HP StorageWorks B-Series Remote Replication Solution Best Practices Guide (5697-6731, June 2007)
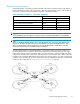
Figure 5 Dedicated bac kbone fabric Me ta SAN
Utilizing a Dedicated Ba ckbone as shown in Figure 5 can solve the backbone fabric scaling and FCIP IP
network issues. By implementing a dedicated backbone fabric, no existing production fabric has the
backbone fabric scaling limitations imposed on it, and generally the number of FC switches and devices
on this dedicated fabric are sm aller and within the current lim i tations.
In a ddition to eliminating the scaling restrictions, when FCIP is used as the SAN extension technology, the
IP network is now part of the backbone fabric rather then any of the individual edge fabrics. Each site
has a piece of the backbone fabric and, if the IP network g oes down, the edge fabrics will only see a
Registered State Change Notification (RSCN) rather than the fabric transition the edge fabric would see if
the IP network were a part of that edge fabric.
The MP Router por tion of the backbone fabric at each site could also contain c om mon devices s h ared
between multiple edge fabrics at that site. For example, if Site #1 had several edge fabrics and wanted
to share a tape library system, the tape subsystem could be placed on the MP Router that is the interface
tothebackbonefabricforthesite’sedgefabrics.
Figure 6 Dedica ted backbone fabric wit h common devices
Sample topologies and configurations
The following includes configu rations that use the HP StorageWorks 400 MP Router and/or the MP
Router blade for implementing a FCIP disaster recovery solution. The configuration concepts from the
previous section are discussed in context with these configurations.
400 MP Router and MP Router blade fabric architecture
There are four proven SAN extension solutions that can be implemented with various director/switch/router
combinations, depending on the size of the SAN and the availability level required:
• 2–fabric architecture: used for smaller SANs with lower throughput and connectivity levels
• 4–fabric architecture: used for smaller SANs, providing higher availability than the 2–fabric
solution.
• 5–fabric architecture : used when larger scalability is required, and for I/O write-intensive
situations
22
Solution setup overview