Manual
Table Of Contents
- Getting the Most from Your Google Search Appliance
- Contents
- Introduction
- Planning
- Setting Up
- Crawling and Indexing
- Search Experience
- Using Features to Enhance the Search Experience
- Using Front Ends
- Forcing Specific Documents to the Top of Search Results
- Suggesting Alternative Search Terms along with Results
- Grouping Search Results by Topic
- Providing Options for Navigating Search Results
- Displaying Expert Profiles with Search Results
- Providing Real-Time Connectivity to Business Applications
- Integrating Personal Content from Google Apps
- Restricting Search Results
- Controlling Automatic Searching of Synonyms
- Influencing Results Rankings
- Segmenting the Index
- Providing User Results
- Enabling User Alerts
- Displaying Translations of Search Results
- Showing Document Previews in Search Results
- Customizing the User Interface
- Collecting Metrics about User Clicks
- Essentials
- Using the Admin Console
- Using Language Options
- Extending Universal Search
- Monitoring a Search Appliance
- Getting Help
- Quick Reference
- Index
Google Search Appliance: Getting the Most from Your Google Search Appliance Crawling and Indexing 26
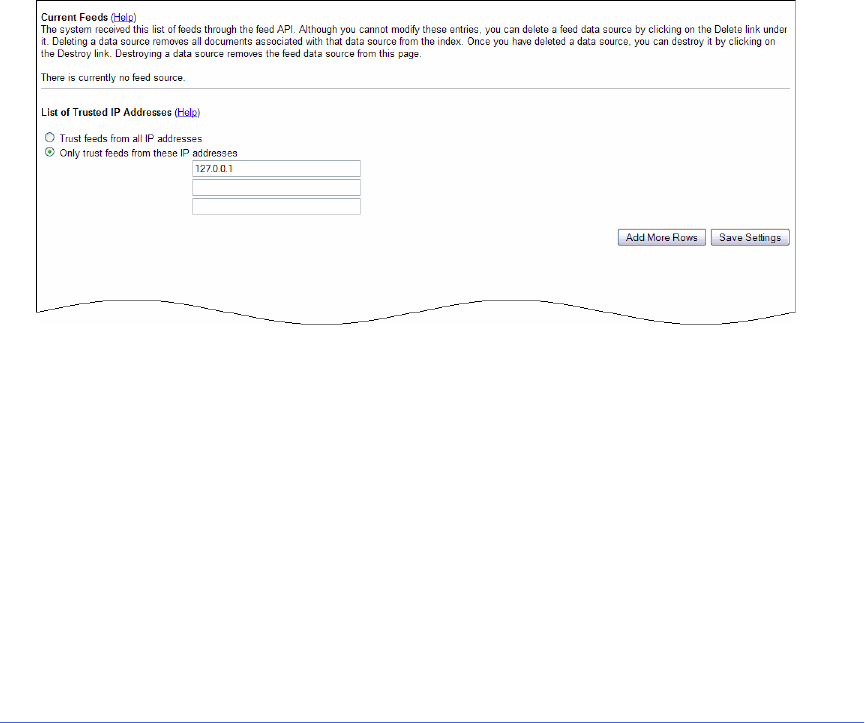
2. Configuring the search appliance to accept the feed by using the Crawl and Index > Feeds page,
shown in the following figure. To prevent unauthorized additions to your index, feeds are only
accepted from machines that are specified on this page.
3. Running the feed client script.
4. Monitoring the feed by using the Admin Console.
5. Checking for search results from the feed within 30 minutes of running the feed client script.
Learn More about Feeds
For complete documentation on feeds, refer to the Feeds Protocol Developer’s Guide.
Indexing Database Content
The Google Search Appliance can also index records in a relational database. The Google Search
Appliance supports indexing of the following relational database management systems:
• IBM DB2
• MySQL
• Oracle
• Microsoft SQL Server
• Sybase
The search appliance provides access to data stored in relational databases by crawling the content
directly from the database and serving the content. The process of crawling a database is called
“synchronizing a database.” To access content in a database, the Google Search Appliance sends SQL
(Structured Query Language) queries using JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) adapters provided by
database companies. It crawls the contents of the database and then pushes records from a database
into the search appliance’s index using feeds.