HP 3PAR InForm OS 3.1.1 Concepts Guide
11 Reclaiming Unused Space
Overview
The InForm OS space consolidation features allow you to change the way that virtual volumes are
mapped to logical disks in a Common Provisioning Group (CPG). Moving virtual volume regions
from one logical disk to another enables you to compact logical disks, and free up disk space so
that it can be reclaimed for use by the system. For more information about virtual volumes, see
“Virtual Volumes” (page 43).
Mapping is the correspondence of Logical Disk (LD) regions to the virtual volume regions. Virtual
volumes are made up of multiple logical disks, and each logical disk contains regions that are
mapped to the virtual volume. All types of volumes are created by mapping data from one or more
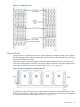
logical disks to the virtual volume. Figure 10 (page 51) shows how data mapped in regions from
logical disks onto a base volume.
Figure 10 Data is mapped from logical disks onto a virtual volume in regions
Logical disks can be shared by multiple virtual volumes. As volumes are deleted or as volume copy
space grows and then shrinks, logical disks can use space less efficiently. When logical disks do
not efficiently use space, the unused space consumes regions on the LD that are not available for
use by the system when creating new logical disks. The space management features enable you
to consolidate used space onto fewer fully-used logical disks so that unused regions are forced
onto one or more logical disks that are then deleted. Deleting these logical disks frees the unused
space for general use by the system. You can also truncate LDs to free up space. The LD’s used
regions are compacted by moving them to the beginning of the LD and then the LD is shortened
so that unused space can be returned to the system’s free chunklet pool.
Reclaiming Unmapped Logical Disk Space from CPGs
Common Provisioning Groups (CPGs) provide a shared pool of logical disk capacity for use by
all virtual volumes that draw space from that pool. See “Virtual Volume Types” (page 43) for a
discussion of volumes that can draw space from a CPG. If volumes that draw from a CPG are
deleted, or if copy space for these volumes grows and then shrinks, the underlying logical disks
in the CPG pool can become less efficient in space usage. One or more logical disks in the CPG
pool may have only a small portion of their regions mapped to existing virtual volumes. However,
the logical disk’s unused regions are not available for use by the volumes mapped to the CPG.
Compacting the logical disk regions mapped to these volumes may recover and free logical disk
space.
Overview 51