Install Manual
Diesel Fuel Systems
Installation Guidelines for Protector Diesel Generators 17
Section 4: Diesel Fuel Systems
General Information
Because diesel fuels are less volatile than gasoline or
gaseous fuels, they are sometimes considered safer.
Due to this perception, careless installation practices can
occur which may lead to serious problems with generator
set performance and reliability.
Periodically inspect and test the system to verify all com-
ponents remain in good working order.
Diesel Fuel Base Tank
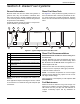
See Figure 4-1. Units provided are typically mounted on
their own base/fuel tank. These are plumbed at the fac-
tory. Tank construction is typically double-wall. The base
tank is the main fuel tank and incorporates the following
items:
Figure 4-1. Typical Integrated Diesel Fuel Base Tank
NOTE: Some fill lines are equipped with overflow con-
tainment.
Some applications require extending the vent line outside
of an enclosure or to outside air along with adequate spill
containment.
Diesel Fuel Recommendations
IMPORTANT NOTE: DO NOT use home heating oil or
bio-diesel fuel.
Use No. 2D diesel fuel when temperatures are above
freezing. When temperatures are below freezing, blend
No. 1D diesel fuel and No. 2D diesel fuel together for a
climate adjusted fuel ratio.
Diesel fuel must also meet the following requirements:
• Sulfur content of 15 parts per million (ppm) maximum.
• Minimum Cetane index of 40.
NOTE: Low ambient temperatures as well as engine
operation at high altitudes may require the use of fuels
with higher Cetane ratings.
Allow at least 5% of tank capacity for fuel expansion. DO
NOT OVERFILL!
Fuel Maintenance
Diesel fuel must be treated for long term storage. Use
approved fuel additive and water abatement material.
Test stored fuel every 90 days and add treatment as
required. Periodically inspect and dry abatement as
needed.
001750
A B C A
FGHJHK
E
D
A Emergency vent—on main tank and rupture basin
B Fuel fill
C Vent
D Fuel return line—from engine; sometimes supplied
with a check valve
E Fuel supply line—to engine fuel pump; includes in-line
check valve
F Stub-up area
G Rupture basin leak detector
H Baffle
J Leak containment area
K Fuel level sensor—electrical, mechanical, or both