User manual
32 GFI Backup 2011 Server backups
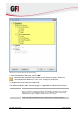
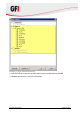
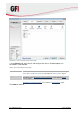
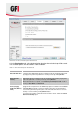
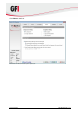
5. In the Options tab, select the compression and encryption settings as well as the type of
backup. The available options are described in Table 11 below.
Table 11 - New server backup task: Options tab
OPTION
DESCRIPTION
No compression
Backup without compressing or encrypting data.
Use ZIP compression
Compress backup data in a single file at the backup destination.
Compression level
Set the Zip compression level. Higher compression ratios result in smaller files,
but backups and restores will take longer to complete.
Self extracting archive
Create an executable file instead of a Zip file. Self extracting archives do not
require any third party tools to access the data within.
Split archives at
Specify value to split backup files in specific sizes. This enables you to split
backups in manageable chunks that can then be stored on space-limited media.
For example, Split archived data in 690Mb backup files which can then be
burned on multiple CD drives.
Compress each file
individually
This option will not create a single compressed file, but will instead compress
each file individually
ZIP password
protection
Password protect the compressed files. This is the faster of the two encryption
methods and provides basic cryptographic security against tampering by
unauthorized individuals. To use this feature, Zip compression is automatically
enabled. Specify a password to be used to encrypt and decrypt data.
AES encryption
Uses a stronger encryption algorithm than ZIP encryption. This is GFI Backup‟s
own implementation of the standard 256-bit AES encryption. To use this feature,
Zip compression is automatically enabled. Specify a password to be used to
encrypt and decrypt data.
Replace Backup (Not
applicable for
Microsoft SQL Server
backups)
The fastest backup type to back up and restore. Only the latest version of
backed up files are retained while older files are overwritten. On restore, you will
not be required to restore a full-backup set and merge the regular increment or
differential files; you will only require restoring only a single set of backup files.
Incremental Backup - Only files and folders created or changed in the
period between backups are backed up. Incremental backups are the
fastest and smallest type of backups, but are less efficient when restoring,
since you must restore the full-backup and then restore, in order of
creation, each subsequent incremental backup.
Differential Backup - Files that are deleted from source are also removed
from the backup.
For information on Microsoft SQL Server backup types, refer to Microsoft SQL
Server backup section within the Server backups chapter.
Stack Backup (Not
applicable for
Microsoft SQL Server
backups)
All selected files and folders are backed up. Stack backups are the most time-
consuming (compared to replace backups) and require substantial storage
capacities. Stacked backups label changed files with different version numbers
that allow restoring older versions of files. You can also specify the number of
backup versions to keep. If this number is exceeded, the oldest version is
deleted when taking a new backup.
For information on Microsoft SQL Server backup types, refer to Microsoft SQL
Server backup section within the Server backups chapter.
Click Next to continue.