HP FutureSmart - Preventing cross site request forgery (CSRF) attack using CSRF-tokens (white paper)
6
Impact on Software Tools and Solutions
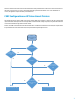
Any web client, whether it is an embedded solution hosted on the device or an external software, will be impacted by the
CSRF security measures when enforced by the device. All HTTP POST requests will be scrutinized by the Embedded Web
Server for CSRF vulnerability (when the CSRF Protection is enforced). If the POST request fails the vulnerability check,
the requests will be rejected with HTTP error code 403. This will break the solutions installed on the device. If such a
request is originating from an external software client, the software client’s functionality will be broken. The web clients
MUST take measures so that they continue to work when CSRF protection if enforced on the device.
Here is what is expected from the solutions and software tools
I. Client MUST have a valid CSRFToken in the HTTP form data.
II. CSRFTokens are unique per HTTP session. SessionId and Token are a pair. Token needs to be fetched by the
client using GET before the POST.
III. Origin and Referer are not mandatory headers. If the web client is including these headers, it MUST have trusted
host-FQDN.
How to address it in Solutions
When the CSRF Prevention feature is enabled, the EWS within the device will require a CSRFToken parameter to be
present in any HTTP POST request. This CSRFToken must match the value originally provided to the client via a previous
HTTP GET request. There are two ways in which a Level-1 EWS controller may generate a valid CSRFToken parameter.
Using a Velocity Template for EWS Content
If the Level-1 solution is using a Velocity template to render the HTML content for a client’s HTTP GET request, then the
template may simply be modified to reference a new FutureSmart Velocity directive in order to have the CSRFToken
generated. This directive is:
$Security.GetCSRFToken()
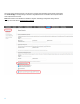
The form input is expected to have the name “CSRFToken”, so in order to generate the complete input tag simply include
the following content within the HTML form definition:
<input type="hidden" id="CSRFToken" name="CSRFToken" value="$Security.GetCSRFToken()" />
Programmatically Generating the CSRF Token
If the Level-1 solution is NOT using Velocity templates to generate content, the CSRF Token may be pulled out of the
IExtHttpSessionState instance of the ExtContext. Specifically, when executing on a FW version that supports the CSRF
Prevention feature, the CSRF token will present in the session data. The following code demonstrates one mechanism in
which it can be pulled out of the header for subsequent use in generating HTML content to return to the client: