Basic Operation Guide 2013/06
Table Of Contents
- Switch Software
- Contents
- 1 Commands found in the Basic Operation Guide
- 2 Getting started
- 3 Using the Menu Interface
- 4 Using the Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Overview
- Accessing the CLI
- Using the CLI
- Return message types with CLI commands
- CLI interactive commands
- CLI control and editing
- 5 Using the HP WebAgent
- 6 Switch memory and configuration
- Overview
- Configuration file management
- Using the CLI to implement configuration changes
- Creating a custom default configuration
- Using the menu and WebAgent to implement configuration changes configuration file
- Zeroization
- Using Primary and Secondary flash image options
- Multiple configuration files
- Display configuration of selected interface
- Automatic configuration update with DHCP Option 66
- 7 Interface access and system information
- 8 Configuring IP addressing
- Overview
- IP configuration
- Loopback interfaces
- IP Preserve: retaining VLAN-1 IP addressing across configuration file downloads
- Configuring a single source IP address
- 9 Software management
- Downloading switch documentation and software from the web
- Viewing or downloading the software manual set
- Downloading software updates for your switch
- Software signing and verification
- Saving configurations while using the CLI
- Important: Best Practices for software updates
- Updating the switch: overview
- Updating the switch: detailed steps
- Rolling back switch software
- Viewing or transferring alternate configuration files
- Downloading switch documentation and software from the web
- Index
6 Switch memory and configuration
Overview
This chapter describes:
• How switch memory manages configuration changes
• How the CLI implements configuration changes
• How the menu interface and WebAgent implement configuration changes
• How the switch provides software options through primary/secondary flash images
• How to use the switch’s primary and secondary flash options, including displaying flash
information, booting or restarting the switch, and other topics
Configuration file management
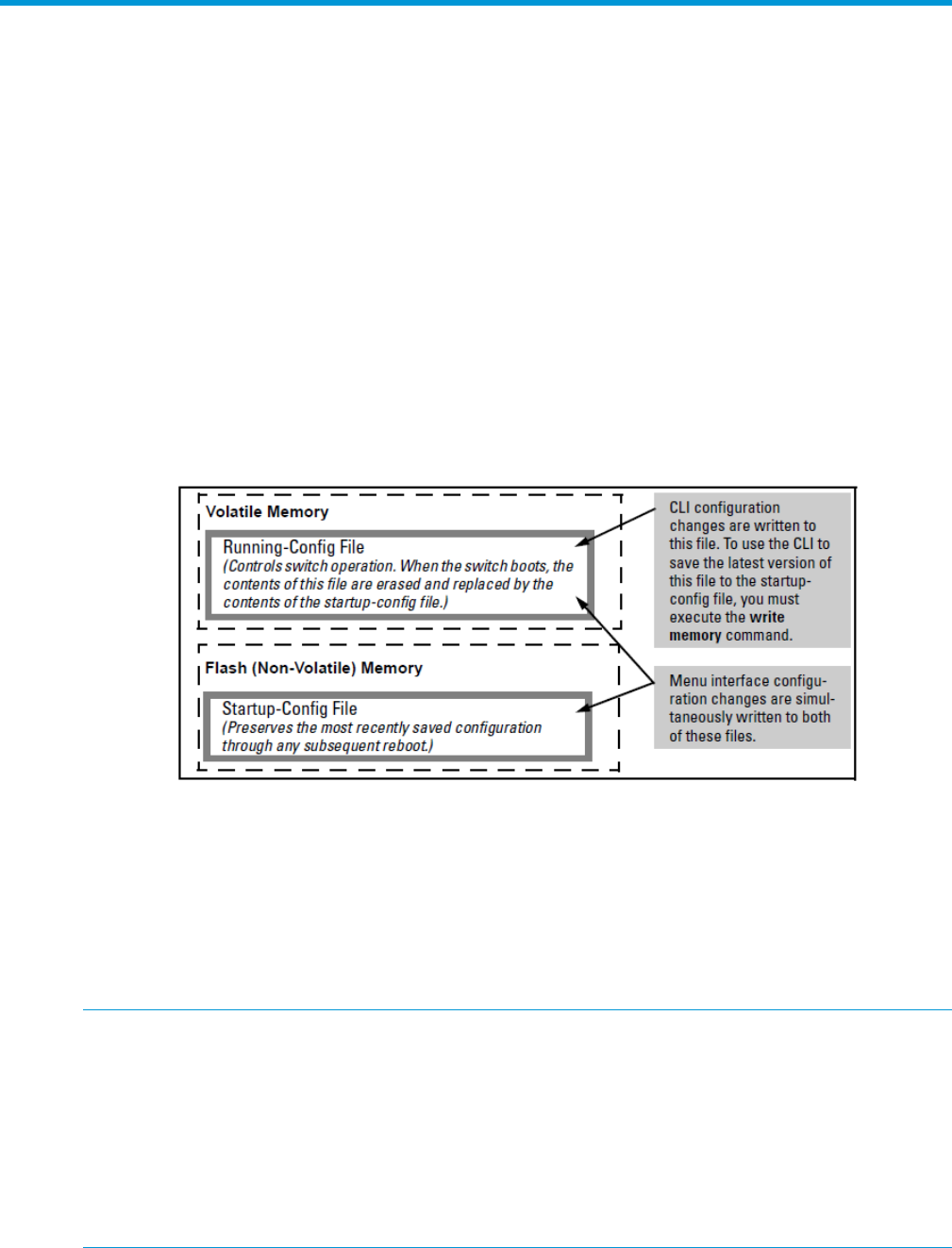
The switch maintains two configuration files, the running-config file and the startup-config file.
Figure 13 Conceptual illustration of switch memory operation
• Running Config File: Exists in volatile memory and controls switch operation. If no configuration
changes have been made in the CLI since the switch was last booted, the running-config file
is identical to the startup-config file.
• Startup-config File: Exists in flash (non-volatile) memory and is used to preserve the most
recently-saved configuration as the “permanent” configuration.
Booting the switch replaces the current running-config file with a new running-config file that is an
exact copy of the current startup-config file.
NOTE: Any of the following actions boots the switch:
• Executing the boot or the reload command in the CLI
• Executing the boot command in the menu interface
• Pressing the Reset button on the front of the switch
• Removing, then restoring power to the switch
For more on reboots and the switch’s dual-flash images, refer to “Using Primary and Secondary
flash image options” (page 64).
Options for saving a new configuration. Making one or more changes to the running-config file
creates a new operating configuration. Saving a new configuration means to overwrite (replace)
the current startup-config file with the current running-config file. This means that if the switch
50 Switch memory and configuration










