Manual
Table Of Contents
- Getting the Most from Your Google Search Appliance
- Contents
- Introduction
- Planning
- Setting Up
- Crawling and Indexing
- Search Experience
- Using Features to Enhance the Search Experience
- Using Front Ends
- Forcing Specific Documents to the Top of Search Results
- Suggesting Alternative Search Terms along with Results
- Grouping Search Results by Topic
- Providing Options for Navigating Search Results
- Displaying Expert Profiles with Search Results
- Providing Real-Time Connectivity to Business Applications
- Integrating Personal Content from Google Apps
- Restricting Search Results
- Controlling Automatic Searching of Synonyms
- Influencing Results Rankings
- Segmenting the Index
- Providing User Results
- Enabling User Alerts
- Displaying Translations of Search Results
- Showing Document Previews in Search Results
- Customizing the User Interface
- Collecting Metrics about User Clicks
- Essentials
- Using the Admin Console
- Using Language Options
- Extending Universal Search
- Monitoring a Search Appliance
- Getting Help
- Quick Reference
- Index
Google Search Appliance: Getting the Most from Your Google Search Appliance Search Experience 47
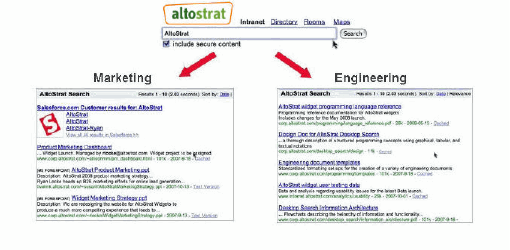
For example, given the search term “AltoStrat,” you might want code or design documents to appear
high in search results for the engineering group, while you might want product specifications to appear
higher for the marketing group. The following figure illustrates two different search results rankings for
the same search term, “AltoStrat.”
Because result biasing is specific to a front end, you can aim result biasing at a specific group of users.
The Google Search Appliance provides three ways for you to influence results ranking:
• Source biasing—For influencing the way that the search appliance documents that belong to a
specified collection, match certain URL patterns., or are fed from a data source..
• Date biasing—For specify the age considerations that should influence a document’s score.
• Metadata and entity biasing—For influencing the way that the search appliance ranks search results
based on metadata or entities associated with documents.
Because increasing the relevancy of specific documents may also decrease the relevancy of others, use
result biasing to boost scores of content sources that you are certain are more authoritative than other
sources.
Setting Up Result Biasing
Set up result biasing by performing the following steps with the Admin Console:
1. Creating a result biasing policy on the Serving > Result Biasing page. A result biasing policy
determines the source biasing, date biasing, and metadata and entity biasing settings that are used
with a front end.










