Data Sheet
Table Of Contents
- Features
- 1. Pin Configurations
- 2. Overview
- 3. Resources
- 4. About Code Examples
- 5. AVR CPU Core
- 6. AVR Memories
- 7. System Clock and Clock Options
- 7.1 Clock Systems and their Distribution
- 7.2 Clock Sources
- 7.3 Low Power Crystal Oscillator
- 7.4 Full Swing Crystal Oscillator
- 7.5 Low Frequency Crystal Oscillator
- 7.6 Calibrated Internal RC Oscillator
- 7.7 128 kHz Internal Oscillator
- 7.8 External Clock
- 7.9 Clock Output Buffer
- 7.10 Timer/Counter Oscillator
- 7.11 System Clock Prescaler
- 7.12 Register Description
- 8. Power Management and Sleep Modes
- 9. System Control and Reset
- 10. Interrupts
- 11. External Interrupts
- 11.1 Pin Change Interrupt Timing
- 11.2 Register Description
- 11.2.1 EICRA - External Interrupt Control Register A
- 11.2.2 EIMSK - External Interrupt Mask Register
- 11.2.3 EIFR - External Interrupt Flag Register
- 11.2.4 PCICR - Pin Change Interrupt Control Register
- 11.2.5 PCIFR - Pin Change Interrupt Flag Register
- 11.2.6 PCMSK2 - Pin Change Mask Register 2
- 11.2.7 PCMSK1 - Pin Change Mask Register 1
- 11.2.8 PCMSK0 - Pin Change Mask Register 0
- 12. I/O-Ports
- 12.1 Overview
- 12.2 Ports as General Digital I/O
- 12.3 Alternate Port Functions
- 12.4 Register Description
- 12.4.1 MCUCR - MCU Control Register
- 12.4.2 PORTB - The Port B Data Register
- 12.4.3 DDRB - The Port B Data Direction Register
- 12.4.4 PINB - The Port B Input Pins Address
- 12.4.5 PORTC - The Port C Data Register
- 12.4.6 DDRC - The Port C Data Direction Register
- 12.4.7 PINC - The Port C Input Pins Address
- 12.4.8 PORTD - The Port D Data Register
- 12.4.9 DDRD - The Port D Data Direction Register
- 12.4.10 PIND - The Port D Input Pins Address
- 13. 8-bit Timer/Counter0 with PWM
- 13.1 Features
- 13.2 Overview
- 13.3 Timer/Counter Clock Sources
- 13.4 Counter Unit
- 13.5 Output Compare Unit
- 13.6 Compare Match Output Unit
- 13.7 Modes of Operation
- 13.8 Timer/Counter Timing Diagrams
- 13.9 Register Description
- 13.9.1 TCCR0A - Timer/Counter Control Register A
- 13.9.2 TCCR0B - Timer/Counter Control Register B
- 13.9.3 TCNT0 - Timer/Counter Register
- 13.9.4 OCR0A - Output Compare Register A
- 13.9.5 OCR0B - Output Compare Register B
- 13.9.6 TIMSK0 - Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register
- 13.9.7 TIFR0 - Timer/Counter 0 Interrupt Flag Register
- 14. 16-bit Timer/Counter1 with PWM
- 14.1 Features
- 14.2 Overview
- 14.3 Accessing 16-bit Registers
- 14.4 Timer/Counter Clock Sources
- 14.5 Counter Unit
- 14.6 Input Capture Unit
- 14.7 Output Compare Units
- 14.8 Compare Match Output Unit
- 14.9 Modes of Operation
- 14.10 Timer/Counter Timing Diagrams
- 14.11 Register Description
- 14.11.1 TCCR1A - Timer/Counter1 Control Register A
- 14.11.2 TCCR1B - Timer/Counter1 Control Register B
- 14.11.3 TCCR1C - Timer/Counter1 Control Register C
- 14.11.4 TCNT1H and TCNT1L - Timer/Counter1
- 14.11.5 OCR1AH and OCR1AL - Output Compare Register 1 A
- 14.11.6 OCR1BH and OCR1BL - Output Compare Register 1 B
- 14.11.7 ICR1H and ICR1L - Input Capture Register 1
- 14.11.8 TIMSK1 - Timer/Counter1 Interrupt Mask Register
- 14.11.9 TIFR1 - Timer/Counter1 Interrupt Flag Register
- 15. Timer/Counter0 and Timer/Counter1 Prescalers
- 16. 8-bit Timer/Counter2 with PWM and Asynchronous Operation
- 16.1 Features
- 16.2 Overview
- 16.3 Timer/Counter Clock Sources
- 16.4 Counter Unit
- 16.5 Output Compare Unit
- 16.6 Compare Match Output Unit
- 16.7 Modes of Operation
- 16.8 Timer/Counter Timing Diagrams
- 16.9 Asynchronous Operation of Timer/Counter2
- 16.10 Timer/Counter Prescaler
- 16.11 Register Description
- 16.11.1 TCCR2A - Timer/Counter Control Register A
- 16.11.2 TCCR2B - Timer/Counter Control Register B
- 16.11.3 TCNT2 - Timer/Counter Register
- 16.11.4 OCR2A - Output Compare Register A
- 16.11.5 OCR2B - Output Compare Register B
- 16.11.6 TIMSK2 - Timer/Counter2 Interrupt Mask Register
- 16.11.7 TIFR2 - Timer/Counter2 Interrupt Flag Register
- 16.11.8 ASSR - Asynchronous Status Register
- 16.11.9 GTCCR - General Timer/Counter Control Register
- 17. SPI - Serial Peripheral Interface
- 18. USART0
- 18.1 Features
- 18.2 Overview
- 18.3 Clock Generation
- 18.4 Frame Formats
- 18.5 USART Initialization
- 18.6 Data Transmission - The USART Transmitter
- 18.7 Data Reception - The USART Receiver
- 18.8 Asynchronous Data Reception
- 18.9 Multi-processor Communication Mode
- 18.10 Register Description
- 18.11 Examples of Baud Rate Setting
- 19. USART in SPI Mode
- 20. 2-wire Serial Interface
- 21. Analog Comparator
- 22. Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 23. debugWIRE On-chip Debug System
- 24. Self-Programming the Flash, ATmega48
- 25. Boot Loader Support - Read-While-Write Self-Programming, ATmega88 and ATmega168
- 25.1 Features
- 25.2 Overview
- 25.3 Application and Boot Loader Flash Sections
- 25.4 Read-While-Write and No Read-While-Write Flash Sections
- 25.5 Boot Loader Lock Bits
- 25.6 Entering the Boot Loader Program
- 25.7 Addressing the Flash During Self-Programming
- 25.8 Self-Programming the Flash
- 25.8.1 Performing Page Erase by SPM
- 25.8.2 Filling the Temporary Buffer (Page Loading)
- 25.8.3 Performing a Page Write
- 25.8.4 Using the SPM Interrupt
- 25.8.5 Consideration While Updating BLS
- 25.8.6 Prevent Reading the RWW Section During Self-Programming
- 25.8.7 Setting the Boot Loader Lock Bits by SPM
- 25.8.8 EEPROM Write Prevents Writing to SPMCSR
- 25.8.9 Reading the Fuse and Lock Bits from Software
- 25.8.10 Preventing Flash Corruption
- 25.8.11 Programming Time for Flash when Using SPM
- 25.8.12 Simple Assembly Code Example for a Boot Loader
- 25.8.13 ATmega88 Boot Loader Parameters
- 25.8.14 ATmega168 Boot Loader Parameters
- 25.9 Register Description
- 26. Memory Programming
- 26.1 Program And Data Memory Lock Bits
- 26.2 Fuse Bits
- 26.3 Signature Bytes
- 26.4 Calibration Byte
- 26.5 Page Size
- 26.6 Parallel Programming Parameters, Pin Mapping, and Commands
- 26.7 Parallel Programming
- 26.7.1 Enter Programming Mode
- 26.7.2 Considerations for Efficient Programming
- 26.7.3 Chip Erase
- 26.7.4 Programming the Flash
- 26.7.5 Programming the EEPROM
- 26.7.6 Reading the Flash
- 26.7.7 Reading the EEPROM
- 26.7.8 Programming the Fuse Low Bits
- 26.7.9 Programming the Fuse High Bits
- 26.7.10 Programming the Extended Fuse Bits
- 26.7.11 Programming the Lock Bits
- 26.7.12 Reading the Fuse and Lock Bits
- 26.7.13 Reading the Signature Bytes
- 26.7.14 Reading the Calibration Byte
- 26.7.15 Parallel Programming Characteristics
- 26.8 Serial Downloading
- 27. Electrical Characteristics
- 27.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings*
- 27.2 DC Characteristics ATmega48/88/168*
- 27.3 Speed Grades
- 27.4 Clock Characteristics
- 27.5 System and Reset Characteristics
- 27.6 2-wire Serial Interface Characteristics
- 27.7 SPI Timing Characteristics
- 27.8 ADC Characteristics - Preliminary Data
- 27.9 Parallel Programming Characteristics
- 28. Typical Characteristics - Preliminary Data
- 28.1 Active Supply Current
- 28.2 Idle Supply Current
- 28.3 Supply Current of I/O modules
- 28.4 Power-Down Supply Current
- 28.5 Power-Save Supply Current
- 28.6 Standby Supply Current
- 28.7 Pin Pull-up
- 28.8 Pin Driver Strength
- 28.9 Pin Thresholds and Hysteresis
- 28.10 BOD Thresholds and Analog Comparator Offset
- 28.11 Internal Oscillator Speed
- 28.12 Current Consumption of Peripheral Units
- 28.13 Current Consumption in Reset and Reset Pulse width
- 29. Register Summary
- 30. Instruction Set Summary
- 31. Ordering Information
- 32. Packaging Information
- 33. Errata
- 34. Datasheet Revision History
- Table of Contents
162
2545K–AVR–04/07
ATmega48/88/168
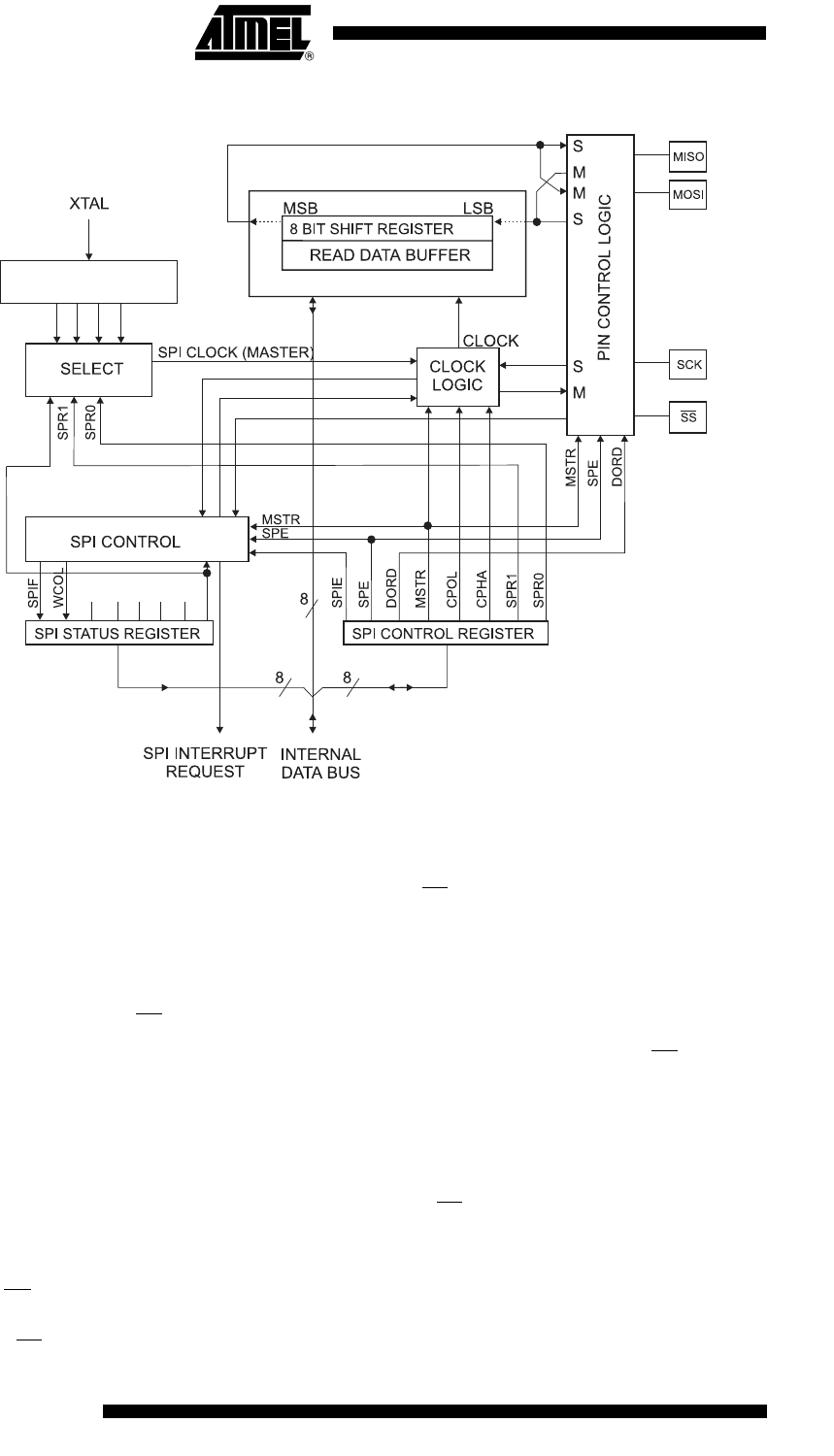
Figure 17-1. SPI Block Diagram
(1)
Note: 1. Refer to Figure 1-1 on page 2, and Table 12-3 on page 78 for SPI pin placement.
The interconnection between Master and Slave CPUs with SPI is shown in Figure 17-2. The sys-
tem consists of two shift Registers, and a Master clock generator. The SPI Master initiates the
communication cycle when pulling low the Slave Select SS
pin of the desired Slave. Master and
Slave prepare the data to be sent in their respective shift Registers, and the Master generates
the required clock pulses on the SCK line to interchange data. Data is always shifted from Mas-
ter to Slave on the Master Out – Slave In, MOSI, line, and from Slave to Master on the Master In
– Slave Out, MISO, line. After each data packet, the Master will synchronize the Slave by pulling
high the Slave Select, SS
, line.
When configured as a Master, the SPI interface has no automatic control of the SS
line. This
must be handled by user software before communication can start. When this is done, writing a
byte to the SPI Data Register starts the SPI clock generator, and the hardware shifts the eight
bits into the Slave. After shifting one byte, the SPI clock generator stops, setting the end of
Transmission Flag (SPIF). If the SPI Interrupt Enable bit (SPIE) in the SPCR Register is set, an
interrupt is requested. The Master may continue to shift the next byte by writing it into SPDR, or
signal the end of packet by pulling high the Slave Select, SS
line. The last incoming byte will be
kept in the Buffer Register for later use.
When configured as a Slave, the SPI interface will remain sleeping with MISO tri-stated as long
as the SS
pin is driven high. In this state, software may update the contents of the SPI Data
Register, SPDR, but the data will not be shifted out by incoming clock pulses on the SCK pin
until the SS
pin is driven low. As one byte has been completely shifted, the end of Transmission
SPI2X
SPI2X
DIVIDER
/2/4/8/16/32/64/128










