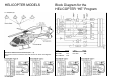
Operation Manual
Throttle and Collective Pitch curves:
Practical Procedure
70 Helicopter
Basic Adjustment
Although the pitch and throttle curves can be set
electronically over a wide range in the mc-1620
transmitter, the hovering point of the helicopter
should be at least approximately correctly preset
mechanically (see introduction). If you pay attention
to the instructions of the respective helicopter kit for
adjusting the controls this is usually the case.
The control of the carburettor must be so adjusted
such that the throttle servo can move during
operation of the throttle control stick, (including both
end positions of the trim lever), over the full travel,
without the carburettor hitting a mechanical stops.
The carburettor must be completely open with the
control stick in the full power position, and with the
control stick and trim at the lower end the carburettor
should be completely closed, without the servo
stalling.
This setting should be achieved as best as possible
mechanically by adjusting the control linkages and
changing of the position on linkages on the servo
and carburettor horns.
Only the remaining small adjustment should
thereafter be made electronically, with the servo
travel setting (“TRV ADJ”, “CH1”). This basic
adjustment is the basis for all further settings and
must therefore be completed as accurately as
possible.
With this basic adjustment the engine should be able
to be started and the idle speed adjusted using the
trim lever.
The model should then with the throttle / collective
pitch control stick in central position, take off and
with the intended RPM hover.
If that is not the case, then one proceeds as follows:
1.) The model takes off only with the stick
above the central position.
a) The rotor RPM is too low
.
Remedy: Using the “TM…” setting open
the carburettor slightly at the stick central
position.
b) The rotor RPM is too high
.
Remedy: Using setting “PM...”, increase of
the blade angle (collective pitch) for the
stick central position.
2.) The model takes off with the stick below the
central position.
a) The rotor RPM is too high
.
Remedy: Using the “TM…” setting close
the carburettor slightly at the stick central
position.
b) The rotor RPM is too low
.
Remedy: Using setting “PM...”, decrease of
the blade angle (collective pitch) for the
stick central position.
WARNING:
A long time should be taken over this setting,
ensuring the model hovers at the correct RPM with
the throttle / collective pitch expensive stick in the
central position. The correct execution the remaining
model parameters is dependent on this!
Climbing Flight Setting
The combination of the options “TM...” (hovering
flight throttle) with “PHN” (maximum collective pitch)
and “PMN” (hovering collective pitch) it makes
possible to achieve problem-free flight from hovering
to maximum climb rate with a constant rotor RPM.
To do this, proceed as follows:
First perform a long vertical climb, with the collective
pitch stick in it’s end position. Whilst doing this the
rotor RPM should not change relative to that during
hovering flight. This is dependent on the power of the
engine and on the model weight. If the rotor RPM
drops in the climb and the carburettor is already
completely open, thus no further increase in output
power is possible, using “PHN” (maximum collective
pitch) reduce the maximum blade angle; with rising
rotor RPM in the climb, increase the value of “PHN”.
If this setting is correct, bring the model back to
hovering flight, which should be achieved with a
central position of the collective pitch stick.
If the stick position for hovering flight has moved
away from centre towards the maximum point,
compensate for this using “PMN” (hovering collective
pitch), by increasing it’s value, until the model hovers
with the stick in the central position. In the opposite
case, with the model hovering with the stick below
the central position, the value of “PMN” is reduced
accordingly. It may also be necessary to reduce the
setting of “TM…” (hovering flight throttle), until an
constant rotor RPM for hovering flight and climb
results.