User's Manual
ZONESCAN net 22 / 56
Version 1.4
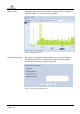
For leakage noise monitoring, the quietest noise detected in the observed
period is of particular interest. It is the smallest dB value for which a
measurement value exists. Because a leakage noise is always present,
one assumes that this value most likely characterizes the leakage noise,
while higher dB sound intensity values arise from the addition of primarily
random noise sources (e.g., vehicle traffic).
The so-determined smallest sound intensity value, found at the left edge of
the histogram curve, is referred to as the dB-min value and plays a key role
in the evaluation of the leakage noise.
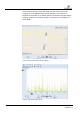
The signal spectrum can be used to make a statement about a possible
leak.
Figure 15 shows a spectrum with electrical influence. If the curve has this
appearance, one can assume that no leakage noise is present.
Figure 15 Spectrum with electrical influence
In Figure 16, you see a typical spectrum of a leakage noise. It is clearly
seen that the curve differs from that of a spectrum with electrical influence.
If the graph has an appearance similar to that shown in Figure 16, one can
assume a leakage noise.
Signal spectrum