled
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.performance.doRefresh
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.performance.startTime
- server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.logicalGroup.doRefresh
- Device Manager MIME type properties (mime.properties file)
- Device Manager client properties (client.properties file)
- Device Manager security properties
- Device Manager SNMP trap log output properties (customizedsnmptrap.properties file)
- Properties for communicating with the host (host.properties file)
- Properties for connecting to Host Data Collector (hostdatacollectors.properties file)
- Properties for migrations (migration.properties file)
- Properties for connecting to PA (hppa.properties file)
- Properties for the CIM/WBEM functions (jserver.properties file)
- B Tiered Storage Manager server properties
- Tiered Storage Manager server property files
- Tiered Storage Manager server operations properties (server.properties file)
- server.rmi.secure
- server.rmi.port
- server.rmi.security.port
- server.base.initialsynchro
- server.mail.smtp.host
- server.mail.from
- server.mail.errorsTo
- server.mail.smtp.port
- server.mail.smtp.auth
- server.eventNotification.mail.to
- server.eventMonitoringIntervalInMinute
- server.migration.multiExecution
- server.checkOutVolumeRange
- server.migration.dataErase.defaultValue
- server.migrationPlan.candidateVolumeCountLimit
- server.migrationPlan.candidateCapacityGroupDisplayMaxCount
- server.migration.maxRetryCount
- server.migration.waitForPairDeleteInMinute
- server.migration.remainTimeForDeletePairInMinute
- Tiered Storage Manager GUI properties (client.properties file)
- Tiered Storage Manager database properties (database.properties file)
- Tiered Storage Manager properties for accessing Device Manager server (devicemanager.properties file)
- Tiered Storage Manager log output properties (logger.properties file)
- Tiered Storage Manager security properties
- C Host Data Collector properties
- Host Data Collector property files
- Properties related to Host Data Collector operation (hdcbase.properties file)
- Host Data Collector logger properties (logger.properties file)
- Properties related to the Host Data Collector's Java environment (javaconfig.properties file )
- Host Data Collector configuration properties (alps.properties file)
- Host Data Collector product properties (about.properties file)
- Host Data Collector logger properties (log4jconfig.properties file)
- D Device Manager agent properties
- Device Manager agent property files
- Device Manager agent properties for connecting to the Replication Manager server (agent.properties file)
- Device Manager agent properties for hldutil command operations (hldutil.properties file)
- Device Manager agent log output properties (logger.properties file)
- Device Manager agent properties for program information (programproductinfo.properties file)
- Device Manager agent operations properties (server.properties file)
- server.agent.port
- server.http.localPort
- server.http.port
- server.http.host
- server.http.socket.agentAddress
- server.http.socket.bindAddress
- server.agent.maxMemorySize
- server.agent.shutDownTime
- server.agent.JRE.location
- server.http.entity.maxLength
- server.http.security.clientIP
- server.server.authorization
- server.server.serverIPAddress
- server.server.serverPort
- server.agent.rm.centralizePairConfiguration
- server.agent.rm.cuLdevForm
- server.agent.rm.exclusion.instance
- server.agent.rm.location
- server.agent.rm.optimization.userHorcmFile
- server.agent.rm.horcm.poll
- server.agent.rm.pairDefinitionForm
- server.agent.rm.moduleTimeOut
- server.http.server.timeOut
- server.util.processTimeOut
- server.agent.evtwait.timeout
- server.agent.rm.ignorePairStatus
- E Commands executed by Host Data Collector
- Acronyms and abbreviations
- Index
Information monitored by Device Manager
Device Manager uses the following information to monitor the operating statuses of managed storage
systems:
• Status of each storage system site (default)
Device Manager regularly monitors storage systems to determine if errors have occurred, and then
outputs error information to the GUI or CLI. The error information includes the site and severity of
the error.
• SNMP traps received from storage systems (optional)
When SNMP traps are received, they are displayed in the GUI or CLI as alerts. SNMP traps are
useful for determining the cause of an error, because they include information about the location
of the error in addition to the site of the error.
To receive SNMP traps in Device Manager, you must specify environment settings.
The alerts that Device Manager can monitor differ by storage system. The following table lists the
alerts that can be monitored by different storage systems.
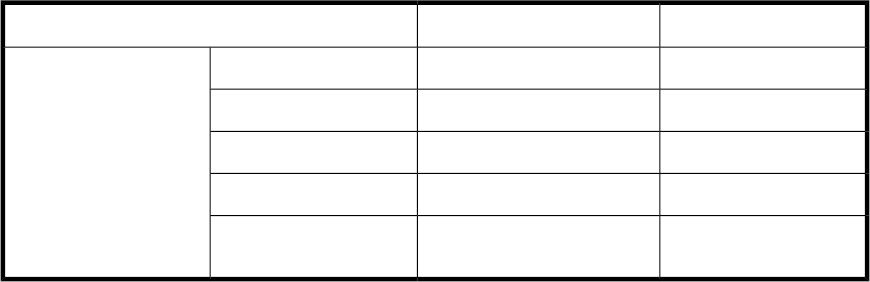
Table 42 Alerts that can be monitored by Device Manager
SNMP trapsStorage system site statusManagement target
YYP9500
Storage system
YYXP24000/XP20000
YYXP12000/XP10000/SVS200
YYXP1024/XP128
----
SMI-S Enabled storage
systems
Legend
Y: Supported
--: Not supported
Required settings for receiving SNMP traps
The following settings must be specified so that Device Manager receives SNMP traps output by
storage systems:
• Device Manager must be able to use port 162/udp of the management server.
• The IP address of the management server must be registered in the SNMP Agent settings for storage
systems as a target for trap notification.
• Specify true for the server.dispatcher.daemon.receiveTrap property.
Receiving email alerts
You can set up Device Manager to automatically send the content of alerts to users by email. This
enables users to be aware of failures that have occurred in storage systems without logging in to the
management client.
The settings required for sending alerts to users by email are described below.
Administrator Guide (Web Version) 133










