User's Manual
Table Of Contents
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of the arteries. Systolic pressure occurs when the
heart contracts. Diastolic pressure occurs when the heart expands. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of
mercury (mmHg). One’s natural blood pressure is represented by the fundamental pressure, which is measured
first thing in the morning while one is still at rest and before eating.
What Is Hypertension And How Is It Controlled?
Hypertension, an abnormally high arterial blood pressure, if left unattended, can cause many health problems
including stroke and heart attack. Hypertension can be controlled by altering one’s lifestyle, avoiding stress, and
with medication under a doctor’s supervision. To prevent hypertension or to keep it under control:
• Do not smoke
• Exercise regularly
• Reduce salt and fat intake
• Have regular physical checkups
• Maintain proper weight
Why Measure Blood Pressure At Home?
Blood pressure measured at a clinic or doctor’s
office may cause apprehension and can produce
an elevated reading, 25 to 30 mmHg higher than
that measured at home. Home measurement
reduces the effects of outside influences on blood
pressure readings, supplements the doctor’s
readings and provides a more accurate, complete
blood pressure history.
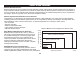
WHO Blood Pressure Classification
Standards to assess high blood pressure, without
regard to age, have been established by the World
Health Organization (WHO), as shown in the chart below.
24
ABOUT BLOOD PRESSURE
Reference Material: Journal of Hypertension 1999, Vol 17 No.2
mmHg
110
105
100
95
90
85
80
Diastolic blood pressure
120 130 140 150 160 170 180
Systolic blood pressure mmHg
Grade 3 hypertension (severe)
Grade 2 hypertension (moderate)
Grade 1 hypertension (mild)
High-normal
Normal
Optimal