Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager Software Users Guide for AIX (7.6)
Table Of Contents
- User Guide for AIX®
- Contents
- Preface
- Overview of HDLM
- HDLM Functions
- Devices Managed by HDLM
- System Configuration
- LU Configuration
- Program Configuration
- Position of the HDLM Driver and hdisk
- Distributing a Load Using Load Balancing
- Performing Failovers and Failbacks Using Path Switching
- Monitoring intermittent errors (functionality when automatic failback is used)
- Detecting errors by using path health checking
- Distributing a Load by Using the Dynamic I/O Path Control Function
- Error management
- Collecting Audit Log Data
- Integrated HDLM management using Global Link Manager
- Cluster support
- Creating an HDLM Environment
- HDLM System Requirements
- Flow for Creating an HDLM Environment
- Types of HDLM Installation
- Notes on Creating an HDLM Environment
- Installing HDLM
- Available Installation Methods
- Preparations for a New Installation of HDLM
- Performing a New Installation of HDLM
- Preparations for an Upgrade Installation or Re-installation of HDLM
- Performing an Upgrade Installation or Re-installation of HDLM
- Migrating from HDLM Version 5.8.1 or Earlier to Version 5.9 or Later
- Installing HDLM in a PowerHA 6.1 Environment
- Installing HDLM in a PowerHA 7.1 Environment
- Performing an Unattended Installation of HDLM
- Checking the Path Configuration
- Setting up HDLM
- Setting up Integrated Traces
- Notes on Using the Hitachi Network Objectplaza Trace Library
- Displaying the Hitachi Network Objectplaza Trace Library setup menu
- Changing the Size of Integrated Trace Files
- Changing the Number of Integrated Trace Files
- Changing the Buffer Size Per Monitoring Interval Duration
- Adjusting the Number of Messages to be Output Per Monitoring Interval
- Finishing the Hitachi Network Objectplaza Trace Library Settings
- Applying the Hitachi Network Objectplaza Trace Library Settings
- About the Reservation Policy
- Settings for Using PowerHA
- Settings for Using GPFS
- Settings for Using Oracle RAC 10g or Oracle RAC 11g
- Settings for Using VCS
- Removing HDLM
- HDLM Operation
- Notes on Using HDLM
- Displaying Path Information
- When a Path Error Is Detected
- Storage System
- Notes on Shutting Down a Host
- Notes on Errors in a Host
- Notes on Enabling Both Primary and Secondary Volumes to Be Viewed From the Same Server
- Notes on an LVM Mirror Configuration
- Notes on When the OS Functionality in Not Available in a Boot Disk Environment
- Notes on Replicating a System
- HDLM Operations Using Commands
- Notes on Using Commands
- Viewing Path Information
- Changing the Status of Paths
- Viewing LU Information
- Displaying the Correspondences Between hdisks, OS Management Path IDs, and LDEVs
- Initializing Statistical Information for Paths
- Viewing and Setting Up the Operating Environment
- Viewing License Information
- Updating the License
- Viewing HDLM Version Information
- Viewing HDLM Component Information
- Starting and Stopping the HDLM Manager
- HDLM Resident Processes
- Changing the Configuration of the HDLM Operating Environment
- Notes on Using HDLM
- Troubleshooting
- Command Reference
- Overview of the HDLM Command dlnkmgr
- clear (Returns the Path Statistics to the Initial Value)
- help (Displays the Operation Format)
- offline (Places Paths Offline)
- online (Places Paths Online)
- set (Sets Up the Operating Environment)
- view (Displays Information)
- add (Adds a Path Dynamically)
- delete (Deletes a Path Dynamically)
- Utility Reference
- Overview of the Utilities
- DLMgetras Utility for Collecting HDLM Error Information
- dlmchpdattr Utility for Changing HDLM Default Settings
- dlmgetrasinst Utility for Collecting HDLM Installation Error Information
- dlminstcomp Utility for HDLM Component Installation
- dlmmigsts Utility for Assisting HDLM Migration
- dlmodmset Utility for Setting the HDLM Execution Environment ODM
- dlmpostrestore Utility for HDLM Restoration Support
- dlmpr Utility for Clearing HDLM Persistent Reservation
- dlmpremkcd Utility for Preparing for a System Backup
- dlmpreremove Utility for Executed Before Removing HDLM
- dlmrmdev Utility for Deleting HDLM Drivers
- dlmrmprshkey Utility for Clearing HDLM Persistent Reservation (Shared-Host Methodology)
- installhdlm Utility for Installing HDLM
- installux.sh Utility for HDLM Common Installer
- Messages
- Before Viewing the List of Messages
- KAPL01001 to KAPL02000
- KAPL03001 to KAPL04000
- KAPL04001 to KAPL05000
- KAPL05001 to KAPL06000
- KAPL06001 to KAPL07000
- KAPL07001 to KAPL08000
- KAPL08001 to KAPL09000
- KAPL09001 to KAPL10000
- KAPL10001 to KAPL11000
- KAPL11001 to KAPL12000
- KAPL13001 to KAPL14000
- KAPL15001 to KAPL16000
- Return Codes for Hitachi Command Suite Common Agent Component
- Functional Differences Between Versions of HDLM
- Differences Between HDLM Version 5.9 or Later and Version 5.8.1 or Earlier
- Add-in HDLM Driver Module
- Simplifying the HDLM Environment Configuration and Operation Procedures by Changes to the Logical Device Files
- Changing the HDLM Environment Configuration and Operation Procedures by Changes to the Logical Device Files
- Migrating Reservation Control Settings
- Support for a Boot Disk Environment
- About Settings when Upgrading the OS
- Changing a Virtual I/O Server's Method of Recognizing Virtual SCSI Disks
- Acronyms and abbreviations
- Glossary
- Index
value will take effect after the next automatic failback successfully
completes. When intermittent error monitoring is not being
performed, the number of errors that determine that an intermittent
error has occurred is not counted and this value is not changed.
The number of times that the error is to occur is stored in the system,
even when -iem off is specified and intermittent error monitoring is
disabled. Therefore, when you re-enable intermittent error monitoring
without specifying the number of times, the error monitoring will be
executed using the value stored in the system.
When the set -iem on operation is executed during error monitoring,
even though you do not change the conditions for intermittent error
monitoring, the number of errors and the time that has passed since the
error monitoring has started are reset to 0. Intermittent error monitoring
will then resume with the changed settings.
If you set the automatic failback function to off while intermittent error
monitoring is on, intermittent error monitoring will be disabled. Note,
however, that if you use the view -sys operation to display the HDLM
functionality configuration, Intermittent Error Monitor will be shown as
on. When the automatic failback function is returned to on, intermittent
error monitoring will once again be enabled.
The executable operations for the automatic failback function and
intermittent error monitoring depend on the settings for those functions.
The table below shows the relationship between the settings and available
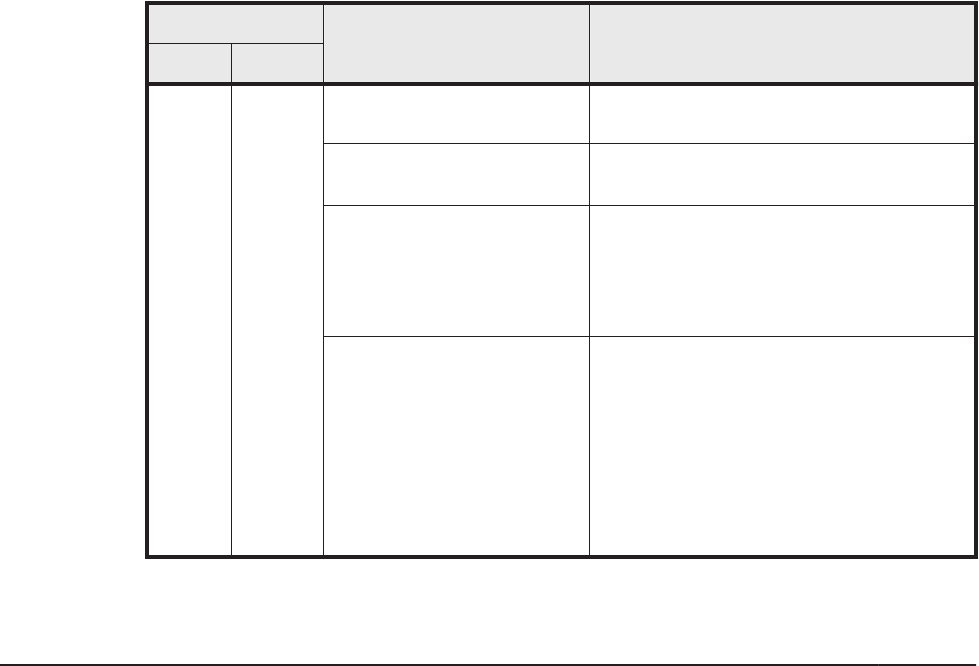
operations for automatic failback and intermittent error monitoring.
Table 6-5 Relationship Between the Setting for the Automatic Failback
Function and Intermittent Error Monitoring and the Executable Operations
Setting
Available operation Result of operation
AFB IEM
on on
Set AFB to on. The operations of AFB and IEM do not
change.
Change the AFB setting. AFB is performed under the new
settings.
#1
Set AFB to off. • AFB and IEM are disabled.
• The error count, elapsed monitoring
time, and information about paths
not subject to automatic failback
are cleared.
Set IEM to on. • When a path is being monitored
(during a period of conditional
intermittent error monitoring), the
value of the error count and the
elapsed monitoring time are reset to
0, and then intermittent error
monitoring will restart.
• When a path is not being
monitored, nothing changes.
6-26
Command Reference
Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager User Guide for AIX
®










